自然语言处理(二)——PTB数据集的预处理
2024-09-04 14:47:40
参考书
《TensorFlow:实战Google深度学习框架》(第2版)
首先按照词频顺序为每个词汇分配一个编号,然后将词汇表保存到一个独立的vocab文件中。
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
# coding=utf-8 """
@author: Li Tian
@contact: 694317828@qq.com
@software: pycharm
@file: word_deal1.py
@time: 2019/2/20 10:42
@desc: 首先按照词频顺序为每个词汇分配一个编号,然后将词汇表保存到一个独立的vocab文件中。
""" import codecs
import collections
from operator import itemgetter # 训练集数据文件
RAW_DATA = "./simple-examples/data/ptb.train.txt"
# 输出的词汇表文件
VOCAB_OUTPUT = "ptb.vocab" # 统计单词出现的频率
counter = collections.Counter()
with codecs.open(RAW_DATA, "r", "utf-8") as f:
for line in f:
for word in line.strip().split():
counter[word] += 1 # 按照词频顺序对单词进行排序
sorted_word_to_cnt = sorted(counter.items(), key=itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
sorted_words = [x[0] for x in sorted_word_to_cnt] # 稍后我们需要在文本换行处加入句子结束符“<eos>”,这里预先将其加入词汇表。
sorted_words = ["<eos>"] + sorted_words
# 在后面处理机器翻译数据时,出了"<eos>",还需要将"<unk>"和句子起始符"<sos>"加入
# 词汇表,并从词汇表中删除低频词汇。在PTB数据中,因为输入数据已经将低频词汇替换成了
# "<unk>",因此不需要这一步骤。
# sorted_words = ["<unk>", "<sos>", "<eos>"] + sorted_words
# if len(sorted_words) > 10000:
# sorted_words = sorted_words[:10000] with codecs.open(VOCAB_OUTPUT, 'w', 'utf-8') as file_output:
for word in sorted_words:
file_output.write(word + "\n")
运行结果:
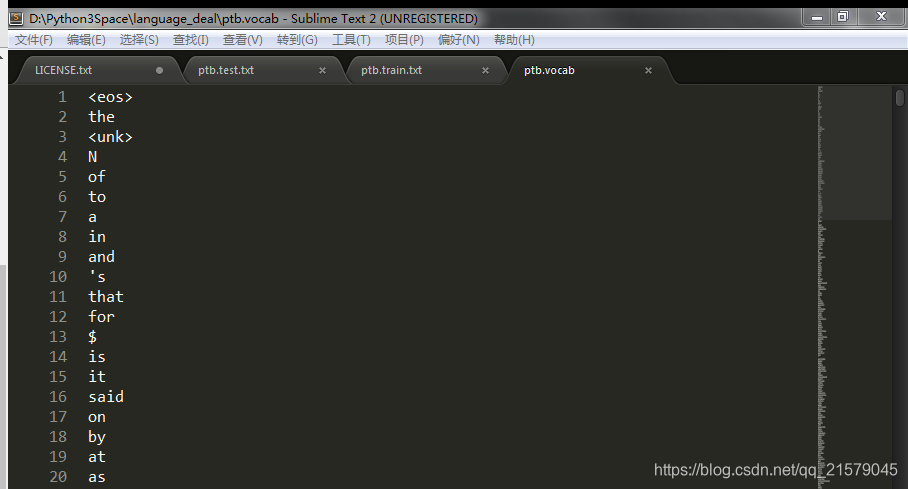
在确定了词汇表之后,再将训练文件、测试文件等都根据词汇文件转化为单词编号。每个单词的编号就是它在词汇文件中的行号。
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
# coding=utf-8 """
@author: Li Tian
