常见的几种java排序算法
2024-10-09 05:32:50
一.分类:
1)插入排序(直接插入排序、希尔排序)
2)交换排序(冒泡排序、快速排序)
3)选择排序(直接选择排序、堆排序)
4)归并排序
5)分配排序(基数排序)
所需辅助空间最多:归并排序
所需辅助空间最少:堆排序
平均速度最快:快速排序
不稳定:快速排序,希尔排序,堆排序。
先来看看 8种排序之间的关系:
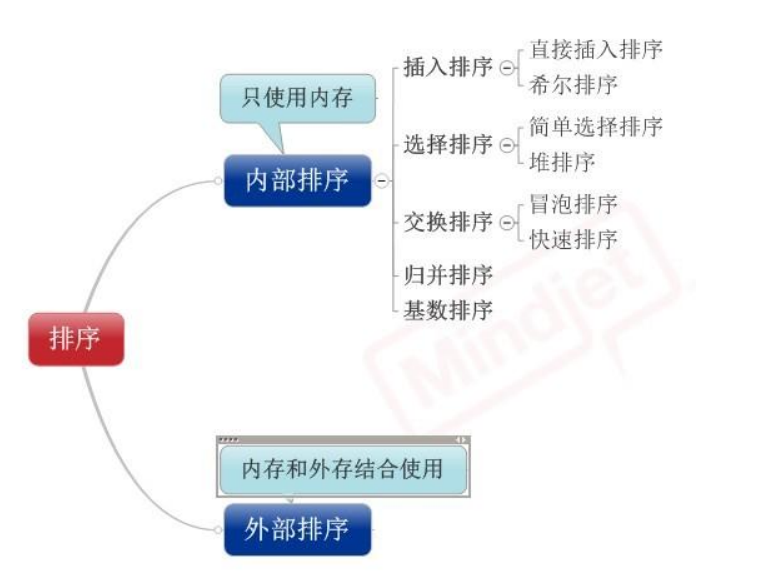
二.常见排序
1.冒泡排序(BubbleSort)
1.依次比较相邻的两个元素,通过一次比较把未排序序列中最大(或最小)的元素放置在未排序序列的末尾。
2.原理图

public class BubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1,42,354,6,5,7,74,4,675,6,45345,3,64,3,4,365,34,3,43,45,34,563,64,457,546,4};
int temp =0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length-1; i++) { //n个数比较n-1次
for (int j = 0; j < a.length-1-i; j++) { //注意j的范围
if (a[j]>a[j+1]) {
temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j+1];
a[j+1] =temp;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.println(a[i]); //遍历排序好的数组
}
}
}
2.快速排序(QuickSort)
1.基本思想:选择一个基准元素,通常选择第一个元素或者最后一个元素,通过一趟扫描,将待排序列分成两部分,一部分比基准元素小,一部分大于等于基准元素,此时基准元素在其排好序后的正确位置,然后再用同样的方法递归地排序划分的两部分。
2.原理图

public class QuickSort {
public static void sort(int data[], int start, int end) {
if (end - start <= 0) {
return;
}
int last = start;
for (int i = start + 1; i <= end; i++) {
if (data[i] < data[start]) {
int temp = data[++last];
data[last] = data[i];
data[i] = temp;
}
}
int temp = data[last];
data[last] = data[start];
data[start] = temp;
sort(data, start, last - 1); //排序所在数的前一部分
sort(data, last + 1, end); //排序所在数的后一部分
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1,42,354,6,5,7,74,4,675,6};
sort(a, 0, a.length-1);
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.println(a[i]); //遍历已经排序好的数组
}
}
}
3.插入排序(InsertSort)
1.将数列分为有序和无序两个部分,每次处理就是将无序数列的第一个元素与有序数列的元素从后往前逐个进行比较,找出插入位置,将该元素插入到有序数列的合适位置中。
2.原理图

public class InsertSort {
public static void Insert(int data[]) {
for (int i = 1; i < data.length; i++) {
for (int j = i; j > 0; j--) { //随着i值增大,j值每次插入的次数也增大
if (data[j] < data[j - 1]) {
int temp = data[j];
data[j] = data[j - 1];
data[j - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1,42,354,6,5,7,74,4,675,6};
Insert(a);
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.println(a[i]); //遍历已经排序好的数组
}
}
}
4.选择排序(SelectionSort)
1.基本思想:在要排序的一组数中,选出最小的一个数与第一个位置的数交换;然后在剩下的数当中再找最小的与第二个位置的数交换,如此循环到倒数第二个数和最后一个数比较为止。
2.原理图

public class SelectionSort {
public static void selectionSort(int data[]){
for (int i = 0; i < data.length-1; i++) {
int minVal = data[i];
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i+1; j < data.length; j++) {
if (data[j]<minVal) { //将当前数与minVal比较
minVal = data[j]; //如果当前数小于minVal则把当前数赋给minVal
minIndex = j; //把当前索引赋给minIndex
}
}
if(minVal != data[i] && minIndex != i){ //如果上一步有交换
data[minIndex] = data[i];//则把当前数放到当前最小数组的位置,如此反复
data[i] = minVal;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1,42,354,6,5,7,74,4,675,6,45345,3,64,3,4,365,34,3,43,45,34,563,64,457,546,4};
selectionSort(a);
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.println(a[i]);//遍历排序好的数组
}
}
}
最新文章
- Collections.unmodifiableMap
- JS产生随机数的几个用法!
- 浅谈 原生javaScript&&react 实现全局触摸按钮(附带对addeventlistener的了解)
- onethink连接操作 sqlite 数据库
- 对list集合中的对象按照对象的某一属性进行排序
- BZOJ 1001 & SPFA
- SQL-学习使用FOR XML PATH
- "SOAP WebService " 和 "RESTful WebService" 的定义分别是什么???
- [教程] 神器i9100刷基带与内核的方法!(兼带ROOT方法)
- [问题解决] VNC连接黑屏或者灰屏+命令行
- POJ 3080 Blue Jeans(后缀数组+二分答案)
- 以太坊RLP用法-go-ethereum学习
- eclipse下出现奇怪字符的解决方法
- DAX和Power BI中的参考日期表
- [转]异常声音检测之kaldi DNN 训练
- 我在 Mac 上都用什么
- windows使用笔记-google-chrome下载地址
- React Router基础教程
- Java中static、final、static final的区别(转)+transient
- Spring整合struts的配置文件存放问题
热门文章
- 感觉shopex现在的升级方式太慢了
- vs2015 cppunit配置及使用
- PAT-1079 Total Sales of Supply Chain (树的遍历)
- docker常用命令,及进入Tomcat的WebApps发布目录(就是进入docker容器后台目录)
- 还不会K8S吗?先从kubeadm开始吧
- wordpress评论回复邮件通知功能
- 解决WordPress网站被利用xmlrpc.php文件攻击问题
- SQLSTATE[42S01]: Base table or view already exists: 1050 Table 'xxx' already exists
- Ef core 如何设置主键
- NodeJS——大汇总(一)(只需要使用这些东西,就能处理80%以上业务需求,全网最全node解决方案,吐血整理)