kaggle 实战 (2): CNN 手写数字识别
2024-09-06 08:13:10
文章目录
Tensorflow 官方示例
import tensorflow as tf
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(x_train, y_train),(x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(512, activation=tf.nn.relu),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.2),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation=tf.nn.softmax)
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=5)
model.evaluate(x_test, y_test)
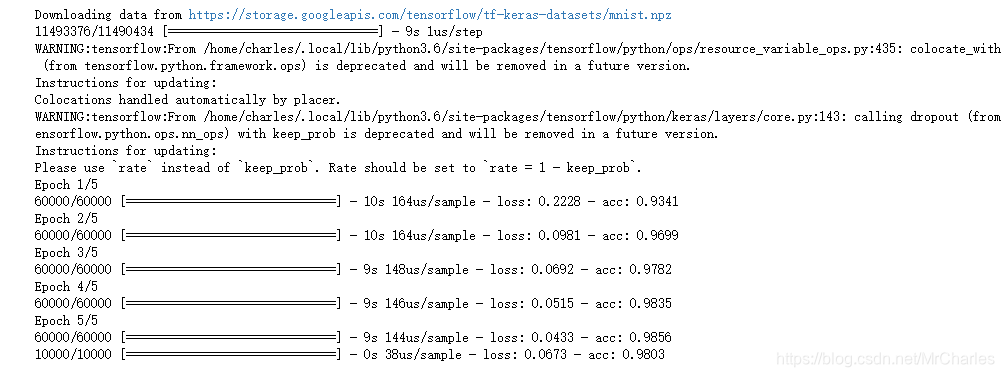
这个本身精度不高,我们可以改变结构提升精度
CNN
from __future__ import division, print_function, absolute_import
# Import MNIST data
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("/tmp/data/", one_hot=False)
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Training Parameters
learning_rate = 0.001
num_steps = 2000
batch_size = 128
# Network Parameters
num_input = 784 # MNIST data input (img shape: 28*28)
num_classes = 10 # MNIST total classes (0-9 digits)
dropout = 0.25 # Dropout, probability to drop a unit
# Create the neural network
def conv_net(x_dict, n_classes, dropout, reuse, is_training):
# Define a scope for reusing the variables
with tf.variable_scope('ConvNet', reuse=reuse):
# TF Estimator input is a dict, in case of multiple inputs
x = x_dict['images']
# MNIST data input is a 1-D vector of 784 features (28*28 pixels)
# Reshape to match picture format [Height x Width x Channel]
# Tensor input become 4-D: [Batch Size, Height, Width, Channel]
x = tf.reshape(x, shape=[-1, 28, 28, 1])
# Convolution Layer with 32 filters and a kernel size of 5
conv1 = tf.layers.conv2d(x, 32, 5, activation=tf.nn.relu)
# Max Pooling (down-sampling) with strides of 2 and kernel size of 2
conv1 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(conv1, 2, 2)
# Convolution Layer with 64 filters and a kernel size of 3
conv2 = tf.layers.conv2d(conv1, 64, 3, activation=tf.nn.relu)
# Max Pooling (down-sampling) with strides of 2 and kernel size of 2
conv2 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(conv2, 2, 2)
# Flatten the data to a 1-D vector for the fully connected layer
fc1 = tf.contrib.layers.flatten(conv2)
# Fully connected layer (in tf contrib folder for now)
fc1 = tf.layers.dense(fc1, 1024)
# Apply Dropout (if is_training is False, dropout is not applied)
fc1 = tf.layers.dropout(fc1, rate=dropout, training=is_training)
# Output layer, class prediction
out = tf.layers.dense(fc1, n_classes)
return out
# Define the model function (following TF Estimator Template)
def model_fn(features, labels, mode):
# Build the neural network
# Because Dropout have different behavior at training and prediction time, we
# need to create 2 distinct computation graphs that still share the same weights.
logits_train = conv_net(features, num_classes, dropout, reuse=False, is_training=True)
logits_test = conv_net(features, num_classes, dropout, reuse=True, is_training=False)
# Predictions
pred_classes = tf.argmax(logits_test, axis=1)
pred_probas = tf.nn.softmax(logits_test)
# If prediction mode, early return
if mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT:
return tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec(mode, predictions=pred_classes)
# Define loss and optimizer
loss_op = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
logits=logits_train, labels=tf.cast(labels, dtype=tf.int32)))
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate)
train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss_op, global_step=tf.train.get_global_step())
# Evaluate the accuracy of the model
acc_op = tf.metrics.accuracy(labels=labels, predictions=pred_classes)
# TF Estimators requires to return a EstimatorSpec, that specify
# the different ops for training, evaluating, ...
estim_specs = tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec(
mode=mode,
predictions=pred_classes,
loss=loss_op,
train_op=train_op,
eval_metric_ops={'accuracy': acc_op})
return estim_specs
# Build the Estimator
model = tf.estimator.Estimator(model_fn)
# Define the input function for training
input_fn = tf.estimator.inputs.numpy_input_fn(
x={'images': mnist.train.images}, y=mnist.train.labels,
batch_size=batch_size, num_epochs=None, shuffle=True)
# Train the Model
model.train(input_fn, steps=num_steps)
# Evaluate the Model
# Define the input function for evaluating
input_fn = tf.estimator.inputs.numpy_input_fn(
x={'images': mnist.test.images}, y=mnist.test.labels,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
# Use the Estimator 'evaluate' method
model.evaluate(input_fn)
import pandas as pd # data processing, CSV file I/O (e.g. pd.read_csv)
#test=pd.read_csv('./input/test.csv')
import numpy
from numpy import genfromtxt
my_data = numpy.double(genfromtxt('./input/test.csv', delimiter=','))
# Prepare the input data
input_fn = tf.estimator.inputs.numpy_input_fn(
x={'images': numpy.float32(my_data[1:,:])}, shuffle=False)
# Use the model to predict the images class
preds2 = list(model.predict(input_fn))
Submission = pd.DataFrame({
"ImageId": range(1, len(preds2)+1),
"Label": preds2
})
Submission.to_csv("cnnMnistSubmission.csv", index=False)
Submission.head(5)
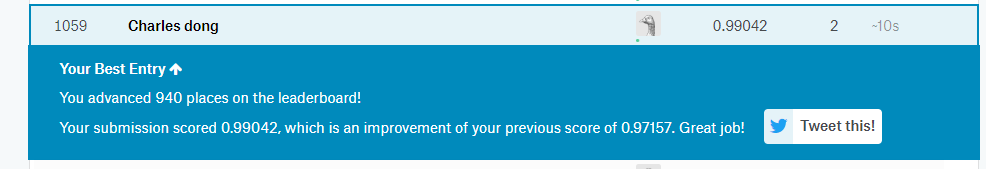
提交结果
最新文章
- Navicat Premium连接Oracle 问题汇总
- Linux学习笔记——重点推荐的Linux网络在线学习资源
- MSSQL 跨数据库连接
- Redis教程(十五):C语言连接操作代码实例
- C语言的几个有趣问题
- Linux多线程——使用互斥量同步线程
- sudo nopasswd
- JDBC中rs.beforeFirst()
- 版本控制工具——Git常用操作(上)
- org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource类
- Docker指令
- 《算法》第四章部分程序 part 13
- ASP.NET MVC2之Model Binder
- 【转载】python import和from import
- JavaScript 中 substr 和 substring的区别
- Java补漏(一)
- 前端工程师(JavaScript)在业余时间如何提高自身能力
- Spark实战练习01--XML数据处理
- Maven如何打包本地依赖包
- fzu2181(点的双连通分量+求奇环)