java的各种日志框架
本文是作者原创,版权归作者所有.若要转载,请注明出处.文章中若有错误和疏漏之处,还请各位大佬不吝指出,谢谢大家.
java日志框架有很多,这篇文章我们来整理一下各大主流的日志框架,
包括log4j logback jul(java.util.logging) jcl(commons-logging) slf4j(simple log facade for java)等常用框架
目前java日志的使用有两种形式:日志接口和日志实现
1.目前日志接口,常用的有两种,jcl(commons logging)和slf4j(simple log facade for java)。
2.日志实现目前有这几类,log4j、jul、logback、log4j2。
我们先从log4j开始
首先,引入maven依赖
<!--log4j-->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
然后是配置log4j.properties文件
### 设置###
log4j.rootLogger = debug,stdout,D,E ### 输出信息到控制抬 ###
log4j.appender.stdout = org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.Target = System.out
log4j.appender.stdout.layout = org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern = [%-5p] %d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss,SSS} method:%l%n%m%n ### 输出DEBUG 级别以上的日志到=E://logs/error.log ###
log4j.appender.D = org.apache.log4j.DailyRollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.D.File = E://logs/log.log
log4j.appender.D.Append = true
log4j.appender.D.Threshold = DEBUG
log4j.appender.D.layout = org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.D.layout.ConversionPattern = %-d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} [ %t:%r ] - [ %p ] %m%n ### 输出ERROR 级别以上的日志到=E://logs/error.log ###
log4j.appender.E = org.apache.log4j.DailyRollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.E.File =E://logs/error.log
log4j.appender.E.Append = true
log4j.appender.E.Threshold = ERROR
log4j.appender.E.layout = org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.E.layout.ConversionPattern = %-d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} [ %t:%r ] - [ %p ] %m%n
最后是代码
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
public class Log4j {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Logger log4j = Logger.getLogger("log4j");
// 记录debug级别的信息
log4j.debug("This is debug message.");
// 记录info级别的信息
log4j.info("This is info message.");
// 记录error级别的信息
log4j.error("This is error message.");
}
}
最后是日志信息
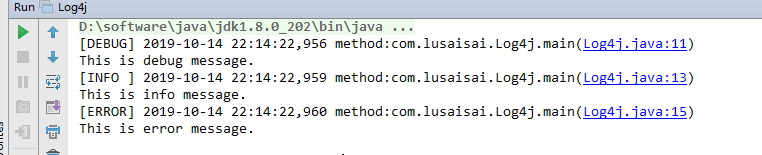
好,到这里,log4j就差不多了
,接下来我们看下 jul(java.util.logging) java官方日志jul,位于java.util.logging包下,不用引入依赖,但功能有限,不太常用看下demo
import java.util.logging.Logger;
public class JUL {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取logger实例,相同名的只能生成一个实例
Logger logger = Logger.getLogger("javaLog");
//日志输出简写形式,有不同的级别
logger.warning("warning log");
logger.info("info log");
}
}
看下控制台输出结果,可以看出和log4j相比,日志的时间和颜色明显不同
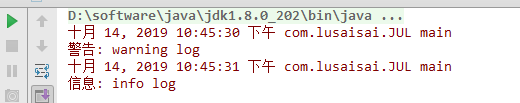
好,到这里,jul就差不多了
我们再看jcl(commons logging)是如何整合log4j和jul的
首先还是加入maven依赖,这里我们先加入log4j的依赖
<!--log4j-->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency> <!--jcl-->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
看下demo
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; /**
* Created by admin on 2019/10/14.
