Java 常见对象 05
常见对象·正则表达式 和 其他类
正则表达式的概述和简单使用
* A:正则表达式
* 是指一个用来描述或者匹配一系列符合某个语法规则的字符串的单个字符串。其实就是一种规则,有自己的特殊应用
* 作用:比如注册邮箱,邮箱 有用户名和密码,一般会限制长度,这个限制长度的事情就是正则表达式做的
* B:案例演示
* 需求:
* 校验qq号
* 1、要求必须是5 - 15位的数字
* 2、不能是0开头
* 3、必须都是数字
* a:非正则表达式实现
* b:正则表达式实现
package com.heima.regex;
public class Demo1_Regex {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(checkQQ("0123")); // false
System.out.println(checkQQ("a123456")); // false
System.out.println(checkQQ("123456")); // true
System.out.println(checkQQ("12345678910101010")); // false
System.out.println("-----------------------------");
String regex = "[1-9]\\d{4,14}";
System.out.println("a12345".matches(regex)); // false
System.out.println("12345".matches(regex)); // true
System.out.println("012345".matches(regex)); // false
System.out.println("345".matches(regex)); // false
}
/*
* 分析校验qq号的方法:
* 1、明确返回值类型:boolean
* 2、明确参数列表:String qq
*/
public static boolean checkQQ(String qq) {
boolean flag = true; // 如果校验不符合要求,就把flag重置为flase,否则直接返回
if (qq.length() >= 5 && qq.length() <= 15) {
if (!qq.startsWith("0")) {
char[] arr = qq.toCharArray();// 将字符串转换为字符数组
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
char ch = arr[i];// 记录每一个字符
if (!(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')) {
flag = false;
break; // 如果不符合要求,直接跳出
}
}
} else {
flag = false;// 以0开头,不符合qq号的注册标准
}
} else {
flag = false; // 长度不符合
}
return flag;
}
}
Regex
字符类演示
* A:字符类
* [abc] :a、b或c (简单类)
* [^abc] :任何字符,除了a、b 或 c (否定)
* [a-zA-Z] :a到z 或者是 A到Z,两头的字幕包括在内 (范围)
* [0-9] :0到9的字符都包括

package com.heima.regex;
public class Demo2_Regex {
/*
* 强调:中括号代表单个字符
* [abc] a、b 或 c(简单类)
* [^abc] 任何字符,除了 a、b 或 c(否定)
* [a-zA-Z] a 到 z 或 A 到 Z,两头的字母包括在内(范围)
* [a-d[m-p]] a 到 d 或 m 到 p:[a-dm-p](并集)
* [a-z&&[def]] d、e 或 f(交集)
* [a-z&&[^bc]] a 到 z,除了 b 和 c:[ad-z](减去)
* [a-z&&[^m-p]] a 到 z,而非 m 到 p:[a-lq-z](减去)
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// demo1();
// demo2();
// demo3();
// demo4();
// demo5();
// demo6();
// demo7();
}
public static void demo7() {
String regex = "[a-z&&[^m-p]]";
System.out.println("a".matches(regex)); // true
System.out.println("m".matches(regex)); // false
System.out.println("o".matches(regex)); // false
}
public static void demo6() {
String regex = "[a-z&&[^bc]]";
System.out.println("a".matches(regex)); // true
System.out.println("b".matches(regex)); // false
System.out.println("1".matches(regex)); // false
}
public static void demo5() {
String regex = "[a-z&&[def]]"; // 取交集
System.out.println("a".matches(regex)); // false
System.out.println("d".matches(regex)); // true
}
public static void demo4() {
String reString = "[a-d[m-p]]"; // 等于[a-dm-p]
System.out.println("a".matches(reString)); // true
System.out.println("m".matches(reString)); // true
