第七届蓝桥杯JavaC组国(决)赛真题
解题代码部分来自网友,如果有不对的地方,欢迎各位大佬评论
题目1、平方末尾
能够表示为某个整数的平方的数字称为“平方数”
比如,25,64
虽然无法立即说出某个数是平方数,但经常可以断定某个数不是平方数。
因为平方数的末位只可能是:[0, 1, 4, 5, 6, 9] 这6个数字中的某个。
所以,4325435332必然不是平方数。
如果给你一个2位或2位以上的数字,你能根据末位的两位来断定它不是平方数吗?
请计算一下,一个2位以上的平方数的最后两位有多少种可能性?
注意:需要提交的是一个整数,表示2位以上的平方数最后两位的不同情况数。
不要填写任何多余内容(比如,说明解释文字等)
答案:22
import java.util.HashSet;
public class Main {
public static HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<String>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(long i = 10;i <= 1000000;i++) {
String a = "" + (i * i / 10 % 10) * 10 + "" +i * i % 10;
set.add(a);
}
System.out.println(set.size());
}
}
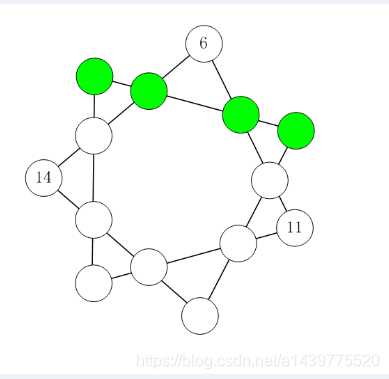
题目2、七星填数
如图【图1.png】所示。
在七角星的14个节点上填入1~14 的数字,不重复,不遗漏。
要求每条直线上的四个数字之和必须相等。
图中已经给出了3个数字。
请计算其它位置要填充的数字,答案唯一。
填好后,请提交绿色节点的4个数字(从左到右,用空格分开)
比如:12 5 4 8
当然,这不是正确的答案。
注意:只提交4个用空格分开的数字,不要填写任何多余的内容。
答案:10 3 9 8
import java.util.HashSet;
public class Main {
public static int sum = 0;
public void swap(int[] A, int i, int j) {
int temp = A[i];
A[i] = A[j];
A[j] = temp;
}
public void dfs(int[] A, int step) {
if(step == A.length) {
int[] count = new int[7];
count[0] = A[0] + A[1] + A[2] + A[3];
count[1] = A[0] + A[4] + A[6] + A[9];
count[2] = A[1] + A[4] + 6 + 14;
count[3] = A[2] + A[5] + 6 + 11;
count[4] = A[6] + A[8] + A[10] + 14;
count[5] = A[7] + A[8] + A[9] + 11;
count[6] = A[3] + A[5] + A[7] + A[10];
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
for(int i = 0;i < 7;i++)
set.add(count[i]);
if(set.size() == 1) {
for(int i = 0;i < A.length;i++)
System.out.print(A[i]+" ");
System.out.println();
}
sum++;
return;
} else {
for(int i = step;i < A.length;i++) {
swap(A, i, step);
dfs(A, step + 1);
swap(A, i, step);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main test = new Main();
int[] A = {1,2,3,4,5,7,8,9,10,12,13};
test.dfs(A, 0);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
题目3、打印数字
打印数字
小明写了一个有趣的程序,给定一串数字。
它可以输出这串数字拼出放大的自己的样子。
比如“2016”会输出为:
00000 1 6666
2 0 0 1 1 6
0 0 1 666666
0 0 1 6 6
0 0 1 6 6
2 0 0 1 6 6
00000 1111 66666
请仔细分析代码,填写划线部分缺少的内容。
public class Main
{
static void f(int n)
{
String[][] di =
{{" 00000 ",
"0 0",
"0 0",
"0 0",
"0 0",
"0 0",
" 00000 "},
{" 1 ",
" 1 1 ",
" 1 ",
" 1 ",
" 1 ",
" 1 ",
" 1111"},
{" 22222 ",
"2 2",
" 2",
" 2 ",
" 2 ",
" 2 2",
"2222222"},
{" 33333 ",
"3 3",
" 3",
" 3333 ",
" 3",
"3 3",
" 33333 "},
{" 44 ",
" 4 4 ",
" 4 4 ",
"4 4 ",
"4 4 ",
"4444444",
" 4 "},
{" 55555 ",
" 5 ",