*/
public class JCL { public static void main(String[] args) {
Log log = LogFactory.getLog("JCL");
log.error("Hello World");
} }
看下输出结果
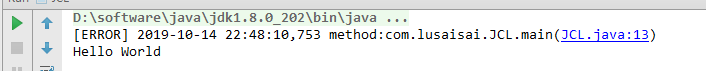
我们看到,这个好像是log4j的实现,我们把log4j的依赖注释,重新运行一次,再看下结果
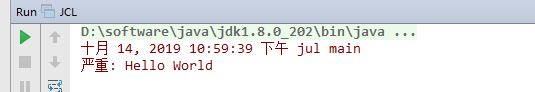
我们发现这次用的好像是jul打印的日志了,下面我们看下源码,看下jcl的底层是如何实现这种切换的
这里也只贴关键代码,看下getInstance方法
public Log getInstance(String name) throws LogConfigurationException {
Log instance = (Log) instances.get(name);
if (instance == null) {
instance = newInstance(name);
instances.put(name, instance);
}
return instance;
}
继续看newInstance方法
protected Log newInstance(String name) throws LogConfigurationException {
Log instance;
try {
if (logConstructor == null) {
instance = discoverLogImplementation(name);//我们看这行代码
}
else {
Object params[] = { name };
instance = (Log) logConstructor.newInstance(params);
}
if (logMethod != null) {
Object params[] = { this };
logMethod.invoke(instance, params);
}
return instance;
} catch (LogConfigurationException lce) {
// this type of exception means there was a problem in discovery
// and we've already output diagnostics about the issue, etc.;
// just pass it on
throw lce;
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
// A problem occurred invoking the Constructor or Method
// previously discovered
Throwable c = e.getTargetException();
throw new LogConfigurationException(c == null ? e : c);
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleThrowable(t); // may re-throw t
// A problem occurred invoking the Constructor or Method
// previously discovered
throw new LogConfigurationException(t);
}
}
看下上面我注释的代码
private Log discoverLogImplementation(String logCategory)
throws LogConfigurationException {
if (isDiagnosticsEnabled()) {
logDiagnostic("Discovering a Log implementation...");
} initConfiguration(); Log result = null; // See if the user specified the Log implementation to use
String specifiedLogClassName = findUserSpecifiedLogClassName(); if (specifiedLogClassName != null) {
if (isDiagnosticsEnabled()) {
logDiagnostic("Attempting to load user-specified log class '" +
specifiedLogClassName + "'...");
} result = createLogFromClass(specifiedLogClassName,
logCategory,
true);
if (result == null) {
StringBuffer messageBuffer = new StringBuffer("User-specified log class '");
messageBuffer.append(specifiedLogClassName);
messageBuffer.append("' cannot be found or is not useable."); // Mistyping or misspelling names is a common fault.
// Construct a good error message, if we can
informUponSimilarName(messageBuffer, specifiedLogClassName, LOGGING_IMPL_LOG4J_LOGGER);
informUponSimilarName(messageBuffer, specifiedLogClassName, LOGGING_IMPL_JDK14_LOGGER);
informUponSimilarName(messageBuffer, specifiedLogClassName, LOGGING_IMPL_LUMBERJACK_LOGGER);
informUponSimilarName(messageBuffer, specifiedLogClassName, LOGGING_IMPL_SIMPLE_LOGGER);
throw new LogConfigurationException(messageBuffer.toString());
} return result;
} if (isDiagnosticsEnabled()) {
logDiagnostic(
"No user-specified Log implementation; performing discovery" +
" using the standard supported logging implementations...");
}
for(int i=0; i<classesToDiscover.length && result == null; ++i) {//这里就是关键代码
result = createLogFromClass(classesToDiscover[i], logCategory, true);
} if (result == null) {
throw new LogConfigurationException
("No suitable Log implementation");
} return result;
}
看下我注释的地方,classesToDiscover对象
private static final String[] classesToDiscover = {
LOGGING_IMPL_LOG4J_LOGGER,
"org.apache.commons.logging.impl.Jdk14Logger",
"org.apache.commons.logging.impl.Jdk13LumberjackLogger",
"org.apache.commons.logging.impl.SimpleLog"
}
这里的Jdk14Logger其实就是jul,我们发现classesToDiscover对象是一个数组,它包含了几个日志框架的的全限定路径
回到刚刚的代码,我看可以看到,jcl就是遍历这个数组,按顺序取值,这里有log4j,就优先log4j,没有的话,就是要jul框架
我们再看下下面一行代码,点进去,看看怎么实现的
private Log createLogFromClass(String logAdapterClassName,
String logCategory,
boolean affectState)
throws LogConfigurationException { if (isDiagnosticsEnabled()) {
logDiagnostic("Attempting to instantiate '" + logAdapterClassName + "'");
} Object[] params = { logCategory };
Log logAdapter = null;
Constructor constructor = null; Class logAdapterClass = null;
ClassLoader currentCL = getBaseClassLoader(); for(;;) {
// Loop through the classloader hierarchy trying to find
// a viable classloader.
