AutoValue —— Generated immutable value classes
本文参考
在《Effective Java》第三版第十条"Obey the general contract when overriding equals"中提到google的AutoValue框架能够自动生成equals()方法,实际上这个框架的作用不仅仅限于生成equals()方法那么简单,它还能够使值类通过静态工厂方法构建实例,并实现Builder构建者模式,省去了程序员对值类的重复性工作
github地址:https://github.com/google/auto/blob/master/value/userguide/index.md
环境
idea 2020.1 + AutoValue 1.7.1
Maven配置
我们需要同时配置auto-value-annotations和auto-value两个dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.auto.value</groupId>
<artifactId>auto-value-annotations</artifactId>
<version>1.7.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.auto.value</groupId>
<artifactId>auto-value</artifactId>
<version>1.7.1</version>
<optional>true</optional>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
Idea配置
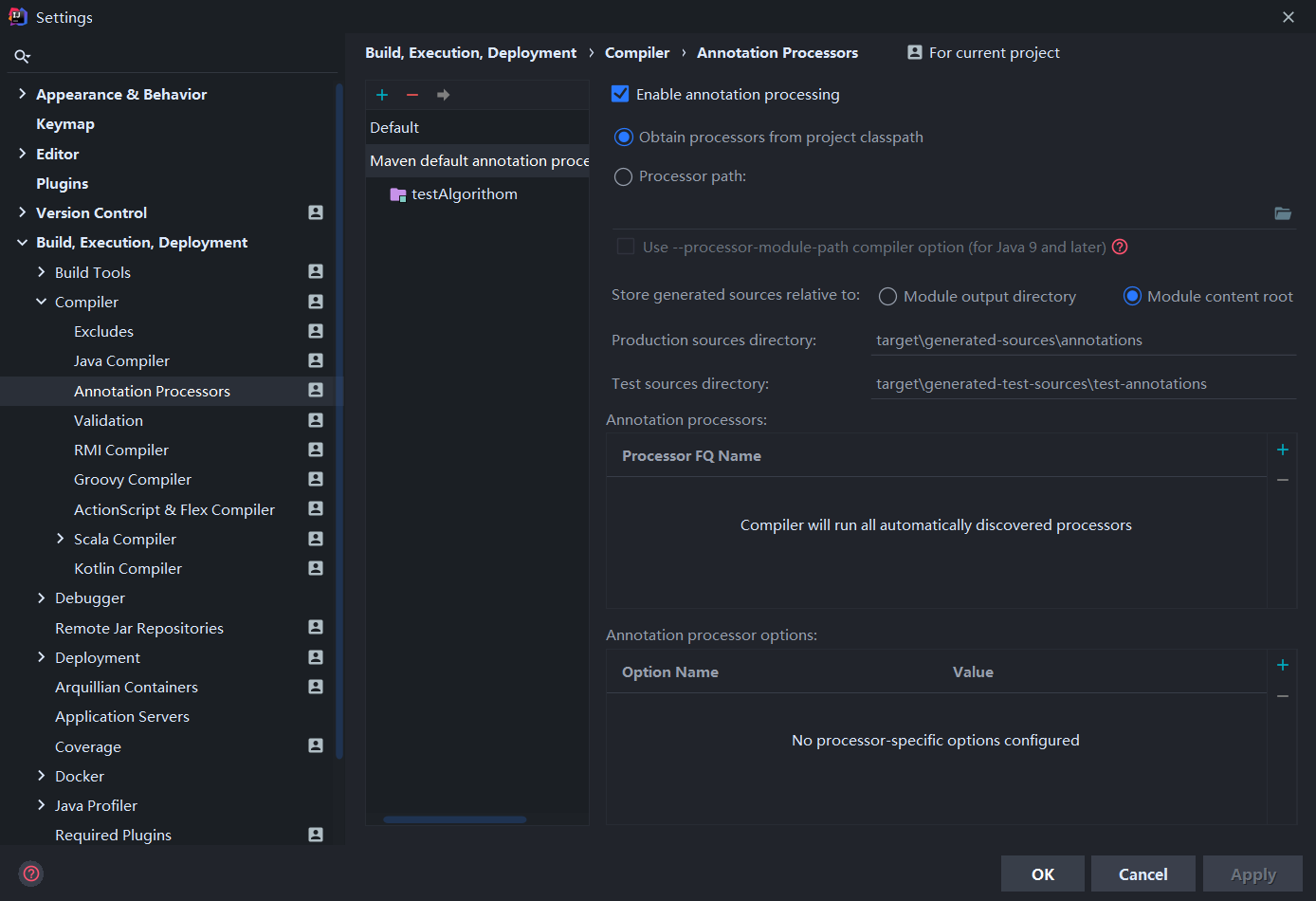
在Build,Execution,Deployment -> Complier -> Annotation Processor中勾选Enable annotation processing
默认的Production source directory和Test sources directory不需要更改
基本用法
如下代码所示,构造Person抽象类,create()静态工厂方法,和抽象的字段方法
@AutoValue
abstract class Person {
abstract String getName();
abstract int getAge();
static Person create(String name, int age) {
return new AutoValue_Person(name, age);
}
}
此时显然还没有AutoValue_Person这个类(固定的前缀写法),因此idea会报错,但是我们暂时不用担心这个问题
编写一个简单的测试类,测试方法如下
@Test
public void test() {
Person person = Person.create("kuluo", 18);
assertEquals("kuluo", person.name());
}
可以先对源代码进行编译而不运行,编译结束后可以看到AutoValue_Person的报错消失
我们可以在默认的target\generated-sources\annotations或target\generated-test-sources\test-annotations文件夹中看到生成的值类
@Generated("com.google.auto.value.processor.AutoValueProcessor")
final class AutoValue_Person extends Person {
private final String name;
private final int age;
AutoValue_Person(String name, int age) {
if (name == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("Null name");
}
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
int getAge() {
return age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{"
+ "name=" + name + ", "
+ "age=" + age
+ "}";
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
}
if (o instanceof Person) {
Person that = (Person) o;
return this.name.equals(that.name()) && this.age == that.age();
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int h$ = 1;
h$ *= 1000003;
h$ ^= name.hashCode();
h$ *= 1000003;
h$ ^= age;
return h$;
}
}
注意:
- 值类被声明为final类型,无法再被继承
- 值类不具备setter方法,实例被创建后就无法被更改
- 若在构造实例时允许传入可变类型的值,如List<String>和String[],则需要在Guava中选择对应的不可变类型,并更改create()静态工厂方法
check if the mutable type has a corresponding immutable cousin. For example, the types List<String> and String[] have the immutable counterpart ImmutableList<String> in Guava. If so, use the immutable type for your property, and only accept the mutable type during construction
@AutoValue
abstract class Person {
abstract ImmutableList<String> getName();
abstract int getAge();
static Person create(List<String> name, int age) {
return new AutoValue_Person(ImmutableList.copyOf(name), age);
