Java多线程系列 JUC线程池01 线程池框架
转载 http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3509903.html
为什么引入Executor线程池框架
new Thread()的缺点
1. 每次new Thread()耗费性能
2. 调用new Thread()创建的线程缺乏管理,而且可以无限创建,大量线程会占用系统资源导致系统瘫痪
3. 不能进行扩展,比如延时执行或者周期执行
线程池的优点
1. 线程可以重复使用,减少线程创建和销毁的成本
2. 可以控制线程最大并发数,避免系统资源被过多的占用
3. 提供延时执行、周期执行、并发数限制的功能
4. 有助于避免this逃逸问题
this逃逸是指在构造器函数返回之前其他线程已持有了该对象的引用,例如:
package concurrent; /**
* this逃逸demo
*/
public class ThisEscape { public ThisEscape() {
new MyThread().start();
} class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
//通过ThisEscape.this就可以引用外围对象,但是此时外围对象还未构造完全,即发生了外围类的this逃逸
}
}
}
一种解决方法
package concurrent; /**
* 避免this逃逸demo
*/
public class ThisEscape {
private Thread myThread; public ThisEscape() {
myThread = new MyThread();
} public void init (){
myThread.start();
}
class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
//通过ThisEscape.this就可以引用外围对象,此时外围对象已构造完全
}
}
}
线程池架构
线程池框架包括:ThreadPoolService(线程池),Executor,Executors,ExecutorService,ScheduledExecutorService,ScheduledThreadPoolService,Future,Callable等。
线程池架构图
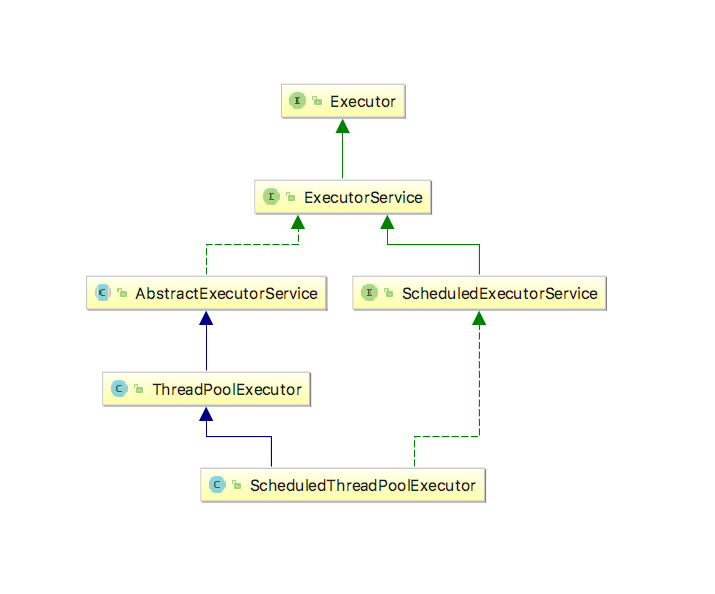
1. Executor
它是"执行者"接口,定义了执行任务方法。Executor提供了execute()接口来执行已提交任务, 任务即一个实现了Runnable接口的类。
它只包含一个函数接口:
package java.util.concurrent; /**
* @since 1.5
* @author Doug Lea
*/
public interface Executor { // 执行任务的方法
void execute(Runnable command);
}
2. ExecutorService
ExecutorService继承于Executor。定义了提交任务(submit方法)、让执行者执行任务(invokeAll, invokeAny方法)、让线程池关闭(shutdown方法、shutdownNow方法)等方法,它是为"执行者接口Executor"服务而存在的;
ExecutorService的函数列表
package java.util.concurrent;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Collection; /**
*
* @since 1.5
* @author Doug Lea
*/
public interface ExecutorService extends Executor { //调用此方法后,不再接受新任务,只完成线程池中正在执行或者等待的任务。线程池处于SHUTDOWN状态
void shutdown(); //调用此方法后,不再接受新任务,暂停处理正在等待的任务,试图停止所有正在执行的任务,并返回等待执行的任务列表。线程池处STOP状态
List<Runnable> shutdownNow(); //线程池已不在接受新的任务时,则返回 true
boolean isShutdown(); //如果关闭后所有任务都已完成,则返回 true
boolean isTerminated(); //请求关闭、发生超时或者当前线程中断,无论哪一个首先发生之后,都将导致阻塞,直到所有任务完成执行
boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)throws InterruptedException; //提交一个Callable任务,返回一个表示该任务结果的Future
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task); //提交一个Runnable任务,返回一个表示该任务结果的Future
<T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result); //提交一个Runnable任务,返回一个表示该任务结果的Future
Future<?> submit(Runnable task); //执行给定的任务,当所有任务完成时,返回保持任务状态和结果Future 列表
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)throws InterruptedException; //执行给定的任务,当所有任务完成或超时期满时(无论哪个首先发生),返回保持任务状态和结果的 Future 列表