logDiagnostic("Trying to load '" + logAdapterClassName + "' from classloader " + objectId(currentCL));
try {
if (isDiagnosticsEnabled()) {
// Show the location of the first occurrence of the .class file
// in the classpath. This is the location that ClassLoader.loadClass
// will load the class from -- unless the classloader is doing
// something weird.
URL url;
String resourceName = logAdapterClassName.replace('.', '/') + ".class";
if (currentCL != null) {
url = currentCL.getResource(resourceName );
} else {
url = ClassLoader.getSystemResource(resourceName + ".class");
} if (url == null) {
logDiagnostic("Class '" + logAdapterClassName + "' [" + resourceName + "] cannot be found.");
} else {
logDiagnostic("Class '" + logAdapterClassName + "' was found at '" + url + "'");
}
} Class c;
try {
c = Class.forName(logAdapterClassName, true, currentCL);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException originalClassNotFoundException) {
// The current classloader was unable to find the log adapter
// in this or any ancestor classloader. There's no point in
// trying higher up in the hierarchy in this case..
String msg = originalClassNotFoundException.getMessage();
logDiagnostic("The log adapter '" + logAdapterClassName + "' is not available via classloader " +
objectId(currentCL) + ": " + msg.trim());
try {
// Try the class classloader.
// This may work in cases where the TCCL
// does not contain the code executed or JCL.
// This behaviour indicates that the application
// classloading strategy is not consistent with the
// Java 1.2 classloading guidelines but JCL can
// and so should handle this case.
c = Class.forName(logAdapterClassName);//这里通过反射获取日志实现类的class对象
} catch (ClassNotFoundException secondaryClassNotFoundException) {
// no point continuing: this adapter isn't available
msg = secondaryClassNotFoundException.getMessage();
logDiagnostic("The log adapter '" + logAdapterClassName +
"' is not available via the LogFactoryImpl class classloader: " + msg.trim());
break;
}
} constructor = c.getConstructor(logConstructorSignature);
Object o = constructor.newInstance(params);//这里实例化了日志实现类对象
if (o instanceof Log) {//这里判断是否是log的实现类
logAdapterClass = c;
logAdapter = (Log) o;//这里将对象传给logAdapter
break;
}
// Oops, we have a potential problem here. An adapter class
// has been found and its underlying lib is present too, but
// there are multiple Log interface classes available making it
// impossible to cast to the type the caller wanted. We
// certainly can't use this logger, but we need to know whether
// to keep on discovering or terminate now.
//
// The handleFlawedHierarchy method will throw
// LogConfigurationException if it regards this problem as
// fatal, and just return if not.
handleFlawedHierarchy(currentCL, c);
} catch (NoClassDefFoundError e) {
// We were able to load the adapter but it had references to
// other classes that could not be found. This simply means that
// the underlying logger library is not present in this or any
// ancestor classloader. There's no point in trying higher up
// in the hierarchy in this case..
String msg = e.getMessage();
logDiagnostic("The log adapter '" + logAdapterClassName +
"' is missing dependencies when loaded via classloader " + objectId(currentCL) +
": " + msg.trim());
break;
} catch (ExceptionInInitializerError e) {
// A static initializer block or the initializer code associated
// with a static variable on the log adapter class has thrown
// an exception.
//
// We treat this as meaning the adapter's underlying logging
// library could not be found.
