爬虫----beautifulsoup的简单使用
beautifulSoup使用:
简单来说,Beautiful Soup是python的一个库,最主要的功能是从网页抓取数据。
pip3 install beautifulsoup4
解析器
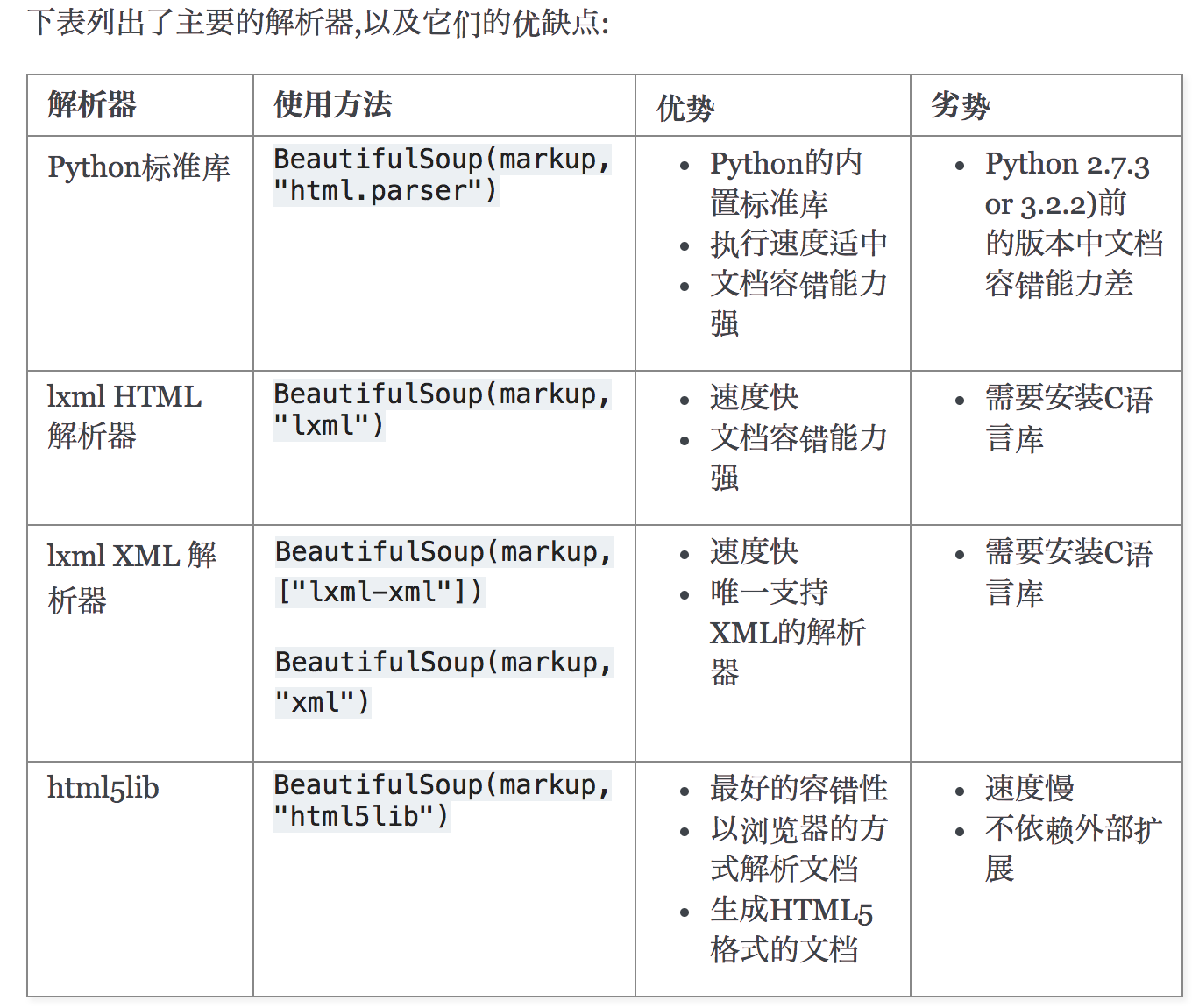
Beautiful Soup支持Python标准库中的HTML解析器,还支持一些第三方的解析器,如果我们不安装它,则 Python 会使用 Python默认的解析器,lxml 解析器更加强大,速度更快,推荐安装。
pip3 install lxml
另一个可供选择的解析器是纯Python实现的 html5lib , html5lib的解析方式与浏览器相同,可以选择下列方法来安装html5lib:
pip install html5lib
使用:
html文档
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p>
"""
使用
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser') #html_doc 可以使用本地的html文档,可以用网络来获取 html文档 ,此时 html_doc 是字符串
print(soup.prettify())
具体
1、soup.title
# <title>The Dormouse's story</title> 2、soup.title.name
# u'title' 2、soup.head.title = soup.find("head").find("title")
# <title>The Dormouse's story</title>
3、soup.title.string
# u'The Dormouse's story'
4、find_parent()/find_parents()
#a_string = soup.find(string="Lacie")
#print(a_string.find_parent())
#print(a_string.find_parent("p"))
#print(a_string.find_parents())
4、soup.title.parent.name
# u'head'
5、soup.p #通过点取属性的方式只能获得当前名字的第一个tag:
# <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> 6、soup.p['class']
# u'title'
7、soup.a
# <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a> 7、soup.find_all('a')
# [<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
# <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>,
# <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>] 7、soup.find_all("a",limit=2) #限制只能找两个 7、soup.find_all("a",recursive=False) #find_all() 会检索所有的子孙节点 ,recursive=False,表示只检索 子节点
8、soup.find_all(id="id1") 9、soup.find_all(["a","p"]) #找到所有的a标签和p标签 10、soup.find_all(True) #True 可以匹配任何值,下面代码查找到所有的tag,但是不会返回字符串节点
11、soup.find_all(id=True) #找到所有的 含有 id 的标签
12、soup.find_all(href=re.compile("elsie"), id='link1') #多条件过滤
# [<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">three</a>]
13、soup.find_all("a", class_="sister") #使用class过滤 ,不能直接使用class;class是python的关键字
#[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
#<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>,
#<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
#]
14、data_soup.find_all(attrs={"data-foo": "value"}) #通过属性查找
