cf #363 d
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
A tree is an undirected connected graph without cycles.
Let's consider a rooted undirected tree with n vertices, numbered 1 through n. There are many ways to represent such a tree. One way is to create an array with n integers p1, p2, ..., pn, where pi denotes a parent of vertex i (here, for convenience a root is considered its own parent).
 For this rooted tree the array p is [2, 3, 3, 2].
For this rooted tree the array p is [2, 3, 3, 2].
Given a sequence p1, p2, ..., pn, one is able to restore a tree:
- There must be exactly one index r that pr = r. A vertex r is a root of the tree.
- For all other n - 1 vertices i, there is an edge between vertex i and vertex pi.
A sequence p1, p2, ..., pn is called valid if the described procedure generates some (any) rooted tree. For example, for n = 3 sequences(1,2,2), (2,3,1) and (2,1,3) are not valid.
You are given a sequence a1, a2, ..., an, not necessarily valid. Your task is to change the minimum number of elements, in order to get a valid sequence. Print the minimum number of changes and an example of a valid sequence after that number of changes. If there are many valid sequences achievable in the minimum number of changes, print any of them.
The first line of the input contains an integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 200 000) — the number of vertices in the tree.
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ n).
In the first line print the minimum number of elements to change, in order to get a valid sequence.
In the second line, print any valid sequence possible to get from (a1, a2, ..., an) in the minimum number of changes. If there are many such sequences, any of them will be accepted.
4
2 3 3 4
1
2 3 4 4
5
3 2 2 5 3
0
3 2 2 5 3
8
2 3 5 4 1 6 6 7
2
2 3 7 8 1 6 6 7
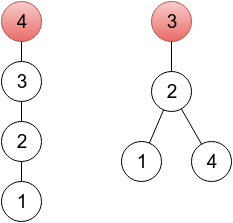
In the first sample, it's enough to change one element. In the provided output, a sequence represents a tree rooted in a vertex 4 (becausep4 = 4), which you can see on the left drawing below. One of other correct solutions would be a sequence 2 3 3 2, representing a tree rooted in vertex 3 (right drawing below). On both drawings, roots are painted red.
 破圈法
破圈法
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#define maxx 200005
using namespace std;
int root=;
int ci=;
int ans=;
int a[maxx];
int vis[maxx];
void find(int x){
vis[x]=ci;
while(!vis[a[x]]){
x=a[x];
vis[x]=ci;
}
if(vis[a[x]]==ci){
if(root==){
root=x;
}
if(a[x]!=root){
a[x]=root;
ans++;
}
}
ci++;
}
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) vis[i]=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
if(i==a[i]) root=i; }
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
if(!vis[i]){
find(i);
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
for(int i=;i<n;i++){
printf("%d ",a[i]);
}
printf("%d\n",a[n]);
return ;
}
最新文章
- 说说 js String
- Web程序的运行原理及流程(二)
- CSS3绘制六边形
- 16年青岛网络赛 1002 Cure
- Java: Difference between ArrayList and LinkedList
- 基于Ogre的DeferredShading(延迟渲染)的实现以及应用
- 数据结构(线段树):SPOJ GSS3 - Can you answer these queries III
- 多条件搜索拼接Sql语句
- Ubuntu部署Jupyter
- Comparable和Comparator的差别
- 【django之Ajax】
- Springboot 生成验证码
- 【转】mysql explain执行计划详解
- Spring + Mybatis项目实现数据库读写分离
- TableLayoutPanel 行高列宽设置
- Linux 下建立 SSH 隧道做 Socket 代理
- Apache Spark 内存管理详解
- JQuery------鼠标双击时,不选中div里面的文字
- 【Css】Layout布局(一)
- Spring框架学习(8)spring mvc上传下载