【推理引擎】ONNX 模型解析
定义模型结构
首先使用 PyTorch 定义一个简单的网络模型:
class ConvBnReluBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, 3)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.maxpool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(3, 1)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(64, 32, 3)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x):
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.maxpool1(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
return out
在导出模型之前,需要提前定义一些变量:
model = ConvBnReluBlock() # 定义模型对象
x = torch.randn(2, 3, 255, 255) # 定义输入张量
然后使用 PyTorch 官方 API(torch.onnx.export)导出 ONNX 格式的模型:
# way1:
torch.onnx.export(model, (x), "conv_bn_relu_evalmode.onnx", input_names=["input"], output_names=['output'])
# way2:
import torch._C as _C
TrainingMode = _C._onnx.TrainingMode
torch.onnx.export(model, (x), "conv_bn_relu_trainmode.onnx", input_names=["input"], output_names=['output'],
opset_version=12, # 默认版本为9,但是如果低于12,将不能正确导出 Dropout 和 BatchNorm 节点
training=TrainingMode.TRAINING, # 默认模式为 TrainingMode.EVAL
do_constant_folding=False) # 常量折叠,默认为True,但是如果使用TrainingMode.TRAINING模式,则需要将其关闭
# way3
torch.onnx.export(model,
(x),
"conv_bn_relu_dynamic.onnx",
input_names=['input'],
output_names=['output'],
dynamic_axes={'input': {0: 'batch_size', 2: 'input_width', 3: 'input_height'},
'output': {0: 'batch_size', 2: 'output_width', 3: 'output_height'}})
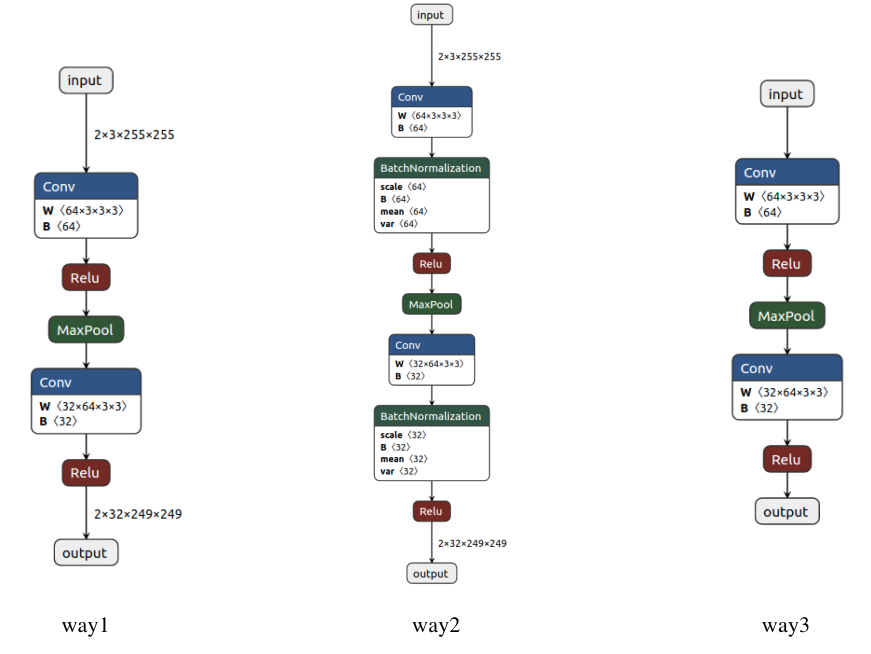
可以看到,这里主要以三种方式导出模型,下面分别介绍区别:
- way1:如果模型中存在 BatchNorm 或者 Dropout,我们在导出模型前会首先将其设置成 eval 模式,但是这里我们即使忘记设置也无所谓,因为在导出模型时会自动设置(export函数中training参数的默认值为TrainingMode.EVAL)。
- way2:如果我们想导出完整的模型结构,包括 BatchNorm 和 Dropout,则应该将 training 属性设置为 train 模式。
- way3:如果想要导出动态输入的模型结构,则需要设置 dynamic_axes 属性,比如这里我们将第一、三和四维设置成动态结构,那么我们就可以输入任何Batch大小、任何长宽尺度的RGB图像。
下图分别将这三种导出方式的模型结构使用 Netron 可视化:
分析模型结构
这里参考了BBuf大佬的讲解:【传送门:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/346511883】
接下来主要针对 way1 方式导出的ONNX模型进行深入分析。
ONNX格式定义:https://github.com/onnx/onnx/blob/master/onnx/onnx.proto
在这个文件中,定义了多个核心对象:ModelProto、GraphProto、NodeProto、ValueInfoProto、TensorProto 和 AttributeProto。
在加载ONNX模型之后,就获得了一个ModelProto,其中包含一些
