洛谷 P3576 [POI2014]MRO-Ant colony
题目描述
The ants are scavenging an abandoned ant hill in search of food.
The ant hill has nn chambers and n-1n−1 corridors connecting them.
We know that each chamber can be reached via a unique path from every other chamber.
In other words, the chambers and the corridors form a tree.
There is an entrance to the ant hill in every chamber with only one corridor leading into (or out of) it.
At each entry, there are gg groups of m_1,m_2,\cdots,m_gm1,m2,⋯,mg ants respectively.
These groups will enter the ant hill one after another, each successive group entering once there are no ants inside.
Inside the hill, the ants explore it in the following way:
Upon entering a chamber with dd outgoing corridors yet unexplored by the group,the group divides into dd groups of equal size. Each newly created group follows one of the d corridors.If d=0d=0, then the group exits the ant hill.
- If the ants cannot divide into equal groups, then the stronger ants eat the weaker until a perfect division is possible.Note that such a division is always possible since eventually the number of ants drops down to zero.Nothing can stop the ants from allowing divisibility - in particular, an ant can eat itself, and the last one remaining will do so if the group is smaller than dd.
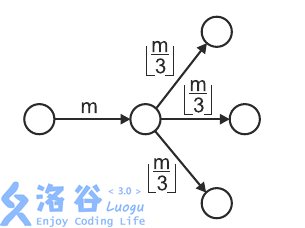
The following figure depicts mm ants upon entering a chamber with three outgoing unexplored corridors, dividing themselves into three (equal) groups of \left \lfloor m/3 \right \rfloor⌊m/3⌋ ants each.
A hungry anteater dug into one of the corridors and can now eat all the ants passing through it.
However, just like the ants, the anteater is very picky when it comes to numbers.
It will devour a passing group if and only if it consists of exactly kk ants.
We want to know how many ants the anteater will eat.
给一棵树,对于每个叶子节点,都有g群蚂蚁要从外面进来,每群蚂蚁在行进过程中只要碰到岔路,就将平均地分成岔路口数-1那么多份,然后平均地走向剩下的那些岔路口,余下的蚂蚁自动消失,树上有一个关键边,假如有一群蚂蚁通过了这条边且数量恰好为k,这k只蚂蚁就被吃掉,问一共有多少只蚂蚁被吃掉
输入输出格式
输入格式:
The first line of the standard input contains three integers nn, gg, kk(2\le n,g\le 1\ 000\ 0002≤n,g≤1 000 000, 1\le k\le 10^91≤k≤109), separated by single spaces.
These specify the number of chambers, the number of ant groups and the number of ants the anteater devours at once. The chambers are numbered from 1 to nn.
The second line contains gg integers m_1,m_2,\cdots,m_gm1,m2,⋯,mg (1\le m_i\le 10^91≤mi≤109), separated by single spaces, where m_imi gives the number of ants in the ii-th group at every entrance to the ant hill. The n-1n−1 lines that follow describe the corridors within the ant hill;the ii-th such line contains two integers a_iai,b_ibi (1\le a_i,b_i\le n1≤ai,bi≤n), separated by a single space, that indicate that the chambers no. a_iai and b_ibi are linked by a corridor. The anteater has dug into the corridor that appears first on input.
输出格式:
Your program should print to the standard output a single line containing a single integer: the number of ants eaten by the anteater.
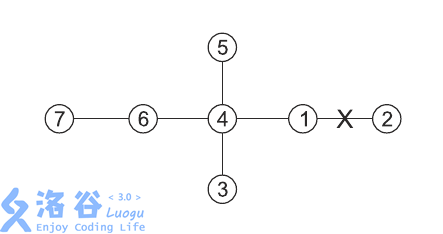
输入输出样例
7 5 3
3 4 1 9 11
1 2
1 4
4 3
4 5
4 6
6 7
21
说明
给一棵树,对于每个叶子节点,都有g群蚂蚁要从外面进来,每群蚂蚁在行进过程中只要碰到岔路,就将平均地分成岔路口数-1那么多份,然后平均地走向剩下的那些岔路口,余下的蚂蚁自动消失,树上有一个关键边,假如有一群蚂蚁通过了这条边且数量恰好为k,这k只蚂蚁就被吃掉,问一共有多少只蚂蚁被吃掉
题意:
题目描述:

#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#define MAXN 1000001
using namespace std;
int n,g,K;
int s,t,tot;
long long ans;
int outo[MAXN],dad[MAXN];
int to[MAXN],net[MAXN],head[MAXN];
long long m[MAXN],minn[MAXN],maxn[MAXN];
void add(int u,int v){
to[++tot]=v;net[tot]=head[u];head[u]=tot;
to[++tot]=u;net[tot]=head[v];head[v]=tot;
}
void dfs(int now){
for(int i=head[now];i;i=net[i])
if(dad[now]!=to[i]){
dad[to[i]]=now;
outo[now]++;
}
for(int i=head[now];i;i=net[i])
if(dad[now]!=to[i]){
minn[to[i]]=minn[now]*outo[now];
maxn[to[i]]=(maxn[now]+)*outo[now]-;
maxn[to[i]]=min(maxn[to[i]],m[g]);
if(minn[to[i]]<=m[g])
dfs(to[i]);
}
}
long long cal(long long x){
int l=,r=g,bns=;
while(l<=r){
int mid=(l+r)/;
if(m[mid]<x){
bns=max(bns,mid);
l=mid+;
}
else r=mid-;
}
return bns;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&g,&K);
for(int i=;i<=g;i++) scanf("%d",&m[i]);
sort(m+,m++g);
scanf("%d%d",&s,&t);
for(int i=;i<n;i++){
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
add(x,y);
}
minn[s]=maxn[s]=minn[t]=maxn[t]=K;
dfs(s);
dfs(t);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
if(!outo[i])
ans+=cal(maxn[i]+)-cal(minn[i]);
cout<<ans*K;
}
最新文章
- Hive函数大全
- JS-underfined is not a function
- java并发包:线程池 executorservice
- MySQL Workbench gnome-keyring-daemon错误的解决
- DBLINK 创建与小结
- 【NOIP 2016 总结】
- Thml 小插件8 天气插件定制
- document.getElementById(), getElementsByname(),getElementsByClassName(),getElementsByTagName()方法表示什么以及其意义
- C#基础知识之属性
- Windows下MySQL绿色版安装配置与使用
- WeexSDK之注册Components
- Java基础——Oracle(一)
- JavaScript —— 数组
- 洛谷 P2257 YY的GCD
- HRBUST - 1818 石子合并 区间dp入门
- __init__.py的作用
- 10 -- 深入使用Spring -- 5...1 使用Quartz
- 读书笔记--C陷阱与缺陷(七)
- 【二分】【预处理】zoj4029 Now Loading!!!
- (转)Linux下部署tomcat及tomcat war包应用程序