subset子集全排序问题
2024-10-19 14:30:24
思路一
可以用递推的思想,观察S=[], S =[1], S = [1, 2] 时解的变化。
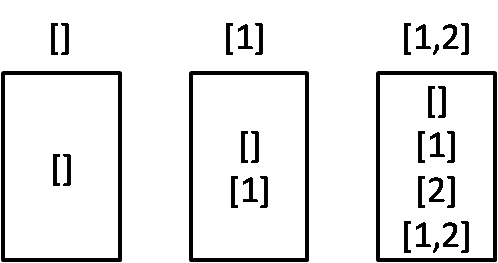
可以发现S=[1, 2] 的解就是 把S = [1]的所有解末尾添上2,然后再并上S = [1]里面的原有解。因此可以定义vector<vector<int> > 作为返回结果res, 开始时res里什么都没有,第一步放入一个空的vecotr<int>,然后这样迭代n次,每次更新res 内容,最后返回res。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std; void subset1(int *a, int n)
{
vector<vector<int>> sub(1);// (pow(2, n) + 1);
//这种初始化方式是直接插入了1个为空的元素。此时sub.size()是1。
//扩展容量用resize,提高性能
sub.reserve(pow(2, n) + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
int len = sub.size();
for (int j = 0; j < len; ++j)
{
auto temp = sub[j];
temp.push_back(a[i]);
sub.push_back(temp);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < sub.size(); ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < sub[i].size(); ++j)
{
cout << sub[i][j];
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
int a[] = { 1,2,3,4 };
subset1(a, 4);
}
结果 第一个空行代表空集。
1
2
12
3
13
23
123
4
14
24
124
34
134
234
1234
请按任意键继续. . .
思路二
所谓子集,就是包含原集合中的一些元素,不包含另一些元素。如果单独看某一个元素,它都有两种选择:"被包含在子集中"和"不被包含在子集中",对于元素个数为n、且不含重复元素的S,子集总数是2n。因此我们可以遍历S的所有元素,然后用递归考虑每一个元素包含和不包含的两种情况。
代码,这种思路需要用到递归
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std; static vector<vector<int>> sub2;
void subset2(int *a, int n, int t, vector<int> temp)
{
if (t == n)
{
sub2.push_back(temp);
return;
}
subset2(a, n, t + 1, temp);
temp.push_back(a[t]);
subset2(a, n, t + 1, temp);
} int main()
{
int a[] = { 1,2,3,4 };
vector<int> temp; subset2(a, 4, 0, temp);
for (int i = 0; i < sub2.size(); ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < sub2[i].size(); ++j)
cout << sub2[i][j];
cout << endl;
}
}
结果 第一个空行代表空集。
4
3
34
2
24
23
234
1
14
13
134
12
124
123
1234
请按任意键继续. . .
思路三
用一个unsigned int 的每个bit位来表示子集的每一个元素的两种情况。前提 原集合中不含重复字符。(含有的话,会出现重复)
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std; static vector<vector<int>> sub2;
void subset3(int *a, int n)
{
unsigned int num = 1 << n;
cout << num << endl;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < num; ++i)
{
unsigned int q = i;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j,q>>=1)
{
if (q & unsigned int ( 1))
{
cout <<a[j];
}
}
cout << endl;
}
} int main()
{
int a[] = { 1,2,3,4 };
subset3(a, 4);
}
结果 第二个空行代表空集。
16 1
2
12
3
13
23
123
4
14
24
124
34
134
234
1234
请按任意键继续. . .
vector<int> temp2 = temp;
subset2(a, n, sum, t, f + 1, temp);//当前的不包含
temp.push_back(a[f]);
subset2(a, n, sum, t +a[f], f,temp);//可重复的重点
temp2.push_back(a[f + 1]);
subset2(a, n, sum, t + a[f+1],f+1, temp2);//当前的包含
元素可重复,求子集的元素和为一个常数
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
using namespace std; static set<vector<int>> sub2;//去重
//a是数组,n数组个数,sum一开始就是0,t是要求的和,f一开始是0
void subset2(int *a, int n,int sum, int t, int f,vector<int> temp)
{
if (t > sum)
return;
if (t == sum)
{
sub2.insert(temp);
return;
}
if (f == n)return;
vector<int> temp2 = temp;
subset2(a, n, sum, t, f + 1, temp);
temp.push_back(a[f]);
subset2(a, n, sum, t +a[f], f,temp);
temp2.push_back(a[f + 1]);
subset2(a, n, sum, t + a[f+1],f+1, temp2); } int main()
{
int a[] = { 4,1,3,2};
vector<int> temp;
subset2(a, 4,7,0,0, temp);
for (auto p = sub2.begin(); p != sub2.end(); ++p)
{
for (int j = 0; j < (*p).size(); ++j)
cout << (*p)[j];
cout << endl;
}
}
结果:和为7
1111111
111112
11113
11122
1132
1222
133
322
4111
412
43
请按任意键继续. . .
最新文章
- [c#基础]关于const和readonly常见的笔试题剖析
- 【日记】搭建一个node本地服务器
- [转] LBYL与EAFP两种防御性编程风格
- appium入门
- 【LeetCode】217 & 219 - Contains Duplicate & Contains Duplicate II
- OpenJudge 2811 熄灯问题 / Poj 1222 EXTENDED LIGHTS OUT
- Sql中的datetime类型的空值和c#中的DateTime的空值的转换方法
- 十进制和n进制的转换(10进制转换为36进制)
- USB系列之二:读取USB设备的描述符
- maple 教程
- Java多机部署下的定时任务处理方案(mysql)
- Amazing ASP.NET Core 2.0
- 关于模拟I2C的一些问题???
- hibernate06--参数的绑定
- git command line 提交代码
- ansible命令及模块
- k8s mongodb 集群配置
- JS-json-1
- SIGTERM等信号含义【转】
- Nginx 关于 location 的匹配规则详解