System.out.println("e".matches(reString)); // false
System.out.println("q".matches(reString)); // false
}
public static void demo3() {
String regexString = "[a-zA-Z]"; //范围内的字符,头尾都包括在内
System.out.println("a".matches(regexString)); // true
System.out.println("z".matches(regexString)); // true
System.out.println("A".matches(regexString)); // true
System.out.println("Z".matches(regexString)); // true
System.out.println("1".matches(regexString)); // false
}
public static void demo2() {
String regex = "[^abc]"; // 除了a或b或c都行
System.out.println("d".matches(regex)); // true
System.out.println("a".matches(regex)); // false
System.out.println("1".matches(regex)); // true
System.out.println("%".matches(regex)); // true
System.out.println("10".matches(regex));// 10 代表 1字符 和 0字符,多个字符 -> false
System.out.println("".matches(regex));// 空字符串 -> false
}
public static void demo1() {
String regex = "[abc]"; // []表示单个字符,代表a或者b或者c
System.out.println("a".matches(regex)); // true
System.out.println("b".matches(regex)); // true
System.out.println("c".matches(regex)); // true
System.out.println("d".matches(regex)); // false
}
}
Regex
预定义字符类演示
* A:预定义字符类
* . : 任何字符
* \d :数字 [0-9]
* \w :单词字符 [a-zA-Z_0-9]

package com.heima.regex;
public class Demo3_Regex {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// demo1();
// demo2();
// demo3();
// demo4();
// demo5();
// demo6();
// demo7();
}
public static void demo7() {
String regex = "\\W"; //非单词字符
System.out.println("a".matches(regex)); // false
System.out.println("_".matches(regex)); // false
System.out.println("1".matches(regex)); // false
System.out.println("%".matches(regex)); // true
}
public static void demo6() {
String regex = "\\w"; // 单词字符
System.out.println("a".matches(regex)); // true
System.out.println("_".matches(regex)); // true
System.out.println("1".matches(regex)); // true
System.out.println("%".matches(regex)); // false
}
public static void demo5() {
String regex = "\\S"; // 非空白字符
System.out.println(" ".matches(regex)); // false
System.out.println("a".matches(regex)); // true
System.out.println(" ".matches(regex)); //一个tab键,false
}
public static void demo4() {
String regex = "\\s"; // 空白字符
System.out.println(" ".matches(regex)); // 一个空格 ,true
System.out.println(" ".matches(regex)); // 一个tab键,true
System.out.println(" ".matches(regex)); // 4个空格,flase
}
public static void demo3() {
String regex = "\\D"; // 非数字
System.out.println("0".matches(regex)); // false
System.out.println("a".matches(regex)); // true
System.out.println("9".matches(regex)); // false
}
public static void demo2() {
String regex = "\\d"; // 数字
System.out.println("0".matches(regex)); // true
System.out.println("a".matches(regex)); // false
