09.C语言:预处理(宏定义)、字节序、地址对齐
一、预处理

预处理
gcc -E Hello.c -o hello.i
编译
gcc -S hello.i -o hello.s
汇编
gcc -c hello.s -o hello.o
链接
gcc hello.o -o hello
Makefile
# "hello.c"
# "<built-in>"
# "<command-line>"
# "/usr/include/stdc-predef.h"
# "<command-line>"
# "hello.c" # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
# "/usr/include/features.h"
# "/usr/include/features.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/sys/cdefs.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/sys/cdefs.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/wordsize.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/sys/cdefs.h"
# "/usr/include/features.h"
# "/usr/include/features.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/gnu/stubs.h" # "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/gnu/stubs-32.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/gnu/stubs.h"
# "/usr/include/features.h"
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" # "/usr/lib/gcc/i686-linux-gnu/4.8/include/stddef.h"
# "/usr/lib/gcc/i686-linux-gnu/4.8/include/stddef.h"
typedef unsigned int size_t;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" # "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/types.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/types.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/wordsize.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/types.h" typedef unsigned char __u_char;
typedef unsigned short int __u_short;
typedef unsigned int __u_int;
typedef unsigned long int __u_long; typedef signed char __int8_t;
typedef unsigned char __uint8_t;
typedef signed short int __int16_t;
typedef unsigned short int __uint16_t;
typedef signed int __int32_t;
typedef unsigned int __uint32_t; __extension__ typedef signed long long int __int64_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned long long int __uint64_t; __extension__ typedef long long int __quad_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned long long int __u_quad_t;
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/types.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/typesizes.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/types.h" __extension__ typedef __u_quad_t __dev_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned int __uid_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned int __gid_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned long int __ino_t;
__extension__ typedef __u_quad_t __ino64_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned int __mode_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned int __nlink_t;
__extension__ typedef long int __off_t;
__extension__ typedef __quad_t __off64_t;
__extension__ typedef int __pid_t;
__extension__ typedef struct { int __val[]; } __fsid_t;
__extension__ typedef long int __clock_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned long int __rlim_t;
__extension__ typedef __u_quad_t __rlim64_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned int __id_t;
__extension__ typedef long int __time_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned int __useconds_t;
__extension__ typedef long int __suseconds_t; __extension__ typedef int __daddr_t;
__extension__ typedef int __key_t; __extension__ typedef int __clockid_t; __extension__ typedef void * __timer_t; __extension__ typedef long int __blksize_t; __extension__ typedef long int __blkcnt_t;
__extension__ typedef __quad_t __blkcnt64_t; __extension__ typedef unsigned long int __fsblkcnt_t;
__extension__ typedef __u_quad_t __fsblkcnt64_t; __extension__ typedef unsigned long int __fsfilcnt_t;
__extension__ typedef __u_quad_t __fsfilcnt64_t; __extension__ typedef int __fsword_t; __extension__ typedef int __ssize_t; __extension__ typedef long int __syscall_slong_t; __extension__ typedef unsigned long int __syscall_ulong_t; typedef __off64_t __loff_t;
typedef __quad_t *__qaddr_t;
typedef char *__caddr_t; __extension__ typedef int __intptr_t; __extension__ typedef unsigned int __socklen_t;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
struct _IO_FILE; typedef struct _IO_FILE FILE; # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
typedef struct _IO_FILE __FILE;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
# "/usr/include/_G_config.h"
# "/usr/include/_G_config.h"
# "/usr/lib/gcc/i686-linux-gnu/4.8/include/stddef.h"
# "/usr/include/_G_config.h" # "/usr/include/wchar.h"
# "/usr/include/wchar.h"
typedef struct
{
int __count;
union
{ unsigned int __wch; char __wchb[];
} __value;
} __mbstate_t;
# "/usr/include/_G_config.h"
typedef struct
{
__off_t __pos;
__mbstate_t __state;
} _G_fpos_t;
typedef struct
{
__off64_t __pos;
__mbstate_t __state;
} _G_fpos64_t;
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
# "/usr/lib/gcc/i686-linux-gnu/4.8/include/stdarg.h"
# "/usr/lib/gcc/i686-linux-gnu/4.8/include/stdarg.h"
typedef __builtin_va_list __gnuc_va_list;
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
struct _IO_jump_t; struct _IO_FILE;
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
typedef void _IO_lock_t; struct _IO_marker {
struct _IO_marker *_next;
struct _IO_FILE *_sbuf; int _pos;
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
}; enum __codecvt_result
{
__codecvt_ok,
__codecvt_partial,
__codecvt_error,
__codecvt_noconv
};
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
struct _IO_FILE {
int _flags; char* _IO_read_ptr;
char* _IO_read_end;
char* _IO_read_base;
char* _IO_write_base;
char* _IO_write_ptr;
char* _IO_write_end;
char* _IO_buf_base;
char* _IO_buf_end; char *_IO_save_base;
char *_IO_backup_base;
char *_IO_save_end; struct _IO_marker *_markers; struct _IO_FILE *_chain; int _fileno; int _flags2; __off_t _old_offset; unsigned short _cur_column;
