java实现跳跃表
2024-10-19 04:32:07
先贴上一个MIT跳跃表公开课链接:http://open.163.com/movie/2010/12/7/S/M6UTT5U0I_M6V2TTJ7S.html
redis中的有序链表结构就是在跳跃表的基础上实现的。详细的可以参考http://blog.csdn.net/acceptedxukai/article/details/17333673
我的实现方法是,最左侧使用数值的最小值(Double.MIN_VALUE)当作下界。因此,规定存储的值至少大于该值。
下面是跳跃表的图例
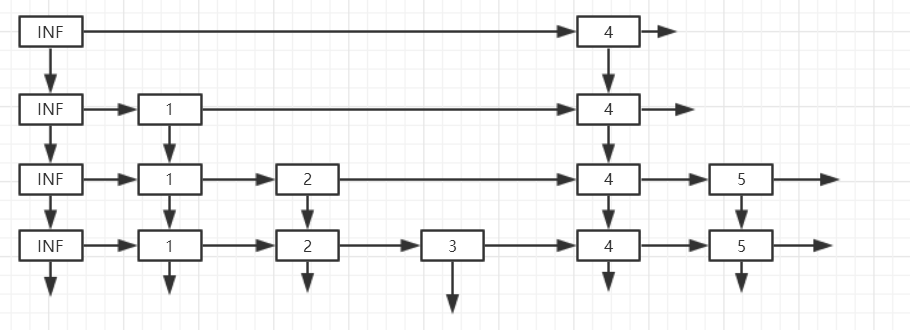
1,实现每个节点类
包含 分值score,val,以及next和down指针
/**
* 跳跃表的节点的构成
*
* @param <E>
*/
private static class SkipNode<E> {
E val;//存储的数据
double score;//跳跃表按照这个分数值进行从小到大排序。
SkipNode<E> next, down;//next指针,指向下一层的指针 SkipNode() {
} SkipNode(E val, double score) {
this.val = val;
this.score = score;
}
}
2,查找,插入,删除方法:即整个类的全部代码
package com.ljd.skiplist; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random; /**
* Created by author on 2017/10/9.
* 实现跳跃表:能够对递增链表实现logN的查询时间
*/
public class SkipList<T> {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试随机数生成的结果对二取模,结果是否是接近于0.5
// Random r = new Random(47);
// int t = 1, a = 1;
// while (a < 10000000) {
// a++;
// if (r.nextInt() % 2 == 0)
// t++;
// }
// System.out.println(t * 1.0 / a); SkipList<String> list = new SkipList<>();
list.put(1.0, "1.0");
System.out.println(list);
list.put(2.0, "2.0");
System.out.println(list);
list.put(3.0, "3.0");
System.out.println(list);
list.put(4.0, "4.0");
System.out.println(list);
list.put(4.0, "5.0");
System.out.println(list);
list.delete(3.0);
list.delete(3.5);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println("查找4.0" + list.get(4.0));
} /**
* 跳跃表的节点的构成
*
* @param <E>
*/
private static class SkipNode<E> {
E val;//存储的数据
double score;//跳跃表按照这个分数值进行从小到大排序。
SkipNode<E> next, down;//next指针,指向下一层的指针 SkipNode() {
} SkipNode(E val, double score) {
this.val = val;
this.score = score;
}
} private static final int MAX_LEVEL = 1 << 6; //跳跃表数据结构
private SkipNode<T> top;
private int level = 0;
//用于产生随机数的Random对象
private Random random = new Random(); public SkipList() {
//创建默认初始高度的跳跃表
this(4);
} //跳跃表的初始化
public SkipList(int level) {
this.level = level;
int i = level;
SkipNode<T> temp = null;
SkipNode<T> prev = null;
while (i-- != 0) {
temp = new SkipNode<T>(null, Double.MIN_VALUE);
temp.down = prev;
prev = temp;
}
top = temp;//头节点
} /**
* 产生节点的高度。使用抛硬币
*
* @return
*/
private int getRandomLevel() {
int lev = 1;
while (random.nextInt() % 2 == 0)
lev++;
return lev > MAX_LEVEL ? MAX_LEVEL : lev;
} /**
* 查找跳跃表中的一个值
*
* @param score
* @return
*/
public T get(double score) {
SkipNode<T> t = top;
while (t != null) {
if (t.score == score)
return t.val;
if (t.next == null) {
if (t.down != null) {
t = t.down;
continue;
} else
return null;
}
if (t.next.score > score) {
t = t.down;
} else
t = t.next;