System.out.println("9".matches(regex)); // true
}
public static void demo1() {
String regex = "."; // 任意字符
System.out.println("a".matches(regex)); // true
System.out.println("ab".matches(regex)); // false
}
}
Regex
数量词
* A:Greedy 数量词
* X? :一个或没有X字符
* X* :零个或多个X字符
* X+ :一个或多个X字符
* X{n} :恰好n个X字符
* X{n, } :至少n个X字符
* X{n, m} :至少n个X字符,但是不超过m个

package com.heima.regex;
public class Demo4_Regex {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// demo1();
// demo2();
// demo3();
// demo4();
// demo5();
// demo6();
}
public static void demo6() {
String regex = "[abc]{5,15}"; // 5到15个中括号内的字符
System.out.println("abcac".matches(regex)); // 5个,true
System.out.println("abc".matches(regex)); // 3个,false
System.out.println("abcabcabc".matches(regex));// 9个,true
System.out.println("abcabcabcabcabcabc".matches(regex)); // 18个,false
}
public static void demo5() {
String regex = "[abc]{5,}"; // 至少5个中括号内的字符
System.out.println("abcac".matches(regex)); // 5个,true
System.out.println("abc".matches(regex)); // 3个,false
System.out.println("abcabcabc".matches(regex));// 9个,true
}
public static void demo4() {
String regex = "[abc]{5}"; // 恰好5个中括号内的字符
System.out.println("abcac".matches(regex)); // 5个,true
System.out.println("abc".matches(regex)); // 3个,false
System.out.println("abcabcabc".matches(regex));// 9个,false
}
public static void demo3() {
String regex = "[abc]+"; // 一次或多次中括号内的字符
System.out.println("".matches(regex)); // false,0次
System.out.println("a".matches(regex)); // true,1次
System.out.println("aacbc".matches(regex)); // true,多次
}
public static void demo2() {
String regex = "[abc]*"; // 零次或多次中括号内的字符,包括1次
System.out.println("".matches(regex)); // true,0次
System.out.println("a".matches(regex)); // true,1次
System.out.println("aacbc".matches(regex)); // true,多次
}
public static void demo1() {
String regex = "[abc]?"; // 一次或0次中括号内的字符
System.out.println("a".matches(regex)); // true
System.out.println("b".matches(regex)); // true
System.out.println("c".matches(regex)); // true
System.out.println("".matches(regex)); // true,出现0次
System.out.println("d".matches(regex)); // false
}
}
Regex
正则表达式的分割功能
* A:正则表达式的分割功能
* String类的功能:publc String[] split(String regex)
* B:案例演示
* 正则表达式的分割功能

package com.heima.regex;
public class Demo5_Split {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "cly.wo.shi.zhen.de.xi.huan.ni"; // 待切割的字符串
String regex = "\\."; // 设定正则表达式,双斜杠转义 .号
String[] arr = str.split(regex); // 依据正则表达式切割字符串
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}
Regex
把给定字符串中的数字进行排序
* A:案例演示
* 需求:我有如下一个字符串: "91 27 46 38 50", 请写代码使其输出结果是:"27 38 46 50 91"
package com.heima.test;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Test1 {
/*
* 分析:
* 1、将字符串切割成字符串数组
* 2、将字符串转换成数字并将其存储在一个等长度的 int数组中
