Learning-Python【4】:Python流程控制与循环
一、if...else分支
1、什么是if判断
判断一个条件如果成立则如何,不成立则如何
2、为何要有if判断
让计算机能像人一样具有判断能力
语法1:if...else
if 判断条件:
代码块1
else:
代码块2
语法2:if嵌套
if 条件1:
if 条件2:
代码块1
代码块2
语法3:if...elif...else
if 条件1:
代码块1
elif 条件2:
代码块2
else:
代码块3
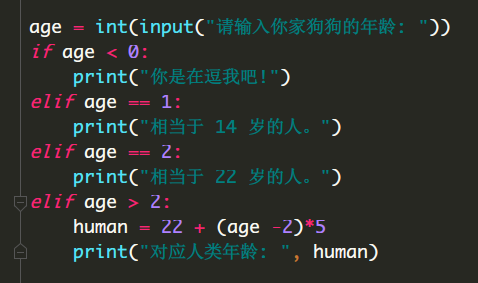

二、while 循环
1、什么是循环
循环指的是一个重复做某件事的过程
2、为什么要有循环
为了让计算机能够像人一样重复做某件事
while 循环又叫条件循环,循环的次数取决于条件
语法:
while 判断条件:
代码块

上面这个循环是一个死循环,因为条件永远成立,会不停的执行下去,要想结束while循环,有两种方式:
方式一:操作 while 循环的条件让其结束。即设置一个标志位让其为 True,一旦想终止循环,让标志位为 False,等到下一次循环判断标志位不成立,就会结束循环
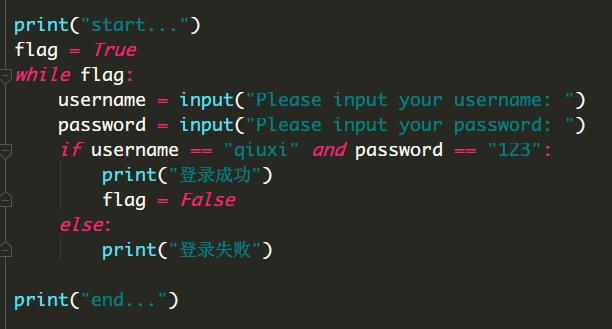
方式二:break 强行终止本层循环

