《Java程序设计》实验1实验报告
2024-09-01 07:31:42
20145318 《Java程序设计》实验1实验报告
实验题目
- 通过对500个数据进行操作,实现快速排序、选择排序、直接插入排序算法时间复杂度的比较;并在排序数据中快速查找某一数据,给出查找是否成功,以及数据所在的位置信息。
设计思路
- 本次实验利用数据结构实验的C转换成Java,设计思路见下图。

源代码
import java.util.Scanner;
class Sort
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N=20;
int[] a={5,2,8,9,4,3,1,7,0,6,15,12,18,19,14,13,11,17,10,16};
/*直接插入排序*/
long beginTime1=System.currentTimeMillis();//计算时间
for(int i=0;i<1000000;i++)
InsertSort(a, N);
long endTime1=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(endTime1-beginTime1+" 毫秒");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
System.out.printf("%d\t", a[i]);
System.out.printf("\n");
/*快速排序*/
long beginTime2=System.currentTimeMillis();//计算时间
for(int i=0;i<1000000;i++)
QuickSort(a, 0, N-1);
long endTime2=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(endTime2-beginTime2+" 毫秒");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
System.out.printf("%d\t", a[i]);
System.out.printf("\n");
/*选择排序*/
long beginTime3=System.currentTimeMillis();//计算时间
for(int i=0;i<1000000;i++)
SelectSort(a, N);
long endTime3=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(endTime3-beginTime3+" 毫秒");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
System.out.printf("%d\t", a[i]);
System.out.printf("\n");
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
/*快速查找(直接遍历查找)*/
int add=0;
System.out.printf("Input key=");
//输入数据
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int key = sc.nextInt();
while (add<N-1&&a[add] != key)
add++;
if (a[add]==key)
System.out.printf("%d的位置为%d\n", key, add + 1);
else
System.out.printf("不存在%d\n", key);
}
}
/*直接插入排序:*/
public static void InsertSort(int a[], int n)
{
int i, j, t;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
t = a[i];
for (j = i; j>0 && t < a[j - 1]; j--)
{
a[j] = a[j - 1];
}
a[j] = t;
}
}
/*快速排序:*/
public static void QuickSort(int b[], int low, int high)
{
int i, j, middle;
i = low;
j = high;
middle = b[low];
while (i < j)
{
while (i < j&&middle <= b[j])
j--;
if (i < j)
{
b[i] = b[j];
i++;
}
while (i < j&&b[i] < middle)
i++;
if (i < j)
{
b[j] = b[i];
j--;
}
}
b[i] = middle;
if (low < i)
QuickSort(b, low, i - 1);
if (i < high)
QuickSort(b, j + 1, high);
}
/*选择排序:*/
public static void SelectSort(int c[], int n)
{
int i, j, k, t;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
k = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < n;j++)
if (c[k]>c[j])
k = j;
if (k != i)
{
t = c[i];
c[i] = c[k];
c[k] = t;
}
}
}
}
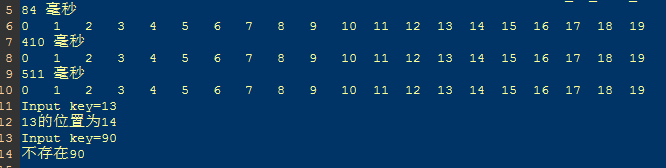
结果截图
- 三种排序算法的结果和所消耗的时间分别显示,输入需要查找的关键字,若存在即输出位置,若不存在则说明。
问题及解决
Java中时间计算的语句与C中不同,这样比较方便。
long beginTime3=System.currentTimeMillis();//计算时间
执行语句
long endTime3=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(endTime3-beginTime3+" 毫秒");
排序过程可能耗时很短,可以通过循环执行排序来计算时间。
调试过程中出现了查找数组溢出的情况。
比较语句原代码:
while (a[add] != key&&add<=N) add++; if (add>=0&&add<=N)····问题:
&&先比较前者,为false即不比较后者;add<=N不满足再跳出循环,此时已经执行到add=N,所以溢出。改正后代码:
while (add<N-1&&a[add] != key) add++; if (a[add]==key)....改正:先判断add是否溢出再判断是否找到关键字;跳出循环时
add++执行,此时add=N-1,不会溢出。
在一个类中,直接int N可以代替C中的#define N,但是多个类中用此方法定义常量不行。
PSP

其他(感悟、思考等,可选)
- 本次实验直接引用数据结构的C,在设计过程上没有费太多时间,在Java和C不同的地方做些修改。
- 排序算法比较基本,掌握其排序本质即可。
最新文章
- 使用原生JS实现一个风箱式的demo,并封装了一个运动框架
- SharePoint 2013 状态机工作流之UpdateItemActivity
- hadoop(2014/0619)
- oracle 表类型变量的使用
- POJ 2082 Terrible Sets
- mysql 学习碎片
- 【转】ContextMenuStrip菜单应用
- POJ 2891 Strange Way to Express Integers【扩展欧几里德】【模线性方程组】
- 【python】元组的插入
- android自定义实现抽屉SlidingDrawer的功能
- 工作中遇到的http返回码
- poj3264 最大值与最小值的差
- DDGScreenShot—图片擦除功能
- 从壹开始前后端分离 40 || 完美基于AOP的接口性能分析
- Hibernate处理事务并发问题
- spring源码学习2
- 【LInux】统计某文件夹下目录的个数
- SRM-供应商关系管理-组织模式
- Java之基于S2SH与手机数据交互(一)
- LeetCode: Balanced Binary Tree 解题报告