}
}
- 值类在构建实例时会检查每一个字段是否为null,若某字段为null,则抛出空指针异常
- 若允许某个字段为null,则必须在抽象类create()静态工厂方法的声明中,为该字段和它对应的getter方法同时添加@Nullable注解
if @Nullable is only added to the parameter in create (or similarly the setter method of AutoValue.Builder), but not the corresponding accessor method, it won't have any effect.
@AutoValue
abstract class Person {
@Nullable abstract String getName();
abstract int getAge();
static Person create(@Nullable String name, int age) {
return new AutoValue_Person(name, age);
}
}
下面仅展示发生变化的方法,我们可以看到在equals()方法和hashCode()方法中也自动增加了对null的判断
AutoValue_Person(@Nullable String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Nullable
@Override
String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
}
if (o instanceof Person) {
Person that = (Person) o;
return (this.name == null ? that.getName() == null : this.name.equals(that.getName()))
&& this.age == that.getAge();
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int h$ = 1;
h$ *= 1000003;
h$ ^= (name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode();
h$ *= 1000003;
h$ ^= age;
return h$;
}
Builder构建者模式用法
涉及抽象静态内部类Builder,并为它添加@AutoValue.Builder注解
@AutoValue
abstract class PersonWithBuilder {
abstract String getName();
abstract int getAge();
static Builder builder() {
return new AutoValue_PersonWithBuilder.Builder();
}
@AutoValue.Builder
abstract static class Builder {
abstract Builder name(String name);
abstract Builder age(int age);
abstract PersonWithBuilder build();
}
}
编写一个简单的测试类,测试代码如下:
@Test
public void testWithBuilder() {
PersonWithBuilder personWithBuilder = PersonWithBuilder
.builder()
.name("kuluo")
.age(18)
.build();
assertEquals("kuluo", personWithBuilder.getName());
assertEquals(18, personWithBuilder.getAge());
}
编译运行后生成AutoValue_PersonWithBuilder类
@Generated("com.google.auto.value.processor.AutoValueProcessor")
final class AutoValue_PersonWithBuilder extends PersonWithBuilder {
private final String name;
private final int age;
private AutoValue_PersonWithBuilder(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
String getName() { return name; }
@Override
int getAge() { return age; }
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PersonWithBuilder{"
+ "name=" + name + ", "
+ "age=" + age
+ "}";
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) { return true; }
if (o instanceof PersonWithBuilder) {
PersonWithBuilder that = (PersonWithBuilder) o;
return this.name.equals(that.getName()) && this.age == that.getAge();
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int h$ = 1;
h$ *= 1000003;
h$ ^= name.hashCode();
h$ *= 1000003;
h$ ^= age;
return h$;
}
static final class Builder extends PersonWithBuilder.Builder {
private String name;
private Integer age;
Builder() {
}
@Override
PersonWithBuilder.Builder name(String name) {
if (name == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("Null name");
}
this.name = name;