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,long timeout, TimeUnit unit)throws InterruptedException; //执行给定的任务,如果某个任务已成功完成(也就是未抛出异常),则返回其结果
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException; //执行给定的任务,如果在给定的超时期满前某个任务已成功完成(也就是未抛出异常),则返回其结果
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,long timeout, TimeUnit unit)throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}
3. AbstractExecutorService
AbstractExecutorService是一个抽象类,它实现了ExecutorService接口。
AbstractExecutorService存在的目的是为ExecutorService中的函数接口提供了默认实现。
4. ThreadPoolExecutor
ThreadPoolExecutor就是大名鼎鼎的"线程池"。它继承于AbstractExecutorService抽象类。
ThreadPoolExecutor函数列表
public class ThreadPoolExecutor extends AbstractExecutorService{
//用给定的初始参数、默认的线程工厂、被拒绝后的执行处理程序构造新的 ThreadPoolExecutor
ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue)
//用给定的初始参数、默认的线程工厂构造新的ThreadPoolExecutor
ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
//用给定的初始参数、默认被拒绝的执行处理程序构造新的ThreadPoolExecutor
ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory)
//用给定的初始参数构造新的ThreadPoolExecutor
ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
//在给定线程中的给定 Runnable 执行后所调用的方法。
protected void afterExecute(Runnable r, Throwable t)
//如果在保持活动时间内没有任务到达,新任务到达时正在替换(如果需要),则设置控制核心线程是超时还是终止的策略。
void allowCoreThreadTimeOut(boolean value)
//如果此池允许核心线程超时和终止,如果在 keepAlive 时间内没有任务到达,新任务到达时正在替换(如果需要),则返回 true。
boolean allowsCoreThreadTimeOut()
//请求关闭、发生超时或者当前线程中断,无论哪一个首先发生之后,都将导致阻塞,直到所有任务完成执行。
boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
//在给定线程中的给定 Runnable 执行之前调用的方法。
protected void beforeExecute(Thread t, Runnable r)
//在将来某个时间执行给定任务。
void execute(Runnable command)
//当不再引用此执行程序时,调用 shutdown。
protected void finalize()
//返回主动执行任务的近似线程数。
int getActiveCount()
//返回已完成执行的近似任务总数。
long getCompletedTaskCount()
//返回核心线程数。
int getCorePoolSize()
//返回线程保持活动的时间,该时间就是超过核心池大小的线程可以在终止前保持空闲的时间值。
long getKeepAliveTime(TimeUnit unit)
//返回曾经同时位于池中的最大线程数。
int getLargestPoolSize()
//返回允许的最大线程数。
int getMaximumPoolSize()
//返回池中的当前线程数。
int getPoolSize()
//返回此执行程序使用的任务队列。
BlockingQueue<Runnable> getQueue()
//返回用于未执行任务的当前处理程序。
RejectedExecutionHandler getRejectedExecutionHandler()
//返回曾计划执行的近似任务总数。
long getTaskCount()
//返回用于创建新线程的线程工厂。
ThreadFactory getThreadFactory()
//如果此执行程序已关闭,则返回 true。
boolean isShutdown()
//如果关闭后所有任务都已完成,则返回 true。
boolean isTerminated()
//如果此执行程序处于在 shutdown 或 shutdownNow 之后正在终止但尚未完全终止的过程中,则返回 true。
boolean isTerminating()
//启动所有核心线程,使其处于等待工作的空闲状态。
int prestartAllCoreThreads()
//启动核心线程,使其处于等待工作的空闲状态。
boolean prestartCoreThread()
//尝试从工作队列移除所有已取消的 Future 任务。
void purge()
//从执行程序的内部队列中移除此任务(如果存在),从而如果尚未开始,则其不再运行。
boolean remove(Runnable task)
//设置核心线程数。
void setCorePoolSize(int corePoolSize)