例如:用户登录程序,登录失败超过三次则退出
方式一:
print("start...")
count = 0
while count < 3:
username = input("Please input your username: ")
password = input("Please input your password: ")
if username == 'qiuxi' and username == '':
print('登录成功')
break
else:
print('登录失败, 请重新登录')
count += 1
print('end....')
运行结果: start...
Please input your username: dsa
Please input your password: dsa
登录失败, 请重新登录
Please input your username: ei
Please input your password: qi
登录失败, 请重新登录
Please input your username: dsa
Please input your password: d
登录失败, 请重新登录
end....
方式二:
print("start...")
count = 0
while True:
if count == 3:
print("输入错误过多")
break
username = input("Please input your username: ")
password = input("Please input your password: ")
if username == 'qiuxi' and password == '':
print('登录成功')
break
else:
print('登录失败, 请重新登录')
count += 1
print('end....')
运行结果: start...
Please input your username: xi
Please input your password: 534
登录失败, 请重新登录
Please input your username: ha
Please input your password: ha
登录失败, 请重新登录
Please input your username: ca
Please input your password: dsa
登录失败, 请重新登录
输入错误过多
end....
continue:表示结束本次循环,进入下一次循环
# 打印1 2 3 5
count = 1
while count < 6:
if count == 4:
count += 1
continue
print(count, end=' ') # end=' '表示使print不换行打印
count += 1
注意:continue的位置,不能将它作为循环体最后一步执行的代码,否则continue不会起到作业
while True:
print('')
print('')
print('')
continue # continue不起作用
while - else的应用:当while循环正常执行完毕,不被break打断的情况下,会执行else语句的内容
print("start...")
count = 0
while count < 3:
username = input("Please input your username: ")
password = input("Please input your password: ")
if username == 'qiuxi' and username == '':
print('登录成功')
break
else:
print('登录失败, 请重新登录')
count += 1
else:
print("输错的次数过多")
print('end....')
运行结果: start...
Please input your username: qi
Please input your password: 43
登录失败, 请重新登录
Please input your username: ad
Please input your password: jhg
登录失败, 请重新登录
Please input your username: cs
Please input your password: 765
登录失败, 请重新登录
输错的次数过多
end....
while循环嵌套
name_of_db = 'qiuxi'
pwd_of_db = ''
print("start...")
count = 0
while count < 3:
username = input("Please input your username: ")
password = input("Please input your password: ")
if username == name_of_db and password == pwd_of_db:
print('登录成功')
while True:
print('''
1 浏览商品
2 添加购物车
3 支付
4 退出
''')
choice = input("请输入你的操作: ")
if choice == '':
print("开始浏览商品...")
elif choice == '':
print("正在添加购物车...")
elif choice == '':
print("正在支付...")
elif choice == '':
break
break
else:
print('登录失败, 请重新登录')
count += 1
else:
print("输错的次数过多") print('end....')
运行结果: start...
Please input your username: qiuxi
Please input your password: 123
登录成功 1 浏览商品
2 添加购物车
3 支付
4 退出 请输入你的操作: 1
开始浏览商品... 1 浏览商品
2 添加购物车
3 支付
4 退出 请输入你的操作: 2
正在添加购物车... 1 浏览商品
2 添加购物车
3 支付
4 退出 请输入你的操作: 3
正在支付... 1 浏览商品
2 添加购物车
3 支付
4 退出 请输入你的操作: 4
end....
上面的代码,要想终止循环,每一个while都需要对应一个break,不好配对,使用设置标志位即可控制所有循环终止条件。
name_of_db = 'qiuxi'
pwd_of_db = ''
print("start...")
flag = True
count = 0
while flag:
if count == 3:
print("尝试次数过多")
break
username = input("Please input your username: ")
password = input("Please input your password: ")
if username == name_of_db and password == pwd_of_db:
print('登录成功')
while flag:
print('''
1 浏览商品
2 添加购物车
3 支付
4 退出
''')
choice = input("请输入你的操作: ")
if choice == '':
print("开始浏览商品...")
elif choice == '':
print("正在添加购物车...")
elif choice == '':
print("正在支付...")
elif choice == '':
flag = False else:
print('登录失败, 请重新登录')
count += 1 print('end....')
运行结果: start...
Please input your username: qiuxi
Please input your password: 123
登录成功 1 浏览商品
2 添加购物车
3 支付
4 退出 请输入你的操作: 1
开始浏览商品... 1 浏览商品
2 添加购物车
3 支付
4 退出 请输入你的操作: 4
end....
四、for 循环
Python的for循环主要用于取值,可以遍历任何序列的项目,如一个列表或者一个字符串。
语法:
for <variable> in <sequence>:
<statements>
else:
<statements>
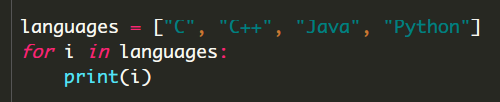
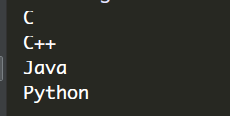
range( ) 函数
如果需要遍历数字序列,可以使用内置 range( ) 函数。它会生成数列,例如:
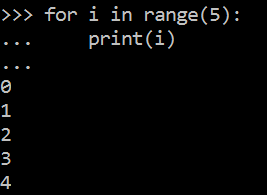
range( )也可以指定区间的值:
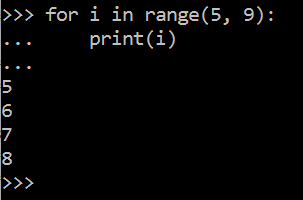
也可以使 range 以指定数字开始并指定不同的步长
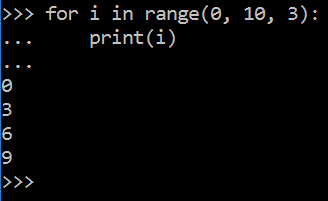
可以结合 range( ) 和 len( ) 函数以遍历一个序列的索引
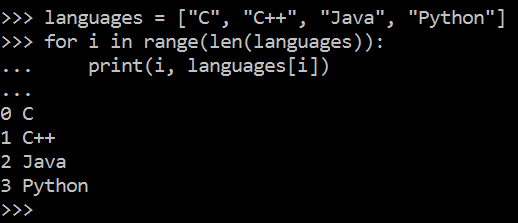
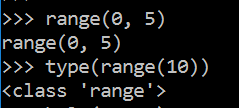
补充:Python2中 range( ) 和 Python3中 range( ) 的区别
Python2中 range( ) 函数可创建一个整数列表
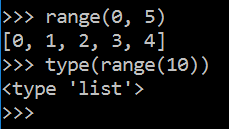
Python3 range() 函数返回的是一个可迭代对象(后面会学到),而不是列表类型
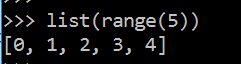
但是可以利用 list 函数返回列表
最新文章
- LeetCode[3] Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
- 基于MySQL MEB的备份恢复
- 毕业论文中使用的技术—FileReader接口
- 初用eclipse和svn遇见的问题以及解决方法
- setNeedsDisplay和setNeedsLayout
- 必须知道的八大种排序算法【java实现】(一) 冒泡排序、快速排序
- mac系统xcode升级等软件更换appid账户
- Python迭代器:捕获Generator的返回值
- Linux 之dhcp服务搭建
- Android Service 简介
- 禁止多行文本框textarea拖拽
- NodeJS爬虫系统初探
- js上拉跳转原理
- IOLI-crackme0x01-0x05 writeup
- api-gateway实践(08)新服务网关 - 云端发布和日志查看
- 强力推荐各位攻城狮查看,收藏IT职业技能图谱(全套13张)
- mysql 半同步复制~ 整体概述与改进
- sublime 成对括号高亮显示设置
- 【iCore1S 双核心板_FPGA】例程十:乘法器实验——乘法器的使用
- win7英文版