signed char _vtable_offset;
char _shortbuf[]; _IO_lock_t *_lock;
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
__off64_t _offset;
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
void *__pad1;
void *__pad2;
void *__pad3;
void *__pad4;
size_t __pad5; int _mode; char _unused2[ * sizeof (int) - * sizeof (void *) - sizeof (size_t)]; }; typedef struct _IO_FILE _IO_FILE; struct _IO_FILE_plus; extern struct _IO_FILE_plus _IO_2_1_stdin_;
extern struct _IO_FILE_plus _IO_2_1_stdout_;
extern struct _IO_FILE_plus _IO_2_1_stderr_;
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
typedef __ssize_t __io_read_fn (void *__cookie, char *__buf, size_t __nbytes); typedef __ssize_t __io_write_fn (void *__cookie, const char *__buf,
size_t __n); typedef int __io_seek_fn (void *__cookie, __off64_t *__pos, int __w); typedef int __io_close_fn (void *__cookie);
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
extern int __underflow (_IO_FILE *);
extern int __uflow (_IO_FILE *);
extern int __overflow (_IO_FILE *, int);
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
extern int _IO_getc (_IO_FILE *__fp);
extern int _IO_putc (int __c, _IO_FILE *__fp);
extern int _IO_feof (_IO_FILE *__fp) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int _IO_ferror (_IO_FILE *__fp) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); extern int _IO_peekc_locked (_IO_FILE *__fp); extern void _IO_flockfile (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern void _IO_funlockfile (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int _IO_ftrylockfile (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
# "/usr/include/libio.h"
extern int _IO_vfscanf (_IO_FILE * __restrict, const char * __restrict,
__gnuc_va_list, int *__restrict);
extern int _IO_vfprintf (_IO_FILE *__restrict, const char *__restrict,
__gnuc_va_list);
extern __ssize_t _IO_padn (_IO_FILE *, int, __ssize_t);
extern size_t _IO_sgetn (_IO_FILE *, void *, size_t); extern __off64_t _IO_seekoff (_IO_FILE *, __off64_t, int, int);
extern __off64_t _IO_seekpos (_IO_FILE *, __off64_t, int); extern void _IO_free_backup_area (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" typedef __gnuc_va_list va_list;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
typedef __off_t off_t;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
typedef __ssize_t ssize_t; typedef _G_fpos_t fpos_t; # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/stdio_lim.h"
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" extern struct _IO_FILE *stdin;
extern struct _IO_FILE *stdout;
extern struct _IO_FILE *stderr; extern int remove (const char *__filename) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); extern int rename (const char *__old, const char *__new) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); extern int renameat (int __oldfd, const char *__old, int __newfd,
const char *__new) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); extern FILE *tmpfile (void) ;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern char *tmpnam (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; extern char *tmpnam_r (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern char *tempnam (const char *__dir, const char *__pfx)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) __attribute__ ((__malloc__)) ; extern int fclose (FILE *__stream); extern int fflush (FILE *__stream); # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern int fflush_unlocked (FILE *__stream);
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" extern FILE *fopen (const char *__restrict __filename,
const char *__restrict __modes) ; extern FILE *freopen (const char *__restrict __filename,
const char *__restrict __modes,
FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern FILE *fdopen (int __fd, const char *__modes) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern FILE *fmemopen (void *__s, size_t __len, const char *__modes)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; extern FILE *open_memstream (char **__bufloc, size_t *__sizeloc) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; extern void setbuf (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); extern int setvbuf (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf,
int __modes, size_t __n) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); extern void setbuffer (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf,
size_t __size) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); extern void setlinebuf (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); extern int fprintf (FILE *__restrict __stream,
const char *__restrict __format, ...); extern int printf (const char *__restrict __format, ...); extern int sprintf (char *__restrict __s,
const char *__restrict __format, ...) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__)); extern int vfprintf (FILE *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format,
__gnuc_va_list __arg); extern int vprintf (const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg); extern int vsprintf (char *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format,
__gnuc_va_list __arg) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__)); extern int snprintf (char *__restrict __s, size_t __maxlen,
const char *__restrict __format, ...)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, , ))); extern int vsnprintf (char *__restrict __s, size_t __maxlen,
const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, , ))); # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern int vdprintf (int __fd, const char *__restrict __fmt,
__gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, , )));
extern int dprintf (int __fd, const char *__restrict __fmt, ...)