* 3、排序
* 4、将排序后的结果遍历,拼接成一个字符串
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "91 27 46 38 50"; // 待处理的字符串
String[] arr = str.split(" "); // 依据正则表达式切割字符串,返回字符串数组
int[] arr1 = new int[arr.length];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr1[i] = Integer.parseInt(arr[i]); // 将字符数字转换为数字
} // 将字符串转换成数字并且存储在一个等长度的 int数组中
Arrays.sort(arr1); // 排序
StringBuffer s = new StringBuffer(); // 新建字符串缓冲区用于拼接字符串
for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++) { // 遍历 int数组,将每个元素添加到字符串中
if (i == arr.length - 1) {
s.append(arr1[i]); // 27 38 46 50 91
} else {
s.append(arr1[i]).append(" "); // 27 38 46 50
}
}
System.out.println(s);
}
}
Test1
正则表达式的替换功能
* A:正则表达式的替换功能
* String类的功能:public String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement)
* B:案例演示
* 正则表达式的替换功能
package com.heima.regex;
public class Demo6_ReplaceAll {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "woai2cly"; // 待替换的字符串
String regexString = "\\d"; // 定义正则表达式,\\d代表任意数字
System.out.println(s);
String s2 = s.replaceAll(regexString, ""); // 用""替代符合regexString的字符串
System.out.println(s2);
}
}
Regex
正则表达式的分组功能
* A:正则表达式的分组功能
* 捕获组可以通过从左到右计算其小括号来编号。例如:在表达式( (A) (B (C) ) ) 中,存在如下4组:
* 1、( (A) (B (C) ) )
* 2、( A
* 3、( B (C) )
* 4、( C )
组零始终代表整个字符串
* B:案例演示
* a:切割
* 需求:请按照叠词切割:"sdqqfgkkkjhpppkl";
* b:替换
* 需求:我我...我...我.要...要要...要学...学学..学.编...编编编...编编...编.程..程程...程
* 将字符串还原成:"我要学编程"

package com.heima.regex;
public class Demo7_Regex {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// demo1();
// demo2();
// demo3();
// demo4();
}
public static void demo4() {
// 替换
String s = "我我...我...我.要...要要...要学....学学..学.编..编编.编.程.程.程..程";
String regex1 = "\\.";
String s2 = s.replaceAll(regex1, ""); // 我我我我要要要要学学学学编编编编程程程程
String regex2 = "(.)\\1+";
String s3 = s2.replaceAll(regex2, "$1"); // $1代表符合匹配的第一组内容
System.out.println(s3);
}
public static void demo3() {
// 按照叠词切割
String regex = "(.)\\1+"; // 加号代表第一组出现一次到多次
String s = "sdqqfgkkkhjppppkl";
String[] arr = s.split(regex);
for (String string : arr) {
System.out.println(string);
}
}
public static void demo2() {
// 叠词:死啦死啦,高兴高兴
String regex2 = "(..)\\1";
System.out.println("死啦死啦".matches(regex2)); // true
System.out.println("快快乐乐".matches(regex2)); // false
}
public static void demo1() {
// 叠词: 快快乐乐,高高兴兴
String regex = "(.)\\1(.)\\2"; // \\1代表第一组又出现一次,\\2代表第二组又出现一次
System.out.println("高高兴兴".matches(regex)); // true
System.out.println("高兴高兴".matches(regex)); // false
}
}
Regex
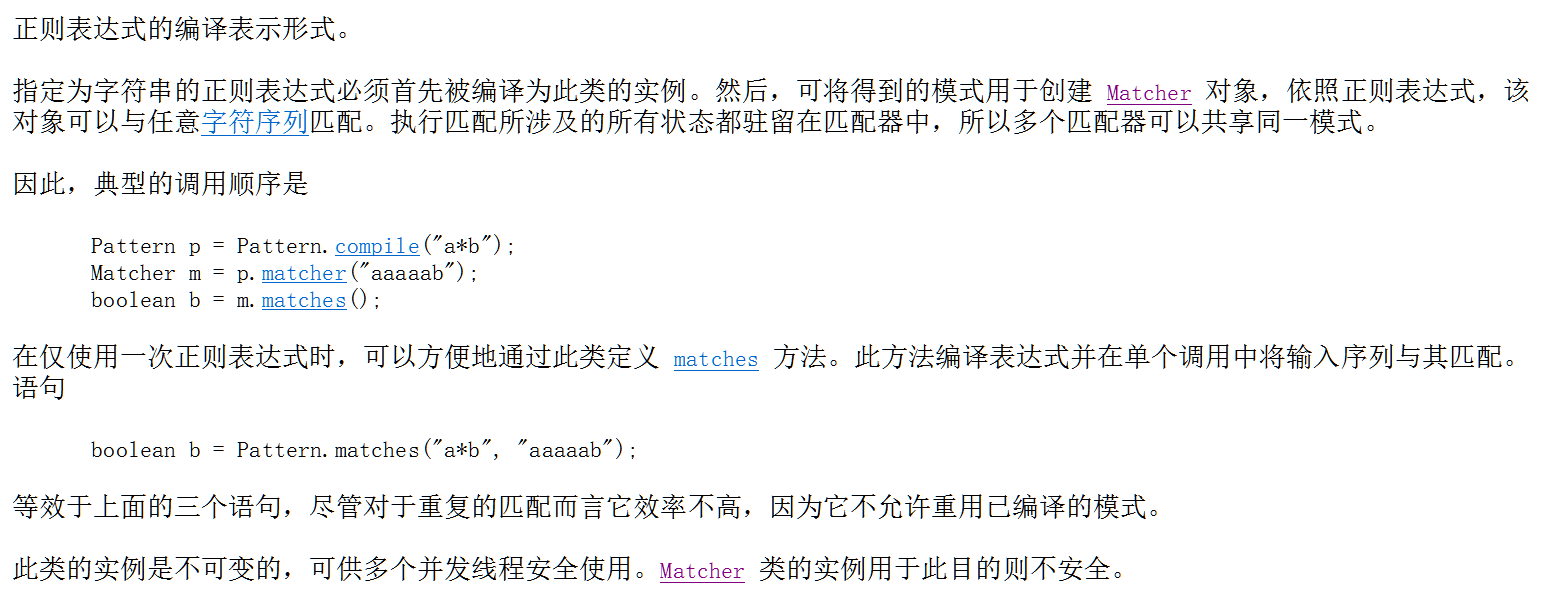
Pattern和Matcher的概述
* A:Pattern 和 Matcher的概述
* B:模式和匹配器的典型调用顺序
* 通过JDK提供的API,查看Pattern类的说明
* 典型的调用顺序是
* Pattern P = Pattern.compile("a*b");
* Matcher m =p.matcher("aaaab");
* boolean b = m.matches();