"555555 ",
" 5",
" 5",
"5 5",
" 55555 "},
{" 6666 ",
"6 ",
"666666 ",
"6 6",
"6 6",
"6 6",
" 66666 "},
{"7777777",
"7 7 ",
" 7 ",
" 7 ",
" 7 ",
" 7 ",
" 7 "},
{" 88888 ",
"8 8",
"8 8",
" 88888 ",
"8 8",
"8 8",
" 88888 "},
{" 99999 ",
"9 9",
"9 9",
" 999999",
" 9",
"9 9",
" 99999 "}};
char[] cc = (""+n).toCharArray();
for(int i=0; i<di[0].length; i++){
for(int j=0; j<cc.length; j++){
System.out.print( ____________________ + " "); //填空位置
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
f(2016);
}
}
注意:只提交划线部分缺少的代码,不要添加任何题面已有代码或符号。
也不要提交任何说明解释文字等。
答案:di[cc[j]-'0'][i]
题目4、赢球票
某机构举办球票大奖赛。获奖选手有机会赢得若干张球票。
主持人拿出 N 张卡片(上面写着 1~N 的数字),打乱顺序,排成一个圆圈。
你可以从任意一张卡片开始顺时针数数: 1,2,3…
如果数到的数字刚好和卡片上的数字相同,则把该卡片收入囊中,从下一个卡片重新数数。
直到再无法收获任何卡片,游戏结束。囊中卡片数字的和就是赢得球票的张数。
比如:
卡片排列是:1 2 3
我们从1号卡开始数,就把1号卡拿走。再从2号卡开始,但数的数字无法与卡片对上,
很快数字越来越大,不可能再拿走卡片了。因此这次我们只赢得了1张球票。
还不算太坏!如果我们开始就傻傻地从2或3号卡片数起,那就一张卡片都拿不到了。
如果运气好,卡片排列是 2 1 3
那我们可以顺利拿到所有的卡片!
本题的目标就是:已知顺时针卡片序列。
随便你从哪里开始数,求最多能赢多少张球票(就是收入囊中的卡片数字之和)
输入数据:
第一行一个整数N(N<100),表示卡片数目
第二行 N 个整数,表示顺时针排列的卡片
输出数据:
一行,一个整数,表示最好情况下能赢得多少张球票
比如:
用户输入:
3
1 2 3
程序应该输出:
1
比如:
用户输入:
3
2 1 3
程序应该输出:
6
资源约定:
峰值内存消耗 < 256M
CPU消耗 < 1000ms
请严格按要求输出,不要画蛇添足地打印类似:“请您输入…” 的多余内容。
所有代码放在同一个源文件中,调试通过后,拷贝提交该源码。
注意:不要使用package语句。不要使用jdk1.7及以上版本的特性。
注意:主类的名字必须是:Main,否则按无效代码处理。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static int n;
public static int max = 0;
public static int[] value;
public void getResult() {
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) {
int[] temp = new int[n];
for(int k = 0;k < n;k++)
temp[k] = value[k];
int sum = 0;
int count = 1;
int start = i;
while(true) {
boolean judge = true;
for(int k = 0;k < n;k++)
if(temp[k] >= count) {
judge = false;
break;
}
if(judge)
break;
int j = start % n;
if(temp[j] == count) {
sum = sum + count;
temp[j] = -1;
count = 1;
} else if(temp[j] != -1)
count++;
start++;
}
max = Math.max(max, sum);
}
System.out.println(max);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main test = new Main();
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
n = in.nextInt();
value = new int[n];
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
value[i] = in.nextInt();
test.getResult();
}
}
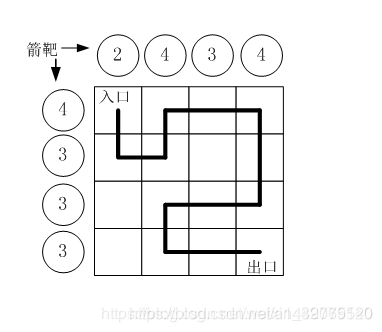
题目5、路径之谜
题目描述
小明冒充X星球的骑士,进入了一个奇怪的城堡。
城堡里边什么都没有,只有方形石头铺成的地面。
假设城堡地面是 n x n 个方格。【如图1.png】所示。
按习俗,骑士要从西北角走到东南角。
可以横向或纵向移动,但不能斜着走,也不能跳跃。
每走到一个新方格,就要向正北方和正西方各射一箭。
(城堡的西墙和北墙内各有 n 个靶子)
同一个方格只允许经过一次。但不必做完所有的方格。
如果只给出靶子上箭的数目,你能推断出骑士的行走路线吗?