String msg = e.getMessage();
logDiagnostic("The log adapter '" + logAdapterClassName +
"' is unable to initialize itself when loaded via classloader " + objectId(currentCL) +
": " + msg.trim());
break;
} catch (LogConfigurationException e) {
// call to handleFlawedHierarchy above must have thrown
// a LogConfigurationException, so just throw it on
throw e;
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleThrowable(t); // may re-throw t
// handleFlawedDiscovery will determine whether this is a fatal
// problem or not. If it is fatal, then a LogConfigurationException
// will be thrown.
handleFlawedDiscovery(logAdapterClassName, currentCL, t);
}
if (currentCL == null) {
break;
}
// try the parent classloader
// currentCL = currentCL.getParent();
currentCL = getParentClassLoader(currentCL);
}
if (logAdapterClass != null && affectState) {
// We've succeeded, so set instance fields
this.logClassName = logAdapterClassName;
this.logConstructor = constructor;
// Identify the <code>setLogFactory</code> method (if there is one)
try {
this.logMethod = logAdapterClass.getMethod("setLogFactory", logMethodSignature);
logDiagnostic("Found method setLogFactory(LogFactory) in '" + logAdapterClassName + "'");
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleThrowable(t); // may re-throw t
this.logMethod = null;
logDiagnostic("[INFO] '" + logAdapterClassName + "' from classloader " + objectId(currentCL) +
" does not declare optional method " + "setLogFactory(LogFactory)");
}
logDiagnostic("Log adapter '" + logAdapterClassName + "' from classloader " +
objectId(logAdapterClass.getClassLoader()) + " has been selected for use.");
}
return logAdapter;//返回此对象
}
我们可以看到底层是用了反射获取的对象,截个图
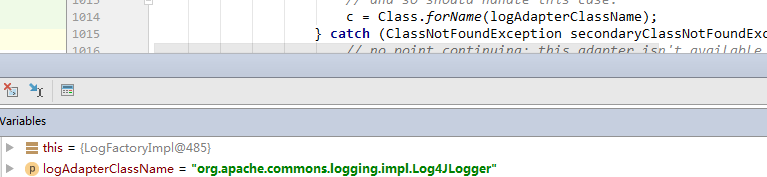
我们可以看到,这里是jcl包里的log4j.
好了,到这里jcl就差不多了,我们从源码可以看出jcl是如何切换日志框架的,
接下来学习下目前流行的slf4j,它支持所有主流的日志实现框架,非常强大,推荐使用
老规矩,添加依赖
<!--slf4j-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>1.7.25</version>
</dependency>
看下demo
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.slf4j.Logger; /**
* Created by admin on 2019/10/14.
*/
public class Slf4j { public static void main(String[] args) {
Logger logger= LoggerFactory.getLogger("slf4j");
logger.error("Hello World");
} }
看下控制台
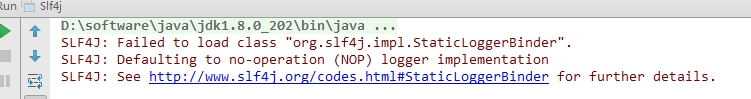
哎,好像没打印,这里可以看出,只引入slf4j是不打印日志的,我们可以看下官网http://www.slf4j.org/
Simple Logging Facade for Java (SLF4J) 它是简单日志门面,不自己实现
好,我们再引入log4j的绑定器依赖
<!--log4j的绑定器-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>1.7.25</version>
</dependency>
,再运行一次,看下结果

成了,如何我们要切换日志呢,注释掉log4j,试试jul吧
<!--log4j的绑定器-->
<!--<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>1.7.25</version>
</dependency>--> <!--jul的绑定器-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-jdk14</artifactId>
<version>1.7.25</version>
</dependency>
再看下控制台
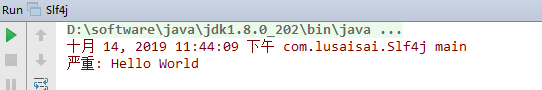