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, , ))); extern int fscanf (FILE *__restrict __stream,
const char *__restrict __format, ...) ; extern int scanf (const char *__restrict __format, ...) ; extern int sscanf (const char *__restrict __s,
const char *__restrict __format, ...) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern int fscanf (FILE *__restrict __stream, const char *__restrict __format, ...) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_fscanf") ;
extern int scanf (const char *__restrict __format, ...) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_scanf")
;
extern int sscanf (const char *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format, ...) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_sscanf") __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" extern int vfscanf (FILE *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format,
__gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, , ))) ; extern int vscanf (const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, , ))) ; extern int vsscanf (const char *__restrict __s,
const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, , )));
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern int vfscanf (FILE *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_vfscanf") __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, , ))) ;
extern int vscanf (const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_vscanf") __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, , ))) ;
extern int vsscanf (const char *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_vsscanf") __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, , )));
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" extern int fgetc (FILE *__stream);
extern int getc (FILE *__stream); extern int getchar (void); # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern int getc_unlocked (FILE *__stream);
extern int getchar_unlocked (void);
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern int fgetc_unlocked (FILE *__stream); extern int fputc (int __c, FILE *__stream);
extern int putc (int __c, FILE *__stream); extern int putchar (int __c); # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern int fputc_unlocked (int __c, FILE *__stream); extern int putc_unlocked (int __c, FILE *__stream);
extern int putchar_unlocked (int __c); extern int getw (FILE *__stream); extern int putw (int __w, FILE *__stream); extern char *fgets (char *__restrict __s, int __n, FILE *__restrict __stream)
;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern char *gets (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__deprecated__)); # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern __ssize_t __getdelim (char **__restrict __lineptr,
size_t *__restrict __n, int __delimiter,
FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
extern __ssize_t getdelim (char **__restrict __lineptr,
size_t *__restrict __n, int __delimiter,
FILE *__restrict __stream) ; extern __ssize_t getline (char **__restrict __lineptr,
size_t *__restrict __n,
FILE *__restrict __stream) ; extern int fputs (const char *__restrict __s, FILE *__restrict __stream); extern int puts (const char *__s); extern int ungetc (int __c, FILE *__stream); extern size_t fread (void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream) ; extern size_t fwrite (const void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __s); # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern size_t fread_unlocked (void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
extern size_t fwrite_unlocked (const void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream); extern int fseek (FILE *__stream, long int __off, int __whence); extern long int ftell (FILE *__stream) ; extern void rewind (FILE *__stream); # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern int fseeko (FILE *__stream, __off_t __off, int __whence); extern __off_t ftello (FILE *__stream) ;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" extern int fgetpos (FILE *__restrict __stream, fpos_t *__restrict __pos); extern int fsetpos (FILE *__stream, const fpos_t *__pos);
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" # "/usr/include/stdio.h" extern void clearerr (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); extern int feof (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; extern int ferror (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; extern void clearerr_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int feof_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
extern int ferror_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; extern void perror (const char *__s); # "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/sys_errlist.h"
# "/usr/include/i386-linux-gnu/bits/sys_errlist.h"
extern int sys_nerr;
extern const char *const sys_errlist[];
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" extern int fileno (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; extern int fileno_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern FILE *popen (const char *__command, const char *__modes) ; extern int pclose (FILE *__stream); extern char *ctermid (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
# "/usr/include/stdio.h"
extern void flockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); extern int ftrylockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; extern void funlockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
# "/usr/include/stdio.h" # "hello.c" int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("Hello , world !\n"); return ;
}
hello.i
.file "hello.c"
.section .rodata
.LC0:
.string "Hello , world !"