- 版本信息(本例中:ir_version = 7)
- 生成者信息:producer_name: pytorch,producer_version: 1.10,这两个属性主要用来说明由哪些框架哪个版本导出的onnx
- 核心组件:GraphProto
在 GraphProto 中,有如下几个属性需要注意:
- name:本例中:name = 'torch-jit-export'
- input 数组:
[name: "input"
type {
tensor_type {
elem_type: 1
shape {
dim {
dim_value: 2
}
dim {
dim_value: 3
}
dim {
dim_value: 255
}
dim {
dim_value: 255
}
}
}
}
]
- output 数组:
[name: "output"
type {
tensor_type {
elem_type: 1
shape {
dim {
dim_value: 2
}
dim {
dim_value: 32
}
dim {
dim_value: 249
}
dim {
dim_value: 249
}
}
}
}
]
- node 数组,该数组中包含了模型中所有的计算节点(本例中:"Conv_0"、"Relu_1"、"MaxPool_2"、"Conv_3"、"Relu_4"),以及各个节点的属性,:
[input: "input"
input: "23"
input: "24"
output: "22"
name: "Conv_0"
op_type: "Conv"
attribute {
name: "dilations"
ints: 1
ints: 1
type: INTS
}
attribute {
name: "group"
i: 1
type: INT
}
attribute {
name: "kernel_shape"
ints: 3
ints: 3
type: INTS
}
attribute {
name: "pads"
ints: 0
ints: 0
ints: 0
ints: 0
type: INTS
}
attribute {
name: "strides"
ints: 1
ints: 1
type: INTS
}
,
input: "22"
output: "17"
name: "Relu_1"
op_type: "Relu"
, input: "17"
output: "18"
name: "MaxPool_2"
op_type: "MaxPool"
attribute {
name: "kernel_shape"
ints: 3
ints: 3
type: INTS
}
attribute {
name: "pads"
ints: 0
ints: 0
ints: 0
ints: 0
type: INTS
}
attribute {
name: "strides"
ints: 1
ints: 1
type: INTS
}
,
input: "18"
input: "26"
input: "27"
output: "25"
name: "Conv_3"
op_type: "Conv"
attribute {
name: "dilations"
ints: 1
ints: 1
type: INTS
}
attribute {
name: "group"
i: 1
type: INT
}
attribute {
name: "kernel_shape"
ints: 3
ints: 3
type: INTS
}
attribute {
name: "pads"
ints: 0
ints: 0
ints: 0
ints: 0
type: INTS
}
attribute {
name: "strides"
ints: 1
ints: 1
type: INTS
}
,
input: "25"
output: "output"
name: "Relu_4"
op_type: "Relu"
]
通过以上 node 的输入输出信息,可提取出节点之间的拓扑关系,构建出一个完整的神经网络。
- initializer 数组:存放模型的权重参数。
[dims: 64
dims: 3
dims: 3
dims: 3
data_type: 1
name: "23"
raw_data: "\220\251\001>\232\326&>\253\227\372 ... 省略一眼望不到头的内容 ... " dims: 64
data_type: 1
name: "24"
raw_data: "Rt\347\275\005\203\0 ..." dims: 32
dims: 64
dims: 3
dims: 3
data_type: 1
name: "26"
raw_data: "9\022\273;+^\004\2 ..." ...