//设置线程在终止前可以保持空闲的时间限制。
void setKeepAliveTime(long time, TimeUnit unit)
//设置允许的最大线程数。
void setMaximumPoolSize(int maximumPoolSize)
//设置用于未执行任务的新处理程序。
void setRejectedExecutionHandler(RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
//设置用于创建新线程的线程工厂。
void setThreadFactory(ThreadFactory threadFactory)
//按过去执行已提交任务的顺序发起一个有序的关闭,但是不接受新任务。
void shutdown()
//尝试停止所有的活动执行任务、暂停等待任务的处理,并返回等待执行的任务列表。
List<Runnable> shutdownNow()
//当 Executor 已经终止时调用的方法。
protected void terminated()
}
5. ScheduledExecutorService
ScheduledExecutorService是一个接口,它继承于ExecutorService。它相当于提供了"延时"和"周期执行"功能的ExecutorService。
ScheduledExecutorService提供了相应的函数接口,可以安排任务在给定的延迟后执行,也可以让任务周期的执行。
ScheduledExecutorService函数列表
public interface ScheduledExecutorService extends ExecutorService{
//创建并执行在给定延迟后启用的 ScheduledFuture。
<V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable, long delay, TimeUnit unit)
//创建并执行在给定延迟后启用的一次性操作。
ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit)
//创建并执行一个在给定初始延迟后首次启用的定期操作,后续操作具有给定的周期;也就是将在 initialDelay 后开始执行,然后在 initialDelay+period 后执行,接着在 initialDelay + 2 * period 后执行,依此类推。
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit)
//创建并执行一个在给定初始延迟后首次启用的定期操作,随后,在每一次执行终止和下一次执行开始之间都存在给定的延迟。
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit)
}
6. ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor继承于ThreadPoolExecutor,并且实现了ScheduledExecutorService接口。它相当于提供了"延时"和"周期执行"功能的ScheduledExecutorService。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor类似于Timer,但是在高并发程序中,ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的性能要优于Timer。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor函数列表
public class ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor extends ThreadPoolExecutor implements ScheduledExecutorService {
//使用给定核心池大小创建一个新 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize)
//使用给定初始参数创建一个新 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
//使用给定的初始参数创建一个新 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory)
//使用给定初始参数创建一个新 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
//修改或替换用于执行 callable 的任务
protected <V> RunnableScheduledFuture<V> decorateTask(Callable<V> callable, RunnableScheduledFuture<V> task)
//修改或替换用于执行 runnable 的任务。
protected <V> RunnableScheduledFuture<V> decorateTask(Runnable runnable, RunnableScheduledFuture<V> task)
//使用所要求的零延迟执行命令。
void execute(Runnable command)
//获取有关在此执行程序已 shutdown 的情况下、是否继续执行现有定期任务的策略。
boolean getContinueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdownPolicy()
//获取有关在此执行程序已 shutdown 的情况下是否继续执行现有延迟任务的策略。
boolean getExecuteExistingDelayedTasksAfterShutdownPolicy()
//返回此执行程序使用的任务队列。
