Mysql ICP(翻译)
2024-10-20 11:37:28
英文版原文链接
https://mariadb.com/kb/en/library/index-condition-pushdown/
ICP 全称 Index Condition Pushdown。这个特性主要是针对索引查找的优化,使得查找数据的时候,无法精确匹配的索引也会做出比较。会在存储引擎层将不满足的数据直接过滤掉。
Index Condition Pushdown is an optimization that is applied for access methods that access table data through indexes: range, ref, eq_ref,
ref_or_null, and Batched Key Access. The idea is to check part of the WHERE condition that refers to index fields (we call it Pushed Index Condition) as soon as we've accessed the index.
If the Pushed Index Condition is not satisfied, we won't need to read the whole table record.
ICP 是一种通过索访问表数据的访问方法的优化,可以优化的类型有range,ref,eq_ref,ref_or_null。只要where后面的条件是索引,那么就可以适用于这个特性。如果ICP不满足(感觉这里应该是满足),则不用访问整个表的记录。
打开和关闭ICP
SET optimizer_switch='index_condition_pushdown=off'
ICP特性是默认打开的,可以通过sql语句关闭这个特性
当ICP特性被打开之后,Explain 字段会显示 “Using index condition”
When Index Condition Pushdown is used, EXPLAIN will show "Using index condition":
MariaDB [test]> explain select * from tbl where key_col1 between 10 and 11 and key_col2 like '%foo%';
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tbl | range | key_col1 | key_col1 | 5 | NULL | 2 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+-----------------------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
The idea behind index condition pushdown 关于ICP背后的秘密
In disk-based storage engines, making an index lookup is done in two steps, like shown on the picture:
在基于磁盘的存储引擎中,完成一个索引查询需要两个步骤
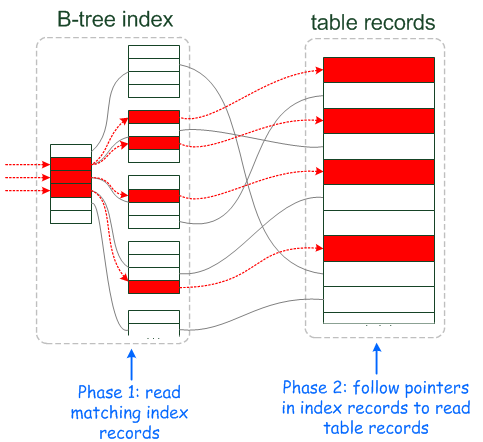
第一步是读入匹配的索引记录,第二步是根据索引中的指针读取表中的记录
Index Condition Pushdown optimization tries to cut down the number of full record reads by checking whether index records satisfy part of the WHERE condition that can be checked for them:
ICP特性 尝试检测where条件中的条件是否,来减少读取整个表的数据
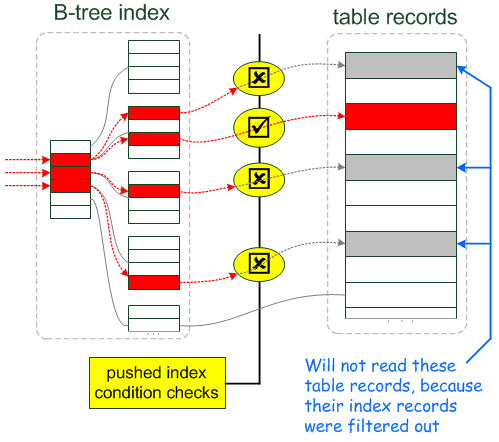
How much speed will be gained depends on - How many records will be filtered out - How expensive it was to read them The former depends on the query and the dataset. The latter is generally bigger when table records are on disk and/or are big, especially when they have blobs.
将获得多少速度取决于 - 多少记录将被过滤掉 - 取决于多去数据需要消耗的花费 前者取决于查询和数据集。 当表记录在磁盘上和/或是大的时候,后者通常更大,特别是当它们具有斑点时。
最新文章
- ECMAScript5之Array
- java设计模式 模板方法模式Template Method
- Spring MVC Integration,Spring Security
- fix eclipse gc overhead limit exceeded in mac
- 分享一个自己写的基于JQuery的一个Web背景切换的Demo
- java,spring,tomcat,跨域设置
- adb shell dumpsys
- document.body.clientHeight的取值
- SignalR来做实时Web聊天
- Argparse简易教程
- Dynamics CRM 导出系统中实体的属性字段到EXCEL
- 面向对象(this的问题一)
- vue实现懒加载
- Pyinstaller (python打包为exe文件)
- Linux c使用gumbo库解析页面表单信息(一)
- Spring中EmptyResultDataAccessException异常产生的原理及处理方法
- 【进阶1-5期】JavaScript深入之4类常见内存泄漏及如何避免(转)
- 【Ansible 文档】【译文】Playbooks 变量
- CF527D
- 本地计算机上的SQLServer(MSSQLSERVER)服务启动后停止,某些服务在未由其他服务或程序使用时将自动停止