package com.heima.regex; import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class Demo8_Pattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("a*b"); // 获取到正则表达式
Matcher m = p.matcher("aaaaab"); // 获取匹配器
boolean b = m.matches(); // 看是否能匹配,匹配就返回true
System.out.println(b); System.out.println("aaaaab".matches("a*b")); // 与上面的结果一样
}
}
Regex
正则表达式的获取功能
* A:正则表达式的获取功能
* Pattern 和 Matcher 的结合使用
* B:案例演示
* 需求:把一个字符串中的手机号码获取出来
package com.heima.regex; import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class Demo9_Pattern { public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "我的手机号码是18858520525曾经用过13336046924";
String regex = "1[3578]\\d{9}";
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(regex);
Matcher m = p.matcher(s);
while (m.find()) { // 必须要先find,再group,否则会报错
System.out.println(m.group());
} }
}
Test
Math类的概述和方法使用
* A:Math类的概述
* Math类 包含用于执行基本数学运算的方法,如初等指数、对数、平方根和三角函数
* B:成员方法
* public static int abs(int a)
* public static double ceil(double a)
* public static double floor(double a)
* public static int max(int a, int b)
* public static double pow(double a, double b)
* public static double random()
* public static int round(float a)
* public static double sqrt(double a)


package com.heima.math;
public class Demo1_Math {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Math.PI); // 静态,可以直接用类名调用
System.out.println(Math.abs(-12)); // 取绝对值
System.out.println(Math.ceil(12.3)); // 向上取整,结果是double值
System.out.println(Math.ceil(12.77));
System.out.println(Math.ceil(-12.77));
System.out.println(Math.floor(12.3)); // 向下取整,返回double值
System.out.println(Math.max(12, 62)); // 取较大的值
System.out.println(Math.pow(2, 3)); // 求幂,返回double数
System.out.println(Math.random()); // 生成0.0 到 1.0 之间的小数,包括0.0, 不包括 1.0
System.out.println(Math.round(-23.6)); // 四舍五入,可传入float值和double值,返回int值
System.out.println(Math.sqrt(5)); // 开方
}
}
Math
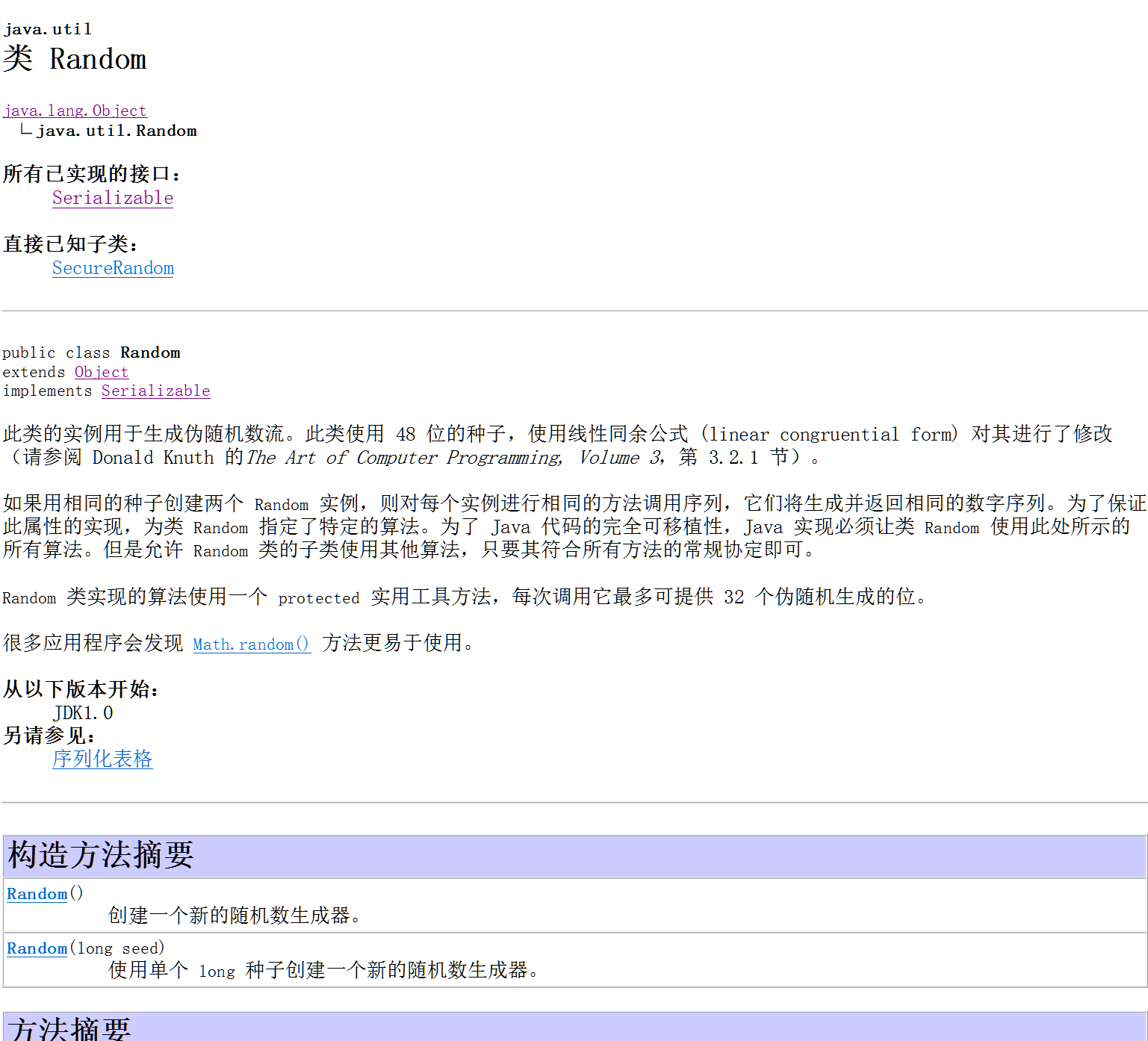
Random类的概述和方法使用
* A:Random类的概述
* 此类用于产生随机数,如果用相同的种子,就创建两个 Random实例
* 则对每个实例进行相同的方法调用序列,它们将生成并返回相同的数字序列
* B:构造方法
* public Random()
* public Random(long seed)
* C:成员方法
* public int nextInt()
* public int nextInt(int n)
package com.heima.math;
import java.util.Random;
public class Demo2_Random {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// demo1();
// demo2();
}
public static void demo2() {
Random r2 = new Random(1000); // 有参构造,指定种子,第一次运行的结果和第二次的一样
int a = r2.nextInt();
int b = r2.nextInt();
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
}
public static void demo1() {
Random random = new Random(); // 默认种子为 纳秒值,每一纳秒种子都在变化
int i = random.nextInt();
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
// System.out.println(random.nextInt()); // 默认int范围内
System.out.println(random.nextInt(100)); // 指定范围,0-100,包含0,不包含100
