03-树3 Tree Traversals Again (25 分)
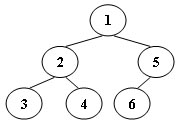
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
Figure 1
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2 lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
Sample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = ; struct Node
{
int data;
Node *lchild, *rchild;
}; int in[maxn] = {}, pre[maxn] = {};
int num = ; Node* createTree(int preL, int preR, int inL, int inR);
void postOrder(Node *root,int n); int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n); int x;
int preIndex = , inIndex = ;
char str[];
stack<int> s; for (int i = ; i < *n; i++)
{
getchar();
scanf("%s",str);
if ( == strcmp(str,"Push"))
{
scanf("%d",&x);
s.push(x);
pre[preIndex++] = x;
}
else
{
x = s.top();
s.pop();
in[inIndex++] = x;
}
} Node *root = createTree(,n-,,n-);
postOrder(root,n);
return ;
} Node* createTree(int preL, int preR, int inL, int inR)
{
if (preL > preR)
{
return NULL;
} Node *root = new Node;
root->data = pre[preL]; int k;
for (k = inL; k <= inR; k++)
{
if (in[k] == pre[preL])
{
break;
}
} int numLeft = k - inL;
root->lchild = createTree(preL+, preL+numLeft, inL, k-);
root->rchild = createTree(preL+numLeft+, preR, k+, inR);
return root;
} void postOrder(Node *root,int n)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
postOrder(root->lchild,n);
postOrder(root->rchild,n);
printf("%d",root->data); num++;
if (num < n)
{
printf(" ");
}
}
最新文章
- 你所不知道的linq(二)
- angular开发单页面应用--页面资源部分
- Sql Server系列:游标
- ubuntu 13.04下MYSQL 5.5环境搭建
- 2014年第五届蓝桥杯C/C++程序设计本科B组决赛
- C#图像处理(4):图像的剪裁
- 在Word中为标题样式添加自动编号功能
- HTML CSS——background的认识(一)
- <global-results>标签来定义全局的<result>
- leetcode算法:Reshape the Matrix
- hdu 5052 树链剖分
- luoguP2526_[SHOI2001]小狗散步_二分图匹配
- Ubuntu 服务器上面--安装和配置mysql 【转】
- Linux实操篇 vi和vim编辑器
- javaMail实现收发邮件(三)
- 阿里云服务器安装SQLServer本地无法远程访问
- ssm框架整合
- PHP如何安装redis扩展(Windows下)
- python scipy stats学习笔记
- php curl批处理--可控并发异步
热门文章
- opencv常用数据结构
- .net core将URL请求格式化为XML或JSON(网站动态生成sitemap.xml)
- 使用Supervisord软件管理go服务进程
- 记一下python的method resolution order(MRO)机制
- 【转载】C#通过Rows.Count属性获取总行数
- MySQL导入数据报错Got a packet bigger than‘max_allowed_packet’bytes错误的解决方法
- Product settype acts as a very important role in CRM WebClient UI architecture
- redis-5.0.5安装(linux centos)
- Python之路(第四十四篇)线程同步锁、死锁、递归锁、信号量
- 一、MySQL基础知识