有时是可以的,比如图1.png中的例子。
本题的要求就是已知箭靶数字,求骑士的行走路径(测试数据保证路径唯一)
输入:
第一行一个整数N(0<N<20),表示地面有 N x N 个方格
第二行N个整数,空格分开,表示北边的箭靶上的数字(自西向东)
第三行N个整数,空格分开,表示西边的箭靶上的数字(自北向南)
输出:
一行若干个整数,表示骑士路径。
为了方便表示,我们约定每个小格子用一个数字代表,从西北角开始编号: 0,1,2,3…
比如,图1.png中的方块编号为:
0 1 2 3
4 5 6 7
8 9 10 11
12 13 14 15
示例:
用户输入:
4
2 4 3 4
4 3 3 3
程序应该输出:
0 4 5 1 2 3 7 11 10 9 13 14 15
资源约定:
峰值内存消耗 < 256M
CPU消耗 < 1000ms
请严格按要求输出,不要画蛇添足地打印类似:“请您输入…” 的多余内容。
所有代码放在同一个源文件中,调试通过后,拷贝提交该源码。
注意:不要使用package语句。不要使用jdk1.7及以上版本的特性。
注意:主类的名字必须是:Main,否则按无效代码处理。
// 常规的深搜+剪枝
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
// 下一步的方向
static int[][] dir = { { 0, 1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0, -1 }, { -1, 0 } };
// 结果
static ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
static int N;
// 记录北边的箭靶
static int[] north;
// 记录西边的箭靶
static int[] west;
// 记录走过的方格
static byte[] visit;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
N = sc.nextInt();
north = new int[N];
west = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
north[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
west[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
// visit[i]为0,表示未被走过;visit[i]为1,表示已经走过。
visit = new byte[N * N];
dfs(0, 0);
sc.close();
}
static void dfs(int x, int y) {
int index = x * N + y;
visit[index] = 1;
north[y]--;
west[x]--;
list.add(index);
if (index == N * N - 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (north[i] > 0 || west[i] > 0)
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(list.get(i) + " ");
}
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < dir.length; i++) {
int nextx = x + dir[i][0];
int nexty = y + dir[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= N || nexty < 0 || nexty >= N)
continue;
if (north[nexty] <= 0 || west[nextx] <= 0)
continue;
dfs(nextx, nexty);
list.remove(list.size() - 1);
north[nexty]++;
west[nextx]++;
visit[nextx * N + y] = 0;
}
}
}
题目6、碱基
题目描述
生物学家正在对n个物种进行研究。
其中第i个物种的DNA序列为s[i],其中的第j个碱基为s[i][j],碱基一定是A、T、G、C之一。
生物学家想找到这些生物中一部分生物的一些共性,他们现在关注那些至少在m个生物中出现的长度为k的连续碱基序列。准确的说,科学家关心的序列用2m元组(i1,p1,i2,p2…im,pm)表示,
满足:
1<=i1<i2<…<im<=n;
且对于所有q(0<=q<k), s[i1][p1+q]=s[i2][p2+q]=…=s[im][pm+q]。
现在给定所有生物的DNA序列,请告诉科学家有多少的2m元组是需要关注的。如果两个2m元组有任何一个位置不同,则认为是不同的元组。
【输入格式】
输入的第一行包含三个整数n、m、k,两个整数之间用一个空格分隔,意义如题目所述。
接下来n行,每行一个字符串表示一种生物的DNA序列。
DNA序列从1至n编号,每个序列中的碱基从1开始依次编号,不同的生物的DNA序列长度可能不同。
【输出格式】
输出一个整数,表示关注的元组个数。
答案可能很大,你需要输出答案除以1000000007的余数。
【样例输入】
3 2 2
ATC
TCG
ACG
【样例输出】
2
再例如:
【样例输入】
4 3 3
AAA
AAAA
AAA
AAA
【样例输出】
7
【数据规模与约定】
对于20%的数据,k<=5,所有字符串总长L满足L <=100