}
}
}
Random
System类的概述和方法使用
* A:System类的概述
* System类包含一些有用的类字段和方法,它不能被实例化
* B:成员方法
* public static void gc()
* public static void exit(int status)
* public static long currentTimeMillis()
* public static void arratcopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length)
* C:案例演示
* System类的成员方法的使用

package com.heima.math;
public class Demo3_System {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// demo1();
// demo2();
// demo3();
// demo4();
}
public static void demo4() {
int[] src = { 11, 22, 33, 44, 55 };
int[] dest = new int[8];
System.arraycopy(src, 0, dest, 3, src.length); // 将数组内容拷贝
for (int i = 0; i < dest.length; i++) {
System.out.println(dest[i]);
}
}
public static void demo3() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 获取当前时间和1970年1月1日午夜之间的时间差,单位是毫秒
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("*");
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 1秒等于1000毫秒
System.out.println(end - start);
}
public static void demo2() {
System.exit(0); // 非0 状态是异常终止,退出jvm虚拟机
System.out.println("------"); // jvm已经退出,程序语句不会执行
}
public static void demo1() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Demo();
System.gc();// 运行垃圾回收器,相当于手动呼喊保洁阿姨
}
}
}
class Demo { // 在一个源文件中不允许定义两个用public修饰的类
public void finalize() { // 自动调用,类似保洁阿姨,当垃圾回收器确定不存在对该对象的更多引用时,由对象的垃圾回收器调用此方法
System.out.println("垃圾被清扫了");
}
}
System
BigInteger类的概述和方法使用
* A:BigInteger的概述
* 可以让超过Integer范围内的数据进行运算
* B:构造方法
* public BigInteger(String val)
* C:成员方法
* public BigInteger add(BigInteger val)
* public BigInteger subtract(BigInteger val)
* public BigInteger multiply(BigInteger val)
* public BigInteger divide(BigInteger val)
* public BigInteger[ ] divideAndRemainder(BigInteger val)

package com.heima.math;
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class Demo4_BigInteger {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigInteger bi1 = new BigInteger("1000000000000000000000000000");
BigInteger bi2 = new BigInteger("101");
System.out.println(bi1.add(bi2)); // 加
System.out.println(bi1.subtract(bi2)); // 减
System.out.println(bi1.multiply(bi1)); // 乘
System.out.println(bi1.divide(bi2)); // 除
BigInteger[] arr = bi1.divideAndRemainder(bi2); // 取除数和余数
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}
BigInteger
BigDecimal类的概述和方法使用
* A:BigDecimal的概述
* 由于在运算的时候,float类型和double很容易丢失精读,演示案例
* 所以,为了能相对更加精确的表示、计算浮点数,Java提供了BigDecimal
* 不可变的、任意精读的有符号十进制数
* B:构造方法
* public BigDecimal(String val)
* C:成员方法
* public BigDecimal add(BigDecimal augend)
* public BigDecimal subtract(BigDecimal subtrahend)
* public BigDecimal multiply(BigDecimal multiplcand)
* public BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal divisor)
* D:案例演示
