C. Hongcow Builds A Nation
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Hongcow is ruler of the world. As ruler of the world, he wants to make it easier for people to travel by road within their own countries.
The world can be modeled as an undirected graph with n nodes and m edges. k of the nodes are home to the governments of the k countries that make up the world.
There is at most one edge connecting any two nodes and no edge connects a node to itself. Furthermore, for any two nodes corresponding to governments, there is no path between those two nodes. Any graph that satisfies all of these conditions is stable.
Hongcow wants to add as many edges as possible to the graph while keeping it stable. Determine the maximum number of edges Hongcow can add.
The first line of input will contain three integers n, m and k (1 ≤ n ≤ 1 000, 0 ≤ m ≤ 100 000, 1 ≤ k ≤ n) — the number of vertices and edges in the graph, and the number of vertices that are homes of the government.
The next line of input will contain k integers c1, c2, ..., ck (1 ≤ ci ≤ n). These integers will be pairwise distinct and denote the nodes that are home to the governments in this world.
The following m lines of input will contain two integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n). This denotes an undirected edge between nodes ui and vi.
It is guaranteed that the graph described by the input is stable.
Output a single integer, the maximum number of edges Hongcow can add to the graph while keeping it stable.
4 1 2
1 3
1 2
2
3 3 1
2
1 2
1 3
2 3
0
For the first sample test, the graph looks like this:
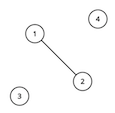 Vertices 1 and 3 are special. The optimal solution is to connect vertex 4 to vertices 1 and 2. This adds a total of 2 edges. We cannot add any more edges, since vertices 1 and 3 cannot have any path between them.
Vertices 1 and 3 are special. The optimal solution is to connect vertex 4 to vertices 1 and 2. This adds a total of 2 edges. We cannot add any more edges, since vertices 1 and 3 cannot have any path between them.
For the second sample test, the graph looks like this:
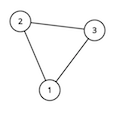 We cannot add any more edges to this graph. Note that we are not allowed to add self-loops, and the graph must be simple.
We cannot add any more edges to this graph. Note that we are not allowed to add self-loops, and the graph must be simple.
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include<string.h>
3 #include<algorithm>
4 #include<queue>
5 #include<math.h>
6 #include<stdlib.h>
7 #include<stack>
8 #include<stdio.h>
9 #include<ctype.h>
10 #include<map>
11 #include<vector>
12 using namespace std;
13 typedef long long LL;
14 int c[100005];
15 int bin[100005];
16 int du[100005];
17 vector<int>vec[100005];
18 int fin(int x);
19 int ask[100005];
20 int id[100005];
21 map<int,int>my;
22 LL bian[100005];
23 int main(void)
24 {
25 int n,m,k;
26 int i,j;
27
28 while(scanf("%d %d %d",&n,&m,&k)!=EOF)
29 {
30 my.clear();
31 memset(bian,0,sizeof(bian));
32 for(i = 0; i <100005; i++)vec[i].clear(),bin[i] = i,du[i] = 1;
33 for(i = 1; i <=k; i++)
34 scanf("%d",&c[i]);
35 while(m--)
36 {
37 int x,y;
38 scanf("%d %d",&x,&y);
39 vec[x].push_back(y);
40 vec[y].push_back(x);
41 int xx = fin(x);
42 int yy = fin(y);
43 if(xx!=yy)
44 {
45 if(du[xx] > du[yy])
46 {
47 du[xx] += du[yy],bin[yy] = xx;
48 bian[xx]+=bian[yy];
49 bian[xx]++;
50 }
51 else
52 {
53 du[yy] += du[xx],bin[xx] = yy;
54 bian[yy]+=bian[xx];
55 bian[yy]++;
56 }
57 }
58 else bian[xx]++;
59 }
60 for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
61 {
62 ask[i] = fin(i);
63 }
64 LL maxx = 0;
65 LL b;
66 for(i = 1; i <= k; i++)
67 {
68 my[ask[c[i]]] = 1;
69 if(du[ask[c[i]]]>maxx)
70 {
71 maxx = max((LL)du[ask[c[i]]],maxx);
72 b = bian[ask[c[i]]];
73 }
74 }
75 LL cnt = 0;
76 LL mc = 0;
77 for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
78 {
79 if(!my.count(ask[i]))
80 {
81 cnt+=du[ask[i]];
82 my[ask[i]] = 1;
83 mc+=bian[ask[i]];
84 }
85 }//printf("%lld\n",maxx);
86 LL acc = cnt*(cnt-1)/(LL)2;
87 LL akk = acc;
88 acc+=maxx*cnt;
89 acc-=mc;
90 for(i = 1;i <= k;i++)
91 {
92 acc+=(LL)du[ask[c[i]]]*(LL)(du[ask[c[i]]]-1)/(LL)2;
93 acc-=bian[ask[c[i]]];
94 }
95 printf("%lld\n",acc);
96 }
97 return 0;
98 }
99 int fin(int x)
100 {
101 int i;
102 for(i = x; i!=bin[i];)
103 i = bin[i];
104 return i;
105 }
最新文章
- Ajax_03之接收数据
- 3. Windows根据端口查进程---ADB 相关报错 ADB server didn't ACK cannot bind ':5037'
- Colored Sticks (字典树哈希+并查集+欧拉路)
- 解决qt5窗口不刷新(测试窗口类型,测试窗口属性)
- codeforces C. Sereja and Swaps
- jQuery中click()与trigger方法的区别
- css 三角
- 人脸识别1:n对比 (二)
- 软件工程实践_Task1
- 转://批量更新sequence的存储
- Spring的后置处理器BeanFactoryPostProcessor
- 模拟spring的IoC
- hpu_newoj_1028-exgcd
- 27.MySQL备份与恢复
- framework7中a标签没反应
- SVG.js 元素操作整理(二)-Transform
- Linux下的ssh远程访问
- Redis(十九):Redis压力测试工具benchmark
- Leetcode 445. 两数相加 II
- 5天不再惧怕多线程——第一天 尝试Thread