至此,我们已经分析完 GraphProto 的内容,下面根据图中的一个节点可视化说明以上内容:
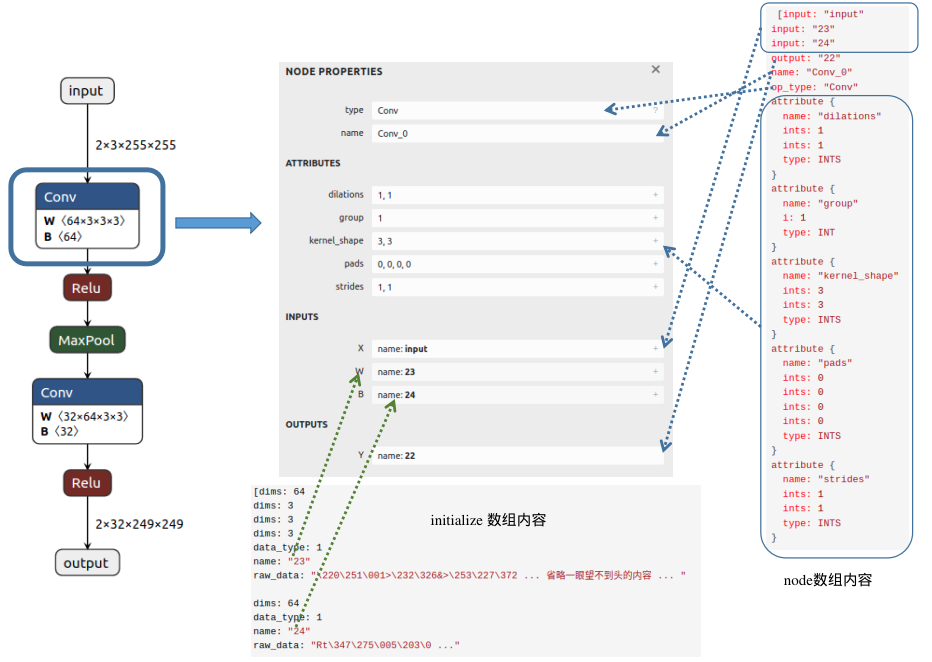
从图中可以发现,Conv 节点的输入包含三个部分:输入的图像(input)、权重(这里以数字23代表该节点权重W的名字)以及偏置(这里以数字24表示该节点偏置B的名字);输出内容的名字为22;属性信息包括dilations、group、kernel_shape、pads和strides,不同节点会具有不同的属性信息。在initializer数组中,我们可以找到该Conv节点权重(name:23)对应的值(raw_data),并且可以清楚地看到维度信息(64X3X3X3)。
最新文章
- mybatis,Spring等工具对xml文件正确性的验证
- 【lattice软核】ROM的使用
- MMORPG大型游戏设计与开发(part2 of net)
- [GE]导入图片至Word,然后按规则命名(2/2)
- Qt入门之信号与槽机制
- Activity的启动模式(android:launchMode)
- Android 获取信号强度
- Asp.Net 之 未能加载文件或程序集 system.web.extensions 解决方法
- Java的序列化与反序列化(一):初识
- Number Sequence(HDU 1005 构造矩阵 )
- 360极速浏览器 HTML5实验室
- Metro UI 界面完全解析 (转载)
- php将字符串转为二进制数据串
- [译文]Domain Driven Design Reference(五)—— 为战略设计的上下文映射
- mybatis 错误
- calc()使用用法
- php static 变量的例子
- Elasticsearch 学习之 节点重启
- 让你明白kvm是什么
- mysql游标错误