* BigDecimal类的构造方法和成员方法使用
package com.heima.math;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class Demo5_BigDecimal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal bc1 = new BigDecimal("2.0"); // 方法1 :通过构造中传入字符串的方式,开发时推荐
BigDecimal bc2 = new BigDecimal("1.1");
System.out.println(bc1.subtract(bc2));
BigDecimal bd1 = BigDecimal.valueOf(2.0);// 方法2:
BigDecimal bd2 = BigDecimal.valueOf(1.1);
System.out.println(bd1.subtract(bd2));
}
}
BigDecimal
Date类的概述和方法使用
* A:Date类的概述
* 类Date表示特定的瞬间,精确到毫秒
* B:构造方法
* public Date()
* public Date(long date)
* C:成员方法
* public long getTime()
* public void setTime(long time)

package com.heima.math;
import java.util.Date;
public class Demo6_Date {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// demo1();
// demo2();
// demo3();
}
public static void demo3() {
Date d1 = new Date();
d1.setTime(100000000); // 设置毫秒值,改变时间对象
System.out.println(d1); // Fri Jan 02 11:46:40 CST 1970
}
public static void demo2() {
Date d1 = new Date();
System.out.println(d1.getTime()); // 通过时间对象获取毫秒值
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()); // 通过系统类的方法获取当前时间的毫秒值,二者可能会有差值
}
public static void demo1() {
Date d1 = new Date();
System.out.println(d1); // 如果没有传参数,代表的是当前时间
Date d2 = new Date(0); // 如果构造方法中参数为0,代表的是 Thu Jan 01 08:00:00 CST 1970
System.out.println(d2); // 通过毫秒值创建时间对象
}
}
Date
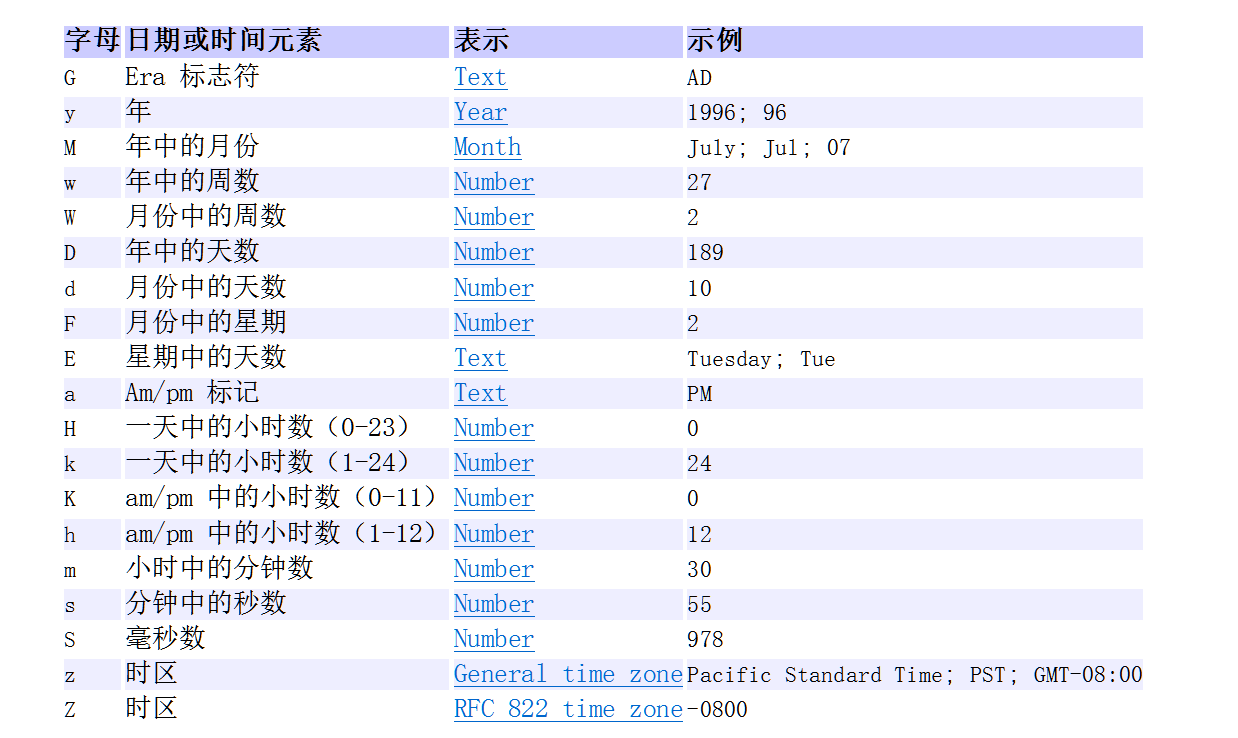
SimpleDateFormat类实现日期和字符串的相互转换
* A:DateFormat类的概述
* DateFormat 是日期/时间格式化子类的抽象类,它以与语言无关的方式格式化并解析日期或时间。是抽象类,所以使用其子类SimpleDateFormat
* B:SimpleDateFormat构造方法
* public SimpleDateFormat()
* public SimpleDateFormat(String pattern)
* C:成员方法
* public final String format(Date date)
* publc date parse(String souce)


package com.heima.math; import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date; public class Demo7_SimpleDateFormat {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
// demo1();
// demo2();
// demo3();
// demo4();
} public static void demo4() throws ParseException {
// 将时间字符串转换成日期对象
String str = "2000年10月31日 11:35:08";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
Date d1 = sdf.parse(str); // 将时间字符串转换为日期对象
System.out.println(d1);
} public static void demo3() {
Date d = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(sdf.format(d)); // 2020/04/04 09:39:15
} public static void demo2() {
Date d = new Date(); // 获取当前时间对象
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(); // 创建日期格式化对象
System.out.println(sdf.format(d)); // 2020/4/4 上午9:29
} public static void demo1() {
// DateFormat df = new DateFormat(); // 抽象类,不能实例化
// DateFormat df1 = new SimpleDateFormat();
DateFormat df1 = DateFormat.getDateInstance(); // 相当于多态,右边的方法返回一个子类对象
}
}
SimpleDateFormat
你来到这个世界多少天案例
* A:案例演示
* 需求:算一下你来到这个世界多少天?