#[<div data-foo="value">foo!</div>]
14、soup.find(id="link3")
# <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
import re #使用正则
15、soup.find(string=re.compile("sisters"))
# u'Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were\n' 15、soup.find_all(text=re.compile("Dormouse") #使用正则 text 参数可以搜搜文档中的字符串内容
# ["The Dormouse's story", "The Dormouse's story"]
import re #使用正则
16、for tag in soup.find_all(re.compile("^b")):
print(tag.name)
#body
#b 通过CSS选择器查找
select 方法返回的结果都是列表形式,可以遍历形式输出,然后用 get_text() 方法来获取它的内容:
1、print(soup.select("title")) #[<title>The Dormouse's story</title>]
2、print(soup.select(".sister")) #找所有的class="sister"
3、print(soup.select("#link1"))
4、print(soup.select("p #link2")) 5、print(soup.select("p > #link2"))
6、print(soup.select("a[href='http://example.com/tillie']")) #属性查找
自定义过滤器
def has_class_but_no_id(tag):
return tag.has_attr('class') and not tag.has_attr('id') print(soup.find_all(has_class_but_no_id)) '''
[
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>,
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>,
<p class="story">...</p>
]
'''
name和attributes属性
每个tag都有自己的名字,通过 .name 来获取
tag['class'] = 'verybold'
tag['id'] = 1
tag
# <blockquote class="verybold" id="1">Extremely bold</blockquote> del tag['class']
del tag['id']
tag
# <blockquote>Extremely bold</blockquote> tag['class']
# KeyError: 'class'
print(tag.get('class'))
# None
用 .string标签内部的文字
字符串常被包含在tag内.Beautiful Soup用 NavigableString 类来包装tag中的字符串,通过 unicode() 方法可以直接将 NavigableString 对象转换成Unicode字符串:
tag.string
# u'Extremely bold'
type(tag.string)
# <class 'bs4.element.NavigableString'> unicode_string = unicode(tag.string)
unicode_string
# u'Extremely bold'
type(unicode_string)
# <type 'unicode'>
tag中包含的字符串不能编辑,但是可以被替换成其它的字符串,用 replace_with() 方法:
tag.string.replace_with("No longer bold")
tag
# <blockquote>No longer bold</blockquote>
从文档中获取所有文字内容:
print(soup.get_text())
beautifulSoup遍历文档树:
1.子节点/子孙节点
tag的
.contents 属性可以将tag的子节点以列表的方式输出:
.children 它返回的不是一个 list,不过我们可以通过遍历获取所有子节点。.childern返回的是一个list生成器对象.descendants属性可以对所有tag的子孙节点进行递归循环 。
2.父节点
.parent 获取某个元素的父节点
.parents 递归得到元素的所有父辈节点 for parent in link.parents:
if parent is None:
print(parent)
else:
print(parent.name)
3.兄弟节点
.next_sibling 获取了该节点的下一个兄弟节点
.previous_sibling 则与之相反
如果节点不存在,则返回 None
注意:实际文档中的tag的 .next_sibling 和 .previous_sibling 属性通常是字符串或空白,因为空白或者换行也可以被视作一个节点,所以得到的结果可能是空白或者换行
全部兄弟节点
.next_siblings .previous_siblings 属性 通过 .next_siblings 和 .previous_siblings 属性可以对当前节点的兄弟节点迭代输出 for sibling in soup.a.next_siblings:
print(repr(sibling))
4.前后节点
.next_element .previous_element #只找一个
注意:与 .next_sibling .previous_sibling 不同,它并不是针对于兄弟节点,而是在所有节点,不分层次
例子
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title><a>ddddd</a></head> print(soup.head.next_element) #<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
print(soup.head.next_element.next_element) #The Dormouse's story
print(soup.head.next_element.next_element.next_element)
print(soup.head.next_element.next_element.next_element.next_element.next_element.next_element.next_element+“........”) #会一直往后找,递归着找,但是每一次只能找一个
所有前后节点
.next_elements .previous_elements 递归搜索所有的
通过 .next_elements 和 .previous_elements 的迭代器就可以向前或向后访问文档的解析内容,就好像文档正在被解析一样
5、节点内容 .string
如果一个标签里面没有标签了,那么 .string 就会返回标签里面的内容。如果标签里面只有唯一的一个标签了,那么 .string 也会返回最里面的内容。
如果tag包含了多个子节点,tag就无法确定,string 方法应该调用哪个子节点的内容, .string 的输出结果是 None
2.1多个内容 .strings
获取多个内容,不过需要遍历获取,比如下面的例子:
for string in soup.strings:
print(repr(string)) #会打印 “/n” 换行符
2.2多个内容 .stripped_strings 输出的字符串中可能包含了很多空格或空行,使用 .stripped_strings 可以去除多余空白内容
for string in soup.stripped_strings:
print(repr(string)) #不会打印换行符
补充
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(open("index.html"))
soup = BeautifulSoup("<html>data</html>")
然后,Beautiful Soup选择最合适的解析器来解析这段文档,如果手动指定解析器那么Beautiful Soup会选择指定的解析器来解析文档。
最新文章
- 6 Candy_Leetcode
- 关于大型网站技术演进的思考(十九)--网站静态化处理—web前端优化—上(11)
- css设置背景图片
- HttpFox插件安装和打开教程
- [安卓]Android窗口、视图、布局
- ViewManager
- redhat enterprixe 5.0 samba 服务器 rpm 安装及配置
- Delphi 连接mysql 的功能, 去除乱码, 需要设置字符集
- JavaScript对象的创建之使用json格式定义
- JQuery 判断某个属性是否存在 hasAttr
- [selenium webdriver Java]显示的等待同步
- C# zip/unzip with ICSharpCode.SharpZipLib
- WPF之application对象
- 【Electron】Electron开发入门(五):项目打包
- 【Egret】Native版本 视频播放器(android)
- Java自学手记——struts2
- 如何禁止App在后台运行以及如何保存和恢复App的状态
- 安卓中不同APP之间的消息通信
- ;(function(){})()这种写法分号的作用 todomvc
- keras使用