对于30%的数据,L<=10000
对于60%的数据,L<=30000
对于100%的数据,n<=5,m<=5,1<=k<=L<=100000
保证所有DNA序列不为空且只会包含’A’ ’G’ ’C’ ’T’四种字母
资源约定:
峰值内存消耗 < 256M
CPU消耗 < 1000ms
请严格按要求输出,不要画蛇添足地打印类似:“请您输入…” 的多余内容。
所有代码放在同一个源文件中,调试通过后,拷贝提交该源码。
注意:不要使用package语句。不要使用jdk1.7及以上版本的特性。
注意:主类的名字必须是:Main,否则按无效代码处理。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static int n, m, k;
public static String[] S;
public static String[] num;
public static int[] start;
public static long MOD = 1000000007;
public static long count = 0;
public static HashSet<String> result = new HashSet<String>();
public void dfs(int step, int sum) {
if(step == n || sum >= m) {
if(sum >= m) {
ArrayList<String> set = new ArrayList<String>();
StringBuffer[] s = new StringBuffer[sum];
for(int i = 0;i < sum;i++)
s[i] = new StringBuffer("");
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) {
if(!num[i].equals("-")) {
if(!set.contains(num[i])) {
set.add(num[i]);
s[set.size() - 1].append(i);
s[set.size() - 1].append(start[i]);
} else {
int j = set.indexOf(num[i]);
s[j].append(i);
s[j].append(start[i]);
}
}
}
if(set.size() == sum - m + 1) {
for(int i = 0;i < sum;i++) {
if(s[i].toString().length() == k * 2) {
if(!result.contains(s[i].toString()))
count = (count + 1) % MOD;
result.add(s[i].toString());
break;
}
}
}
}
return;
} else {
for(int i = 0;i < S[step].length();i++) {
if(i + k <= S[step].length()) {
num[step] = S[step].substring(i, i + k);
start[step] = i;
dfs(step + 1, sum + 1);
num[step] = "-";
}
dfs(step + 1, sum);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main test = new Main();
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
n = in.nextInt();
m = in.nextInt();
k = in.nextInt();
S = new String[n];
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
S[i] = in.next();
num = new String[n + 1];
start = new int[n + 1];
for(int i = 0;i <= n;i++)
num[i] = "-";
test.dfs(0, 0);
System.out.println(count);
}
}
最新文章
- iOS真机运行 Xcode报错(libpng error: CgBI: unhandled critical chunk)问题已解决;
- JavaScript的学习2
- .NET相关操作其他文件的小程序(系列文章)
- codeforces A. IQ Test 解题报告
- Bootstrap列表
- 关于C#中派生类调用基类构造函数的理解
- 【WCF--初入江湖】目录
- ENVI/IDL与ArcGIS集成开发的三种途径
- Qt经典出错信息之”Basic XLib functionality test failed!”
- cypress的EZ-USB对于USB的介绍
- 动态改变ComboBox下拉框的宽度
- uva133 The Dole Queue ( 约瑟夫环的模拟)
- Android官方命令深入分析之Hierarchy Viewer
- 【重构】 代码的坏味道总结 Bad Smell (一) (重复代码 | 过长函数 | 过大的类 | 过长参数列 | 发散式变化 | 霰弹式修改)
- 巩固java(二)----JVM堆内存结构及垃圾回收机制
- 在pycharm中查看内建函数源码
- python之路--BOM和DOM
- emwin之错误使用控件函数导致死机现象
- python 实现有序字典
- 2019.02.09 bzoj4710: [Jsoi2011]分特产(容斥原理)