Pytorch基础(6)----参数初始化
2024-08-31 04:42:01
一、使用Numpy初始化:【直接对Tensor操作】
对Sequential模型的参数进行修改:
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn # 定义一个 Sequential 模型
net1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(30, 40),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(40, 50),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(50, 10)
) # 访问第一层的参数
w1 = net1[0].weight
b1 = net1[0].bias
print(w1) #对第一层Linear的参数进行修改:
# 定义第一层的参数 Tensor 直接对其进行替换
net1[0].weight.data = torch.from_numpy(np.random.uniform(3, 5, size=(40, 30)))
print(net1[0].weight)
23
24 #若模型中相同类型的层都需要初始化成相同的方式,一种更高效的方式:使用循环去访问:
25 for layer in net1:
26 if isinstance(layer, nn.Linear): # 判断是否是线性层
27 param_shape = layer.weight.shape
28 layer.weight.data = torch.from_numpy(np.random.normal(0, 0.5, size=param_shape))
29 # 定义为均值为 0,方差为 0.5 的正态分布
对Module模型 的参数初始化:
对于 Module 的参数初始化,其实也非常简单,如果想对其中的某层进行初始化,可以直接像 Sequential 一样对其 Tensor 进行重新定义,其唯一不同的地方在于,如果要用循环的方式访问,需要介绍两个属性,children 和 modules,下面我们举例来说明:
1、创建Module模型类:
class sim_net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(sim_net, self).__init__()
self.l1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(30, 40),
nn.ReLU()
) self.l1[0].weight.data = torch.randn(40, 30) # 直接对某一层初始化 self.l2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(40, 50),
nn.ReLU()
) self.l3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(50, 10),
nn.ReLU()
) def forward(self, x):
x = self.l1(x)
x =self.l2(x)
x = self.l3(x)
return x
2、创建模型对象:
net2 = sim_net()
3、访问children:
# 访问 children
for i in net2.children():
print(i)
#打印的结果:
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=30, out_features=40)
(1): ReLU()
)
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=40, out_features=50)
(1): ReLU()
)
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=50, out_features=10)
(1): ReLU()
)
4、访问modules:
# 访问 modules
for i in net2.modules():
print(i) #打印的结果
sim_net(
(l1): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=30, out_features=40)
(1): ReLU()
)
(l2): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=40, out_features=50)
(1): ReLU()
)
(l3): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=50, out_features=10)
(1): ReLU()
)
)
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=30, out_features=40)
(1): ReLU()
)
Linear(in_features=30, out_features=40)
ReLU()
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=40, out_features=50)
(1): ReLU()
)
Linear(in_features=40, out_features=50)
ReLU()
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=50, out_features=10)
(1): ReLU()
)
Linear(in_features=50, out_features=10)
ReLU()
通过上面的例子,可以看到:
children 只会访问到模型定义中的第一层,因为上面的模型中定义了三个 Sequential,所以只会访问到三个 Sequential,而 modules 会访问到最后的结构,比如上面的例子,modules 不仅访问到了 Sequential,也访问到了 Sequential 里面,这就对我们做初始化非常方便。
5、采用循环初始化:
for layer in net2.modules():
if isinstance(layer, nn.Linear):
param_shape = layer.weight.shape
layer.weight.data = torch.from_numpy(np.random.normal(0, 0.5, size=param_shape))
二、torch.nn.init初始化
PyTorch 还提供了初始化的函数帮助我们快速初始化,就是 torch.nn.init,其操作层面仍然在 Tensor 上。先介绍一种初始化方法:
Xavier 初始化方法:
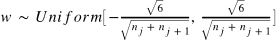
其中 和
表示该层的输入和输出数目。
这种非常流行的初始化方式叫 Xavier,方法来源于 2010 年的一篇论文 Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks,其通过数学的推到,证明了这种初始化方式可以使得每一层的输出方差是尽可能相等的。
torch.nn.init:
from torch.nn import init init.xavier_uniform(net1[0].weight) # 这就是上面我们讲过的 Xavier 初始化方法,PyTorch 直接内置了其实现 #这就直接修改了net1[0].weight的值
最新文章
- 浅谈CommandBehavior枚举的独特之处
- 孙鑫MFC学习笔记5:文本显示
- asp.net 操作excel的一系列问题(未完待续)
- Codeforces Round #219 (Div. 1) C. Watching Fireworks is Fun
- Linux GPT分区
- IOS地图及定位使用
- Aspose.Words组件介绍及使用—基本介绍与DOM概述
- [Ionic] Ionic Quickstart for Windows
- JUnit——(二)注解
- Ajax 下拉加载数据
- C语言第四次作业--嵌套循环
- LeetCode(96): 不同的二叉搜索树
- linux上下载安装mysql,并使用
- 命令行添加subl命令
- Highcharts 柱图 每个柱子外围的白色边框
- flume http source示例讲解
- 深入Animation,在SurfaceView中照样使用Android—Tween Animation!
- USB耳机声卡-音频输入/输出控制器:DP108替代兼容CM108
- CSS绝对定位属性
- Bootstrap学习笔记(7)--轮播