.text
.globl main
.type main, @function
main:
.LFB0:
.cfi_startproc
pushl %ebp
.cfi_def_cfa_offset
.cfi_offset , -
movl %esp, %ebp
.cfi_def_cfa_register
andl $-, %esp
subl $, %esp
movl $.LC0, (%esp)
call puts
movl $, %eax
leave
.cfi_restore
.cfi_def_cfa ,
ret
.cfi_endproc
.LFE0:
.size main, .-main
.ident "GCC: (Ubuntu 4.8.4-2ubuntu1~14.04.3) 4.8.4"
.section .note.GNU-stack,"",@progbits
hello.s
gcc编译过程:http://lib.csdn.net/article/c/66184
1.去掉程序中的注释;
2.文件包含:当对C源程序进行预处理时,文件包含指的是将.c文件包含的头文件内容复制到当前.c文件中。
1》、第一种:#include <stdio.h> 直接去系统头文件目录下寻找所包含的头文件。
2》、第二种:#include "head.h" 先在当前目录下寻找所包含的头文件,如果找不到,则再去系统头文件目录下寻找所包含的头文件。
3.宏替换
当对C源程序进行预处理时,如果程序中有事先定义好的宏,则会将所有的宏后面的字符串替换,例如:
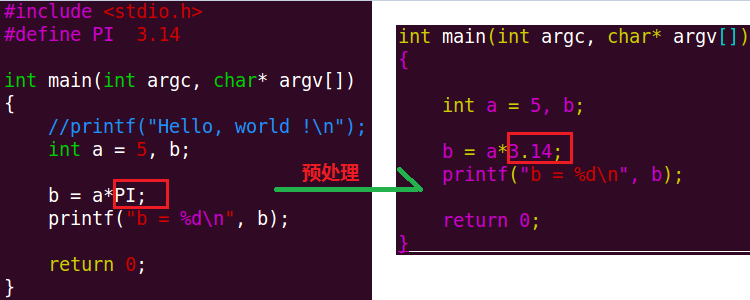
1》预定义宏:
__FILE__ //正在编译的文件名(字符串常量)
__LINE__ //文件当前的行号(整型常量)
__FUNCTION__ //当前所在的函数名(字符串常量)
__DATE__ //预编译文件的日期(字符串常量)
__TIME__ //预编译文件的时间(字符串常量)
__STDC__ //判断编译器是否遵循ANSI C,是则为1(整型常量)
Predefine Macros

2》不带参数的宏:#define 宏名 字符串
/*******************************************************************
* > File Name: noParamMacros.c
* > Author: fly
* > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com
* > Create Time: Sun 17 Sep 2017 01:00:07 PM CST
******************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> #define PI 3.14*2
#define M 60
#define S "HelloWorld" int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
printf("%f\n", PI);
printf("%d\n", M);
printf("%s\n", S); return ;
}
noParamMacros.c
3》带参数的宏:可以像函数一样被调用。
/*******************************************************************
* > File Name: paramMacros.c
* > Author: fly
* > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com
* > Create Time: Sun 17 Sep 2017 01:40:15 PM CST
******************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> #define FUN(a, b) a+b*a #define FALSE 0
#define TRUE 1 int fun(int a, int b){
return a+b*a;
} int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int a = , b =;
int c; c = fun(a, b); //函数调用
printf("c = %d\n", c); c = FUN(a, b); //宏调用 float f; #if (DataType == FALSE)
f = fun(3.1, 4.5); //Data type is error
printf("f = %f\n", f);
#else
f = FUN(3.1, 4.5); //Data type is correct
printf("f = %f\n", f);
#endif return ;
}
paramMacros.c
在上述例子中,由于传参时,可能会传一个表达式,这是调用带参宏就会导致结果不正确,所以一般在定义带参宏时,都会如下去定义: #define FUN(a, b) (a)+(b)*(a)
