963B:Destruction of a Tree
You are given a tree (a graph with n vertices and n - 1 edges in which it's possible to reach any vertex from any other vertex using only its edges).
A vertex can be destroyed if this vertex has even degree. If you destroy a vertex, all edges connected to it are also deleted.
Destroy all vertices in the given tree or determine that it is impossible.
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 2·105) — number of vertices in a tree.
The second line contains n integers p1, p2, ..., pn (0 ≤ pi ≤ n). If pi ≠ 0 there is an edge between vertices i and pi. It is guaranteed that the given graph is a tree.
If it's possible to destroy all vertices, print "YES" (without quotes), otherwise print "NO" (without quotes).
If it's possible to destroy all vertices, in the next n lines print the indices of the vertices in order you destroy them. If there are multiple correct answers, print any.
5
0 1 2 1 2
YES
1
2
3
5
4
4
0 1 2 3
NO
In the first example at first you have to remove the vertex with index 1 (after that, the edges (1, 2) and (1, 4) are removed), then the vertex with index 2 (and edges (2, 3) and (2, 5) are removed). After that there are no edges in the tree, so you can remove remaining vertices in any order.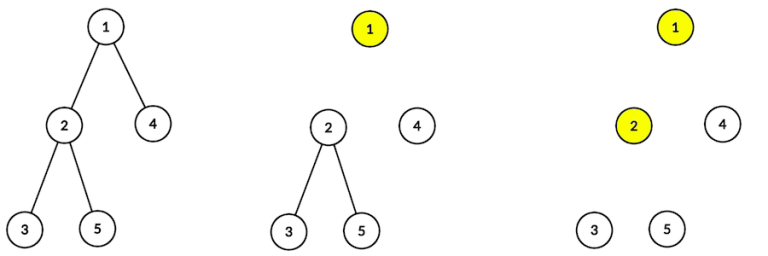
规定一个顺序,使分为父子结点,则每次删除只能往子节点查找
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cmath>
#include <cassert>
#include <ctime>
#include <map>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
#pragma comment(linker, "/stck:1024000000,1024000000")
#define lowbit(x) (x&(-x))
#define max(x,y) (x>=y?x:y)
#define min(x,y) (x<=y?x:y)
#define MAX 100000000000000000
#define MOD 1000000007
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define ei exp(1)
#define PI 3.1415926535897932384626433832
#define ios() ios::sync_with_stdio(true)
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define mem(a) (memset(a,0,sizeof(a)))
#define ll long long
vector<int>v[],ans;
stack<int>q;
int cnt[],vis[];
int n,x,pos,par[];
void bfs(int now)
{
ans.push_back(now);
vis[now]=;
for(int i=;i<v[now].size();i++)
{
cnt[v[now][i]]--;
if(v[now][i]==par[now] || vis[v[now][i]]) continue;//当前节点已经被找过,或者是now节点的父节点
if(!(cnt[v[now][i]]&)) bfs(v[now][i]);
}
}
void dfs(int fa,int now)
{
par[now]=fa;
q.push(now);
for(int i=;i<v[now].size();i++)
{
if(v[now][i]==fa) continue;
dfs(now,v[now][i]);
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
if(x)
{
v[i].push_back(x);
v[x].push_back(i);
cnt[i]++;
cnt[x]++;
}
else pos=i;
}
dfs(,pos);//n-1条边,则必有一个为0,不妨把这点作为根节点遍历。
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
while(!q.empty())
{
int fr=q.top();
q.pop();
if(!(cnt[fr]&)) bfs(fr);//从后向前遍历,若存在,必只有一个结点符合初始为偶数
}
if(ans.size()==n)
{
printf("YES\n");
for(int i=;i<ans.size();i++)
printf("%d\n",ans[i]);
}
else printf("NO\n");
return ;
}
最新文章
- SMP、NUMA、MPP(Teradata)体系结构介绍
- LeetCode----Linked List
- Entity Framework在Asp.net MVC中的实现One Context Per Request(附源码)
- 安装 vsftpd
- SKEffectNode类
- Vs2012于Linux应用程序开发(2):图案
- 世界上速度最快的输入法 Fleksy 为了支持中国
- 201521123045-----《Java程序设计》第3周学习总结
- aws中的路由表
- C语言编对双精度数保留一位小数
- Python_重写集合
- ./runInstaller: Permission denied
- flag.xls
- A - Piece of Cake Kattis - pieceofcake (数学)
- C++ stringstream 简化数据类型转换
- springboot同时使用thymeleaf和jsp模板
- 【转】JS组件系列——Bootstrap组件福利篇:几款好用的组件推荐(二)
- POJ 2411 Mondriaan's Dream 插头dp
- jQuery--Excel插件js-xlsx
- spring+struts整合
热门文章
- 搭建app自动化测试环境(一)
- [terry笔记]11gR2_DataGuard搭建_primary零停机
- Linux防火墙iptables安装配置--使用远程工具Xmanager和ftp服务安装配置
- Geany IDE搭建
- Hive中建表注释为乱码的解决方式
- android将String转化为MD5的方法+一些String经常使用的方法
- SQL Server 运行计划操作符具体解释(3)——计算标量(Compute Scalar)
- ssh跳板登陆太麻烦,使用expect每次自动登录 利用expect 模拟键盘动作,在闲置时间之内模拟地给个键盘响应
- nyoj--1184--为了肾六(动态规划+滚动数组)
- Anaconda升级