package com.heima.test; import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date; public class Test2 {
/*
* 分析:
* 1、将生日字符串和今天日期字符串存在String类型的变量中
* 2、定义日期格式化对象
* 3、将日期字符串转换为日期对象
* 4、通过日期对象获取时间毫秒值
* 5、将两个时间毫秒值相减,再除以1000变成秒,再除以60变成分钟,再除以60变成小时,再除以24得到天
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
String s1 = "2000/10/31";
String s2 = "2020/03/18";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
Date d1 = sdf.parse(s1);
Date d2 = sdf.parse(s2); long time = d2.getTime() - d1.getTime();
System.out.println(time / 1000 / 60 / 60 / 24 / 365);
System.out.println(time / 1000 / 60 / 60 / 24 % 365); }
}
Test2
Calendar类的概述和获取日期的方法
* A:Calendar类的概述
* Calendar类 是一个抽象类,它为特定瞬间与一组诸如 YEAR、MONTH、DAY_OF_MONTH、HOUR 等日历字段之间的转换提供了一些方法,并为操作日历字段(例如获得下星期的日期)提供了一些方法
* B:成员方法
* public static Calender getInstance()
* public int get(int field)
package com.heima.math;
import java.util.Calendar;
public class Demo8_Calender {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//demo1();
demo2();
}
public static void demo2() {
Calendar cal1 = Calendar.getInstance(); // 父类引用指向子类对象
cal1.add(Calendar.MONTH, 10); // 对指定的字段进行向前减或向后加的操作
System.out.println(cal1.get(Calendar.YEAR) + "年" + getNum(cal1.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1) + "月"
+ getNum(cal1.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH))+ "日" + getWeek(cal1.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK)));
cal1.set(2000, 9, 31); // 设置字段,注意月从0开始计数
System.out.println(cal1.get(Calendar.YEAR) + "年" + getNum(cal1.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1) + "月"
+ getNum(cal1.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH))+ "日" + getWeek(cal1.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK)));
}
public static void demo1() {
Calendar cal1 = Calendar.getInstance(); // 父类引用指向子类对象
System.out.println(cal1.get(Calendar.YEAR)); // 通过字段获取年
System.out.println(cal1.get(Calendar.MONTH)); // 通过字段获取月,但是第一个月从0开始计数
System.out.println(cal1.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH)); // 获取月中的第几天
System.out.println(cal1.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK)); // 获取一个礼拜中的第几天,周日是第一天,周六是第七天
System.out.println(cal1.get(Calendar.YEAR) + "年 " + getNum(cal1.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1) + "月 "
+ getNum(cal1.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH))+ "日 " + getWeek(cal1.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK)));
}
/*
* 如果是个位数,数字前面补0
* 1、返回值类型为String
* 2、参数列表为int num
*/
public static String getNum(int num) {
return num > 9 ? "" + num : "0" + num;
}
/*
* 将星期存储在表中进行查表
* 1、返回值类型为String
* 2、参数列表为int week
*/
public static String getWeek(int week) {
String[] arr = { "", "星期日", "星期一", "星期二", "星期三", "星期四", "星期五", "星期六" };
return arr[week];
}
}
Calender
如何获取任意年份并判断是闰年还是平年
* A:案例演示
* 需求:键盘录入任意年份,判断该年是闰年还是平年
package com.heima.test; import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Scanner; public class Test3 {
/*
* 分析:
* 1、键盘录入年Scanner
* 2、创建Calendar对象
* 3、通过set方法将日期设置为那一年的3月1日
* 4、通过add方法将日期减一
* 5、判断二月的最后一天是29还是28
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc1 = new Scanner(System.in); // 创建键盘录入对象
System.out.println("请输入年份,判断该年是闰年还是平年");
String year = sc1.nextLine(); // 录入年份
boolean b = getYear(Integer.parseInt(year)); // 将数字字符串转化为数字
System.out.println(b == true ? "是闰年" : "是平年");
sc1.close();
} private static boolean getYear(int year) {
Calendar c1 = Calendar.getInstance(); // 创建Calendar对象
c1.set(year, 2, 1); // 设置日期
c1.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, -1); // 将日期减一
return c1.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH) == 29;
}
}
Test3
最新文章
- Open-Test 测试驱动模式与版本号管理机制
- C# ~ 从 委托事件 到 观察者模式 - Observer
- volatile简介
- 新手选择使用 Linux 桌面的七个注意点
- 电脑蓝屏分析教程,附工具WinDbg(x86 x64)6.12.0002.633下载
- php gd 生成日历图
- java String字符串进行排序
- windows 编程 —— 消息与参数(滚动条、键盘、鼠标)
- Outlook2007、2010和Foxmail的簽名設計
- Delphi OleVariant 类型的用法
- javaScript 工作必知(五) eval 的使用
- PHP开发人员对JAVA的WEB开发入门(初版-已废弃)
- Travis CI实现持续部署
- 在Django中使用logging模块
- Hanlp汉字转拼音使用python调用详解
- 关于bit,bin文件的一些研究
- [BetterExplained]为什么你应该(从现在开始就)写博客
- luoguP4491 [HAOI2018]染色 广义容斥原理 + FFT
- Informatica 常用组件Expression之二 创建EXP组件
- python 统计时间,写日志