4.条件编译:在编译程序之前,按照某个条件来选择需要编译哪一段代码。
1》第一种方式:
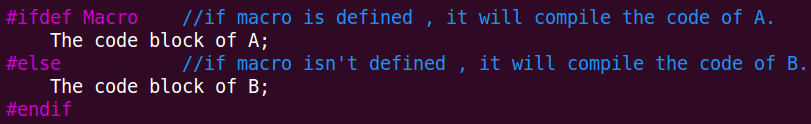
/*******************************************************************
* > File Name: ifdef.c
* > Author: fly
* > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com
* > Create Time: Sun 17 Sep 2017 02:51:43 PM CST
******************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> #define DEBUG //有如下两个函数,如果要测试这两个函数是否正确,则必须写主函数测试
void fun1(void){
printf("hello world\n");
} void fun2(void){
printf("This is a good idea !\n");
} //下面为测试代码
#ifdef DEBUG
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
fun1();
fun2(); return ;
}
#endif
ifdef.c
2》第二种方式:
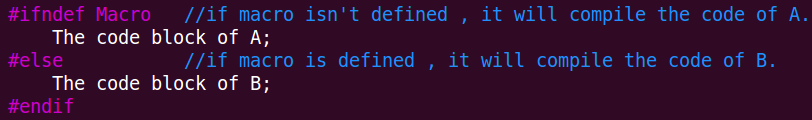
#ifdef __HEAD_H_
#define __HEAD_H_ #include <stdio.h> int x = ; #endif //该条件编译的作用是,防止头文件被多次(重复)包含。
ifndef
3》第三种方式:
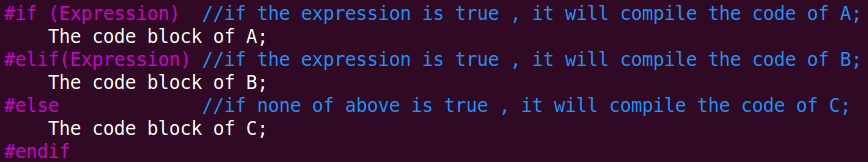
//用于注释一段代码
#if (0)
#include "head.h"
#include "head.h"
#include "head.h"
#include "head.h"
#include "head.h"
#include "head.h"
#include "head.h"
#include "head.h"
#endif
if.c
二、字节序
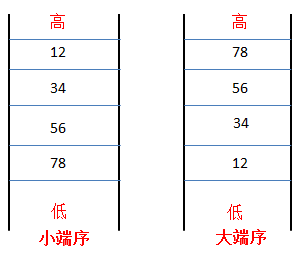
1.计算机在存储多字节数据时,数据内部各个字节的存储顺序称为字节序;
4字节:unsigned int word = 0x12345678;
2.端序
1》小端序(little-endian):最高有效位所在的字节放在最高字节位置,其他字节依次放在低字节位置,则该字节序称为高位优先。
2》大端序(big-endian):最低有效位所在的字节放在最高字节位置,其他字节依次放在低字节位置,则该字节序称为低位优先。
/*******************************************************************
* > File Name: endian.c
* > Author: fly
* > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com
* > Create Time: Sun 17 Sep 2017 04:34:11 PM CST
******************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h> #define FALSE 0
#define TRUE 1 bool is_little_endian(void){
bool ret;
unsigned int word = 0x12345678; unsigned char byte0 = *((unsigned char *)&word + );
unsigned char byte1 = *((unsigned char *)&word + );
unsigned char byte2 = *((unsigned char *)&word + );
unsigned char byte3 = *((unsigned char *)&word + ); printf("%p---->0x%hhx\n", &byte0, byte0);
printf("%p---->0x%hhx\n", &byte1, byte1);
printf("%p---->0x%hhx\n", &byte2, byte2);
printf("%p---->0x%hhx\n", &byte3, byte3); if(byte0 == 0x78){
printf("the machine is little endian !\n");
ret = TRUE;
}else if(byte0 == 0x12){
printf("the machine is big endian !\n");
ret = FALSE;
} return ret;
