CSS3:FlexBox的详解
Flexbox是Flexible box 的简称(灵活的盒子容器),是CSS3引入的新的布局模式。它决定了元素如何在页面上排列,使它们能在不同的屏幕尺寸和设备下可预测地展现出来。
它之所以被称为 Flexbox ,是因为它能够扩展和收缩 flex 容器内的元素,以最大限度地填充可用空间。与以前布局方式(如 table 布局和浮动元素内嵌块元素)相比,Flexbox 是一个更强大的方式:
- 在不同方向排列元素
- 重新排列元素的显示顺序
- 更改元素的对齐方式
- 动态地将元素装入容器
创建一个flex容器:
在父元素的添加这条属性:
display: flex;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.flex-container{
background-color: #131111;
display: flex; /*让这个div变成弹性盒子*/
}
.flex-container .flex-item{
padding: 20px;
background-color: #b1ff84;
}
.flex-container .flex-item:first-child{
background-color: #f5e25f;
}
.flex-container .flex-item:last-child{
background-color: #0B5A79;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="flex-container">
<div class="flex-item">1</div>
<div class="flex-item">2</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
运行效果:

相当于两个div自动向左浮动,默认情况下,所有的直接子元素都被认为是 flex 项,并从左到右依次排列在一行中。如果 flex 项的宽度总和大于容器,那么 flex 项将按比例缩小,直到它们适应 flex 容器宽度。
也可以将这个两个子div排成一列,在.flex-container添加:flex-direction: column;
运行效果:

如果加的属性是flex-direction: column-reverse;即两个div互换(reverse的意思就是相反的),
当在.flex-container添加justify-content: flex-end;里面所有的flex将默认向左对齐变成向右对齐:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.flex-container{
background-color: #131111;
display: flex; /*让这个div变成弹性盒子*/
justify-content: flex-end;
}
.flex-container .flex-item{
padding: 20px;
background-color: #b1ff84;
}
.flex-container .flex-item:first-child{
background-color: #f5e25f;
}
.flex-container .flex-item:last-child{
background-color: #0B5A79;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="flex-container">
<div class="flex-item">1</div>
<div class="flex-item">2</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
运行效果:

当justify-content值为:center时,flex项居中对齐,其运行效果:

justify-content总共有六个值前三个比较好理解:justify-start(默认,向左对齐),center,justify-end,
space-evenly: flex 容器起始边缘和第一个 flex 项之间的间距和每个相邻 flex 项之间的间距是相等。(愚人码头注:该属性以前很少看到,原因是以前浏览器不支持,chrome 也是 60 版本之后才支持。延伸一下,align-content: space-evenly也是这个逻辑 )
space-between: 任何两个相邻 flex 项之间的间距是相同的,但不一定等于第一个/最后一个 flex 项与 flex 容器边缘之间的间距;起始边缘和第一个项目之间的间距和末端边缘和最后一个项目之间的间距是相等的。space-around: flex 容器中的每个 flex 项的每一侧间距都是相等的。请注意,这意味着两个相邻 flex 项之间的空间将是第一个/最后一个 flex 项与其最近边缘之间的空间的两倍
网上流行的一张图,更好的解释了justify-content属性值的表现:

也可以给指定的div让它变成向上或向下对齐:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.flex-container{
background-color: #131111;
display: flex; /*让这个div变成弹性盒子*/
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.flex-container .flex-item{
padding: 20px;
background-color: #b1ff84;
}
.flex-container .flex-item:first-child{
background-color: #f5e25f;
}
.flex-container .flex-item:last-child{
background-color: #0B5A79;
}
.flex-bottom{
/* 让这个div向上 */
align-self: flex-start;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="flex-container">
<!-- 多加个class属性,方便指定 -->
<div class="flex-item flex-bottom">1</div>
<div class="flex-item">2 <br />2 <br/></div>
<div class="flex-item">3 <br />3<br />3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
运行效果:

同样的,algin-item也有五个属性值:
flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | stretch;下图就是对应的效果: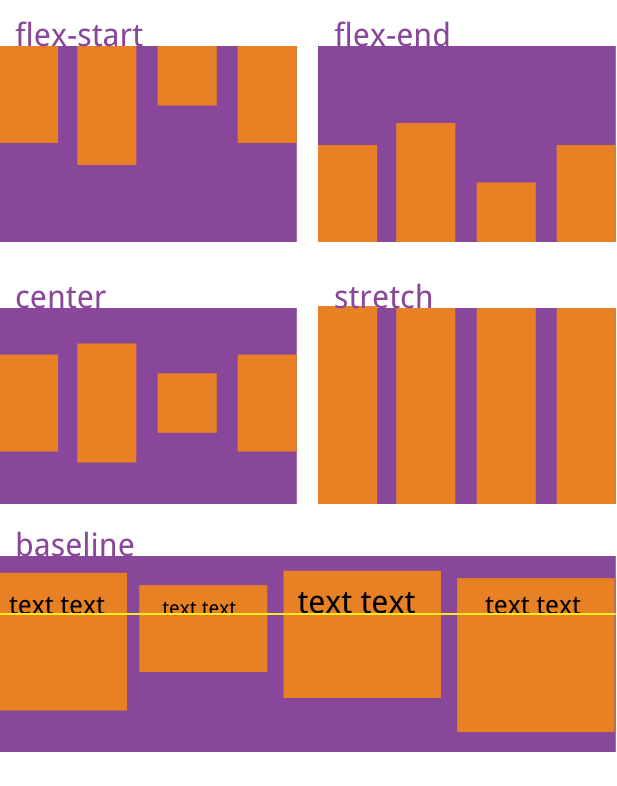
允许 flex 项多行/列排列
.flex-container{
background-color: #131111;
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
默认情况下, flex 项不允许多行/列排列(nowrap),如果 flex 容器尺寸对于所有 flex 项来说不够大,那么flex 项将被调整大小以适应单行或列排列。
通过添加 flex-wrap: wrap ,可以将溢出容器的 flex 项将被排列到另一行/列中,它也有三个取值:
nowrap(默认):不换行.
wrap:换行,第一行在上方

wrap-reverse:换行,第一行在下方

插入一段代码,看下效果:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.flex-container{
background-color: #131111;
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
justify-content: space-evenly;/**/
align-content: space-evenly;
}
.flex-container .flex-item{
padding: 20px;
background-color: #b1ff84;
}
.flex-container .flex-item:first-child{
background-color: #f5e25f;
}
.flex-container .flex-item:last-child{
background-color: #0B5A79;
}
.flex-bottom{
/* 让这个div向下 */
align-self: stretch;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="flex-container">
<!-- 多加个class属性,方便指定 -->
<div class="flex-item">1</div>
<div class="flex-item">2</div>
<div class="flex-item">3</div>
<div class="flex-item">4</div>
<div class="flex-item">5</div>
<div class="flex-item">6</div>
<div class="flex-item">7</div>
<div class="flex-item">8</div>
<div class="flex-item">9</div>
<div class="flex-item">10</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
运行效果:
当长度不够长时,自动换行:
当长度再短时:
拉伸 flex 项
flex-grow 只有在 flex 容器中有剩余空间时才会生效。flex 项的 flex-grow 属性指定该 flex 项相对于其他 flex 项将拉伸多少,以填充 flex 容器。默认值为1。当设置为 0 时,该 flex 项将不会被拉伸去填补剩余空间。在这个例子中,两个项的比例是 1:2,意思是在被拉伸时,第一个 flex 项将占用 1/3,而第二个 flex 项将占据余下的空间,flex-grow控制的是flex项的拉伸比例,而不是占据 flex 容器的空间比例。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.flex-container{
background-color: #131111;
display: flex;
}
.flex-item1{flex-grow: 0;}
.flex-item2{flex-grow: 1;}
.flex-item3{flex-grow: 2;}
.flex-container{
width:400px;
padding:10px;
background-color: #F0f0f0;
}
.flex-container .flex-item{
padding:20px 0;
text-align: center;
width:90px;
background-color: #B1FF84;
}
.flex-container .flex-item:first-child{
background-color: #F5DE25;
}
.flex-container .flex-item:last-child{
background-color: #90D9F7;
} </style>
<body>
<div class="flex-container">
<div class="flex-item flex-item1">1</div>
<div class="flex-item flex-item2">2</div>
<div class="flex-item flex-item3">3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
我将三个div全部设为width:90px;
运行效果:
将flex-container的width变为600时:
可以看出2 3 以不同的比例在填充剩余的空间,grow-shrink则是相反的,默认为1,即如果空间不足,该项目将缩小。
看不理解的话,推荐到这俩个网站:网站一
最新文章
- C#.NET 大型通用信息化系统集成快速开发平台 4.1 版本 - 忘记密码功能改进、手机短信、电子邮件
- Android应用开发基础之十:多媒体编程
- xwamp 目录结构设计
- MVC validation
- C#:数据交互
- Struts – Multiple configuration files example
- 【转贴】gdb中的信号(signal)相关调试技巧
- MySQL引擎简述
- 怎么配置Jupyter Notebook默认启动目录?
- Redis学习笔记(一)关于在windows64位环境下的安装学习使用
- Java基础--接口和抽象类的区别
- centos7 无界面静默安装 oracle
- JS_高阶函数(map and reduce)
- HTML空格占位符
- Mysql 乐观锁
- Sql 重置自动增长列
- 关于MYSQL ERROR1045 报错的解决办法
- Unity5 AssetBundle系列——简单的AssetBundleManager
- Python算法——递归思想
- 乐视max2 在开发中无法打印某些logcat 解决方案