return this;
}
@Override
PersonWithBuilder.Builder age(int age) {
this.age = age;
return this;
}
@Override
PersonWithBuilder build() {
String missing = "";
if (this.name == null) {
missing += " name";
}
if (this.age == null) {
missing += " age";
}
if (!missing.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Missing required properties:" + missing);
}
return new AutoValue_PersonWithBuilder(this.name, this.age);
}
}
}
注意:
- 值类在构建实例时会在build()方法内检查每一个字段是否为null,若某字段为null,则抛出空指针异常
- 若允许某个字段为null,则必须同时在抽象静态内部类的"setter"方法的形参和外侧的"getter"方法同时添加@Nullable注解
@AutoValue
abstract class PersonWithBuilder {
@Nullable abstract String getName();
abstract int getAge();
static Builder builder() {
return new AutoValue_PersonWithBuilder.Builder();
}
@AutoValue.Builder
abstract static class Builder {
abstract Builder name(@Nullable String name);
abstract Builder age(int age);
abstract PersonWithBuilder build();
}
}
我们可以在生成的AutoValue_PersonWithBuilder类中看到已经没有了对name的null判断
@Override
PersonWithBuilder build() {
String missing = "";
if (this.age == null) {
missing += " age";
}
if (!missing.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Missing required properties:" + missing);
}
return new AutoValue_PersonWithBuilder(this.name, this.age);
}
- 若需要为某字段设置默认值,仅需在builder()方法中调用Builder的"setter"方法
@AutoValue
abstract class PersonWithBuilder {
abstract String getName();
abstract int getAge();
static Builder builder() {
return new AutoValue_PersonWithBuilder.Builder().name("kuluo");
}
@AutoValue.Builder
abstract static class Builder {
abstract Builder name(String name);
abstract Builder age(int age);
abstract PersonWithBuilder build();
}
}
- 使用Builder模式后会屏蔽静态工厂方法,若一定要使用静态工厂方法,则需要在静态工厂方法内调用Builder静态内部类来创建实例,而不是私有的构造方法
最新文章
- MySQL初始化的正确姿势
- Spike Notes on Lock based Concurrency Concepts
- ArcEngine批量添加XY数据
- 让spark运行在mesos上 -- 分布式计算系统spark学习(五)
- Linux 磁盘与文件系统管理
- C#执行oracle返回游标类型的存储过程
- Java学习日记8-包、环境变量和访问控制
- 终于懂了:WM_PAINT中应该用BeginPaint与EndPaint这两个api,它们的功能正是使无效区域恢复(所以WM_PAINT里即使什么都不做,也必须写上BeginPaint与EndPaint)——Delphi里WM_PAINT消息的三个走向都做到了这一点 good
- java基础之类与对象1
- [Swift]LeetCode201. 数字范围按位与 | Bitwise AND of Numbers Range
- AngularJS基于MVC的复杂操作案例
- ssm框架中处理json格式的数据步骤
- 20155306 白皎 《网络攻防》 EXP8 Web基础
- Maven运行Selenium报错org/w3c/dom/ElementTraversal
- 【JUnit】@Test 报错,"Test cannot be resolved to a type"
- 尝试用selenium+appium运行一个简单的demo报错:could not get xcode version. /Library/Developer/Info.plist doest not exist on disk
- http的GET和POST
- vim 查找
- 互评Alpha版本——二次元梦之队——“I Do”
- 【有上下界网络流】【ZOJ】2314 Reactor Cooling
热门文章
- 【C# 线程】 volatile 关键字和Volatile类、Thread.VolatileRead|Thread.VolatileWrite 详细 完整
- Java课程设计---新建项目及导入如何jar包
- python浅拷贝与深拷贝浅析
- 【NumPy】 之常见运算(np.around、np.floor、np.ceil、np.where)(转)
- 学习linux(centos7)记录的笔记
- github打开之后下载缓慢或者下载不了问题的解决
- LGP5591题解
- JavaWeb 05_JDBC入门及连接MySQL
- 字符串的高级应用-char a[100] = "1+2=;3-2=;2*5=;8/4=;" 得到char a[100] ="1+2=3;3-2=1;2*5=10;8/4=2;"
- Docker重要容器命令