} int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if(is_little_endian() == TRUE){
printf("Little endian is true !\n");
} return ;
}
执行结果: 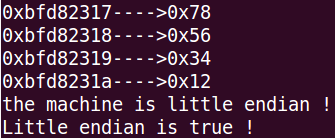
/*******************************************************************
* > File Name: endian1.c
* > Author: fly
* > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com
* > Create Time: Sun 17 Sep 2017 05:02:58 PM CST
******************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> union A{
unsigned int word;
unsigned char byte;
}; int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
union A un; un.word = 0x12345678;
if(un.byte == 0x78){
printf("the machine is little endian !\n");
}else if(un.byte == 0x12){
printf("the machine is big endian !\n");
} return ;
}
使用结构体判断大小端序
三、地址对齐
为了提高CPU从内存中存取数据的效率,在给数据分配内存空间时,会有意的将数据放在某些地址位置,这种分配空间的方式称为地址对齐。
1》自然对齐:在给数据分配空间是时,如果数据的起始地址能够被数据的长度整除,则该分配空间的方式为自然对齐。
2》数据的M值:
对于每一个数据都有M值,M值如下:
1)对于基本数据类型:
如果该数据的长度小于机器字字长,则它的M值为自身的长度;
如果该数据的长度大于或者等于机器字长,则它的M值为机器字长;
2)对于数组:
M值为元素的M值;
3)对于结构体,共用体:
M值为成员中最大的M值;
3》适当对齐:在给数据分配空间时,如果数据的起始地址能够被数据的M值整除,则该分配空间的方式为适当对齐。
4》结构体的存储:
/*******************************************************************
* > File Name: align.c
* > Author: fly
* > Mail: XXXXXXXX@icode.com
* > Create Time: Sun 17 Sep 2017 05:15:23 PM CST
******************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> struct param{
char a;
short b;
int c;
}; struct param1{
char a;
int b;
short c;
}; int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
struct param p1;
printf("sizeof(struct param) = %d\tsizeof p1 = %d\n", sizeof(struct param), sizeof p1); struct param1 p2;
printf("sizeof(struct param1) = %d\tsizeof p2 = %d\n", sizeof(struct param1), sizeof p2); return ;
}
structAlign.c
执行结果:
最新文章
- call,apply,bind的用法
- js框架设计1.1命名空间笔记
- Spark入门实战系列--8.Spark MLlib(上)--机器学习及SparkMLlib简介
- gdb调试汇编堆栈分析
- Linux阵列 RAID详解
- 禁止 IOS 系统 数字 变超链 (自动识别为电话号码)
- struts2文件下载 出现Can not find a java.io.InputStream with the name的错误
- WCF与WebService之间的异同
- c语言_帮助别人
- iOS相机权限、相册权限、定位权限判断
- 关于SQL语言的优化(Oracle)
- Qt编写文件一键命名软件
- vueThink权限配置
- ITU-T Technical Paper: QoS 的参数(非常的全,共计88个)
- CSS网页中导入特殊字体@font-face属性详解
- Liferay7 BPM门户开发之3: Activiti开发环境搭建
- python之OrderedDict类
- Boostrap本地导入js文件
- List 的一个有用的高效的操作 removeAll
- Handlebars.js 预编译(转)