BlockingQueue<Runnable> getQueue()
//从执行程序的内部队列中移除此任务(如果存在),从而如果尚未开始,则其不再运行。
boolean remove(Runnable task)
//创建并执行在给定延迟后启用的 ScheduledFuture。
<V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable, long delay, TimeUnit unit)
//创建并执行在给定延迟后启用的一次性操作。
ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit)
//创建并执行一个在给定初始延迟后首次启用的定期操作,后续操作具有给定的周期;也就是将在 initialDelay 后开始执行,然后在 initialDelay+period 后执行,接着在 initialDelay + 2 * period 后执行,依此类推。
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit)
//创建并执行一个在给定初始延迟后首次启用的定期操作,随后,在每一次执行终止和下一次执行开始之间都存在给定的延迟。
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit)
//设置有关在此执行程序已 shutdown 的情况下是否继续执行现有定期任务的策略。
void setContinueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdownPolicy(
boolean value)
//设置有关在此执行程序已 shutdown 的情况下是否继续执行现有延迟任务的策略。
void setExecuteExistingDelayedTasksAfterShutdownPolicy(
boolean value)
//在以前已提交任务的执行中发起一个有序的关闭,但是不接受新任务。
void shutdown()
//尝试停止所有正在执行的任务、暂停等待任务的处理,并返回等待执行的任务列表。
List<Runnable> shutdownNow()
//提交一个返回值的任务用于执行,返回一个表示任务结果的Future。
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task)
//提交一个Runnable任务用于执行,并返回一个表示该任务的Future。
Future<?> submit(Runnable task)
//提交一个Runnable任务用于执行,并返回一个表示该任务的Future。
<T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result)
}
7. Executors
Executors是个静态工厂类。它通过静态工厂方法返回ExecutorService、ScheduledExecutorService、ThreadFactory 和 Callable 等类的对象。
Executors函数列表
public class Executors {
//返回 Callable 对象,调用它时可运行给定特权的操作并返回其结果。
static Callable<Object> callable(PrivilegedAction<?> action)
//返回 Callable 对象,调用它时可运行给定特权的异常操作并返回其结果。
static Callable<Object> callable(PrivilegedExceptionAction<?> action)
//返回 Callable 对象,调用它时可运行给定的任务并返回 null。
static Callable<Object> callable(Runnable task)
//返回 Callable 对象,调用它时可运行给定的任务并返回给定的结果。
static <T> Callable<T> callable(Runnable task, T result)
//返回用于创建新线程的默认线程工厂。
static ThreadFactory defaultThreadFactory()
//创建一个可缓存的线程池,调用execute将重用以前构造的线程(如果线程可用)。如果现有线程没有可用的,则创建一个新线程并添加到池中。终止并从缓存中移除那些已有 60 秒钟未被使用的线程。
static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool()
//和上面方法一样,只是使用了外部提供的 ThreadFactory 创建新线程。
static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool(ThreadFactory threadFactory)
//创建一个可重用固定线程数的线程池,以共享的无界队列方式来运行这些线程。
static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads)
//创建一个可重用固定线程数的线程池,以共享的无界队列方式来运行这些线程,在需要时使用提供的 ThreadFactory 创建新线程。
static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory)
//创建一个线程池,它可安排在给定延迟后运行命令或者定期地执行。
static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize)
//创建一个线程池,它可安排在给定延迟后运行命令或者定期地执行。
static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory)