成功了,这就是推荐使用slf4j的原因,切换日志框架非常方便
注意,绑定器有且只能有一个
最后,看下logback的使用吧
添加依赖
<!-- logback -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-core</artifactId>
<version>1.1.11</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.1.11</version>
</dependency>
logback,xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!--
scan:当此属性设置为true时,配置文件如果发生改变,将会被重新加载,默认值为true。
scanPeriod:设置监测配置文件是否有修改的时间间隔,如果没有给出时间单位,默认单位是毫秒当scan为true时,此属性生效。默认的时间间隔为1分钟。
debug:当此属性设置为true时,将打印出logback内部日志信息,实时查看logback运行状态。默认值为false。
-->
<configuration debug="false" scan="true" scanperiod="1800 seconds"> <!--当前logger上下文名称-->
<contextName>logbackStudy</contextName> <!--当前日期-->
<timestamp key="nowDate" datePattern="yyyyMMdd" /> <!--输出到控制台-->
<appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<pattern>%date %level %logger : %msg %n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender> <!--输出到文件-->
<appender name="FILE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.FileAppender">
<file>logbackstudy_${nowDate}.log</file> <!--日志滚动的策略,按时间归档,实现了RollingPolicy和TriggeringPolicy接口,RollingPolicy指历史文件归档策略,TriggeringPolicy指历史文件归档时机-->
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<fileNamePattern>logbackStudy_%d{yyyyMMdd}.log.gz</fileNamePattern>
<!--最多保存30天历史-->
<maxHistory>30</maxHistory>
<!--日志文件合起来最大1G,超出后会删除旧日志-->
<totalSizeCap>1G</totalSizeCap>
</rollingPolicy>
<encoder>
<!--日志模板-->
<pattern>%date %level %logger : %msg %n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender> <!--控制指定包或类的日志输出(包括等级和目的地), additivity表示日志信息是否向上传递,false为不传递(即不重复打印)-->
<logger name="com.dragon.study.log.Slf4jAndLogbackMainTwo" level="warn" additivity="false">
<!--可多个appender-->
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT" />
</logger> <root level="info">
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT" />
<appender-ref ref="FILE" />
</root>
</configuration>
demo实例
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.slf4j.Logger; /**
* Created by admin on 2019/10/14.
*/
public class Slf4j { public static void main(String[] args) {
Logger logger= LoggerFactory.getLogger("slf4j");
logger.error("Hello World");
} }
控制台
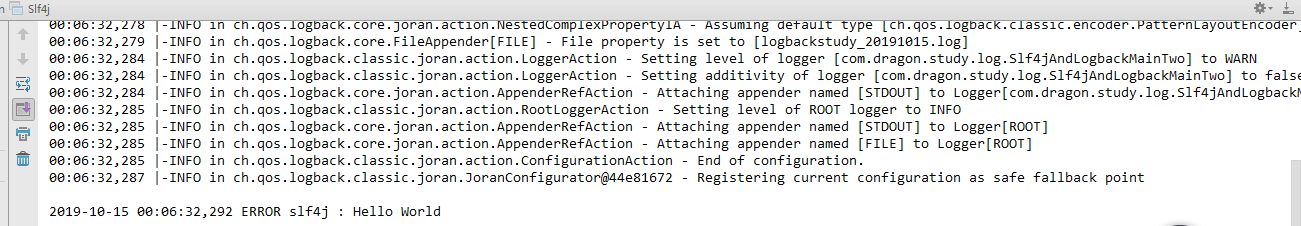
输出的文件
总结:目前来说日志框架推荐使用slf4j日志接口+一个你熟悉的日志实现,这样可以直接切换日志的依赖,不用改已有的代码
最新文章
- jquery1.7.2的源码分析(一)
- VMware Workstation 10.0 正式版官方简体中文下载(附序列号)
- c/c++与函数有关的优化
- Ubuntu换源
- hdu 1698:Just a Hook(线段树,区间更新)
- Linux交叉开发环境搭建 —— 效率之源
- Golang container/ring闭环数据结构的使用方法
- nohup 程序名 & (使程序推到后台运行,即使终端关闭,该程序依然运行)
- Asp.net 将DataTable 或者DataSet 转换为Json 格式
- Android 图片三级缓存之内存缓存(告别软引用(SoftRefrerence)和弱引用(WeakReference))
- mysql命令行方式添加用户及设置权限
- Interface和Abstract class区别
- hdu 2079 选课时间_母函数
- Mybatis使用存储过程(MySql)
- 浅谈stream数据流
- 201521123088 《Java程序设计》第14周学习总结
- python常见模块命令(os/sys/platform)
- jquery获取select选中的值
- java8_api_jni
- LOJ6070 基因 分块+回文自动机