@contact: 694317828@qq.com
@software: pycharm
@file: word_deal2.py
@time: 2019/2/20 11:10
@desc: 在确定了词汇表之后,再将训练文件、测试文件等都根据词汇文件转化为单词编号。每个单词的编号就是它在词汇文件中的行号。
""" import codecs
import sys # 原始的训练集数据文件
RAW_DATA = "./simple-examples/data/ptb.train.txt"
# 上面生成的词汇表文件
VOCAB = "ptb.vocab"
# 将单词替换成为单词编号后的输出文件
OUTPUT_DATA = "ptb.train" # 读取词汇表,并建立词汇到单词编号的映射。
with codecs.open(VOCAB, "r", "utf-8") as f_vocab:
vocab = [w.strip() for w in f_vocab.readlines()]
word_to_id = {k: v for (k, v) in zip(vocab, range(len(vocab)))} # 如果出现了被删除的低频词,则替换为"<unk>"。
def get_id(word):
return word_to_id[word] if word in word_to_id else word_to_id["<unk"] fin = codecs.open(RAW_DATA, "r", "utf-8")
fout = codecs.open(OUTPUT_DATA, 'w', 'utf-8')
for line in fin:
# 读取单词并添加<eos>结束符
words = line.strip().split() + ["<eos>"]
# 将每个单词替换为词汇表中的编号
out_line = ' '.join([str(get_id(w)) for w in words]) + '\n'
fout.write(out_line)
fin.close()
fout.close()
运行结果:
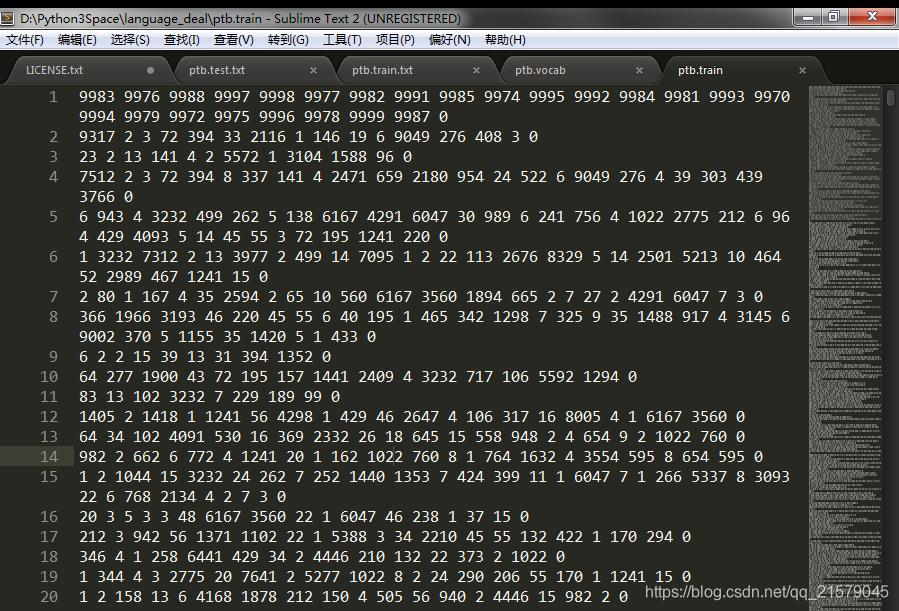
最新文章
- 2D动画的制作
- yaml
- 调试SQLSERVER (一)生成dump文件的方法
- java.net.BindException: address already in use <null>:xxxx
- angular的canvas画图例子
- BJOI2015 Day1
- JS实现 键盘操作
- C++ STL pair
- UVa 11105 (筛法) Semi-prime H-numbers
- eclipse lint工具介绍
- 负电压基准电路(-2.5V/-5V电压基准)
- leetcode--014 Gas station
- 爬虫入门系列(二):优雅的HTTP库requests
- Angular 学习笔记 ( PWA + App Shell )
- 去掉字符空格js
- Linux sed命令 以行为单位编辑文本,或替换文本中的文字
- 深入理解CMA【转】
- Reloading Java Classes 201: How do ClassLoader leaks happen? Translation
- 精选10款超酷的HTML5/CSS3菜单
- 在django项目中使用django-ckeditor