//创建一个使用单个 worker 线程的 Executor,以无界队列方式来运行该线程。
static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor()
//创建一个使用单个 worker 线程的 Executor,以无界队列方式来运行该线程,并在需要时使用提供的 ThreadFactory 创建新线程。
static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory)
//创建一个单线程执行程序,它可安排在给定延迟后运行命令或者定期地执行。
static ScheduledExecutorService newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor()
//创建一个单线程执行程序,它可安排在给定延迟后运行命令或者定期地执行。
static ScheduledExecutorService newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory)
//返回 Callable 对象,调用它时可在当前的访问控制上下文中执行给定的 callable 对象。
static <T> Callable<T> privilegedCallable(Callable<T> callable)
//返回 Callable 对象,调用它时可在当前的访问控制上下文中,使用当前上下文类加载器作为上下文类加载器来执行给定的 callable 对象。
static <T> Callable<T> privilegedCallableUsingCurrentClassLoader(Callable<T> callable)
//返回用于创建新线程的线程工厂,这些新线程与当前线程具有相同的权限。
static ThreadFactory privilegedThreadFactory()
//返回一个将所有已定义的 ExecutorService 方法委托给指定执行程序的对象,但是使用强制转换可能无法访问其他方法。
static ExecutorService unconfigurableExecutorService(ExecutorService executor)
//返回一个将所有已定义的 ExecutorService 方法委托给指定执行程序的对象,但是使用强制转换可能无法访问其他方法。
static ScheduledExecutorService unconfigurableScheduledExecutorService(ScheduledExecutorService executor)
}
线程池示例
在分析线程池之前,先看一个简单的线程池示例。
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; public class ThreadPoolDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个可重用固定线程数的线程池
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
// 创建实现了Runnable接口对象,Thread对象当然也实现了Runnable接口
Thread ta = new MyThread();
Thread tb = new MyThread();
Thread tc = new MyThread();
Thread td = new MyThread();
Thread te = new MyThread();
// 将线程放入池中进行执行
pool.execute(ta);
pool.execute(tb);
pool.execute(tc);
pool.execute(td);
pool.execute(te);
// 关闭线程池
pool.shutdown();
}
} class MyThread extends Thread { @Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ " is running.");
}
}
运行结果:
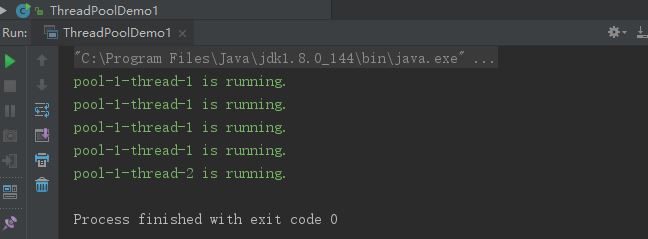
结果说明:
主线程中创建了线程池pool,线程池的容量是2。即,线程池中最多能同时运行2个线程。
紧接着,将ta,tb,tc,td,te这3个线程添加到线程池中运行。
最后,通过shutdown()关闭线程池。
终于到了小时候羡慕的年纪,却没能成为小时候羡慕的人。
最新文章
- 一步一步使用ABP框架搭建正式项目系列教程之本地化详解
- 【repost】JavaScript完美运动框架的进阶之旅
- 引用类型(object、array)
- parentNode、parentElement,childNodes、children 它们有什么区别呢?
- Effective Java 29 Consider typesafe heterogeneous containers
- 恢复被win7覆盖的Ubuntu Grub
- 【转】Android版本和API Level对应关系
- [转]Hulu 2013北京地区校招笔试题
- URAL 1963 Kite 四边形求对称轴数
- POJ 2425 A Chess Game#树形SG
- 在Windows的DOS中运行java编程中的问题
- C# List 集合 交集、并集、差集、去重, 对象集合、 对象、引用类型、交并差补、List<T>
- fixed 相对于父容器定位
- 轻量应用服务器安装 phpMyAdmin
- openzeppelin-solidity/contracts的代码学习——access
- ES6入门之let、cont
- D - Lake Counting
- notepad 正则表达式 复制 文本
- grid的简单使用
- Windows7双系统的启动顺序怎样修改?