}
return null;
} public void put(double score, T val) {
//1,找到需要插入的位置
SkipNode<T> t = top, cur = null;//若cur不为空,表示当前score值的节点存在
List<SkipNode<T>> path = new ArrayList<>();//记录每一层当前节点的前驱节点
while (t != null) {
if (t.score == score) {
cur = t;
break;//表示存在该值的点,表示需要更新该节点
}
if (t.next == null) {
path.add(t);//需要向下查找,先记录该节点
if (t.down != null) {
t = t.down;
continue;
} else {
break;
}
}
if (t.next.score > score) {
path.add(t);//需要向下查找,先记录该节点
if (t.down == null) {
break;
}
t = t.down;
} else
t = t.next;
}
if (cur != null) {
while (cur != null) {
cur.val = val;
cur = cur.down;
}
} else {//当前表中不存在score值的节点,需要从下到上插入
int lev = getRandomLevel();
if (lev > level) {//需要更新top这一列的节点数量,同时需要在path中增加这些新的首节点
SkipNode<T> temp = null;
SkipNode<T> prev = top;//前驱节点现在是top了
while (level++ != lev) {
temp = new SkipNode<T>(null, Double.MIN_VALUE);
path.add(0, temp);//加到path的首部
temp.down = prev;
prev = temp;
}
top = temp;//头节点
level = lev;//level长度增加到新的长度
}
//从后向前遍历path中的每一个节点,在其后面增加一个新的节点
SkipNode<T> downTemp = null, temp = null, prev = null;
// System.out.println("当前深度为"+level+",当前path长度为"+path.size());
for (int i = level - 1; i >= level - lev; i--) {
temp = new SkipNode<T>(val, score);
prev = path.get(i);
temp.next = prev.next;
prev.next = temp;
temp.down = downTemp;
downTemp = temp;
}
}
} /**
* 根据score的值来删除节点。
*
* @param score
*/
public void delete(double score) {
//1,查找到节点列的第一个节点的前驱
SkipNode<T> t = top;
while (t != null) {
if (t.next == null) {
t = t.down;
continue;
}
if (t.next.score == score) {
// 在这里说明找到了该删除的节点
t.next = t.next.next;
t = t.down;
//删除当前节点后,还需要继续查找之后需要删除的节点
continue;
}
if (t.next.score > score)
t = t.down;
else
t = t.next;
}
} @Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
SkipNode<T> t = top, next = null;
while (t != null) {
next = t;
while (next != null) {
sb.append(next.score + " ");
next = next.next;
}
sb.append("\n");
t = t.down;
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
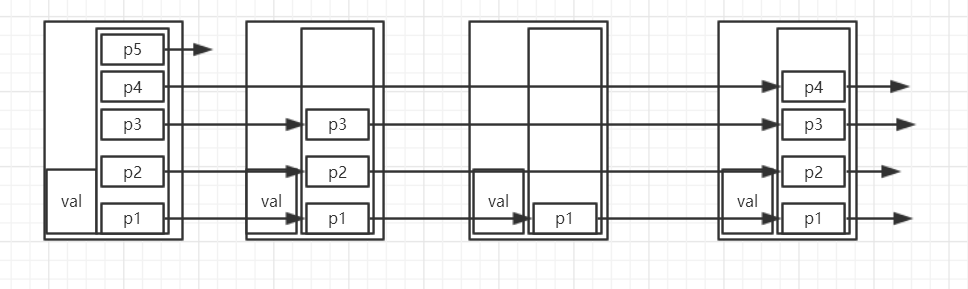
对于插入的时候,在寻找插入位置的同时,我使用了一个ArrayList存储查找方向向下时的节点。这样在构造节点的时候,只需要直接从这个list中拿prev节点就行了。
下面这种方式的实现,比上面的少消耗了很多存val的空间,这个后续看能否实现。
最新文章
- thinkcmf无法使用config.html中的配置量
- c语言数据结构之 快速排序
- Qt实用小技巧(转)
- GridView的 OnRowDataBound 事件用法
- 数据字典 dba_free_space及相对文件号RELATIVE_FNO 小结
- daily news新闻阅读客户端应用源码(兼容iPhone和iPad)
- Python 函数式编程学习
- hdoj 3746 Cyclic Nacklace【KMP求在结尾加上多少个字符可以使字符串至少有两次循环】
- Android开发中用友盟做分享的一些坑
- HDU 1722 Cake
- 浅谈Java的集合框架
- 9.Java 加解密技术系列之 RSA
- Luogu 3402 最长公共子序列(二分,最长递增子序列)
- ASP.NET没有魔法——ASP.NET 身份验证与Identity
- 安卓自定义日期控件(仿QQ,IOS7)
- shell 在手分析服务器日志【转】
- JavaScript+CSS+DIV实现表格变色示例
- 自己的reset.css
- CMFCPropertyGridProperty用法
- Qwe中的数值结算