Netty源码分析 (二)----- ServerBootstrap
BootStrap在netty的应用程序中负责引导服务器和客户端。netty包含了两种不同类型的引导:
1. 使用服务器的ServerBootStrap,用于接受客户端的连接以及为已接受的连接创建子通道。
2. 用于客户端的BootStrap,不接受新的连接,并且是在父通道类完成一些操作。
一般服务端的代码如下所示:
SimpleServer.java
/**
* Created by chenhao on 2019/9/4.
*/
public final class SimpleServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new SimpleServerHandler())
.childHandler(new SimpleServerInitializer())
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true); ChannelFuture f = b.bind(8888).sync(); f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
SimpleServerHandler.java
private static class SimpleServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("channelActive");
}
@Override
public void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("channelRegistered");
}
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("handlerAdded");
}
}
SimpleServerInitializer.java
public class SimpleServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>{
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("framer", new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(8192, Delimiters.lineDelimiter()));
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
pipeline.addLast("handler", new SimpleChatServerHandler());
System.out.println("SimpleChatClient:" + ch.remoteAddress()+"连接上");
}
}
在上篇博文(Netty源码分析 (一)----- NioEventLoopGroup)中 剖析了如下的两行代码内部的构造函数中干了些什么。
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
具体可以见上篇博文,对于如上的两行代码得到的结论是:
1、 如果不指定线程数,则线程数为:CPU的核数*2
2、根据线程个数是否为2的幂次方,采用不同策略初始化chooser
3、产生nThreads个NioEventLoop对象保存在children数组中。
可以理解NioEventLoop就是一个线程,线程NioEventLoop中里面有如下几个属性:
1、NioEventLoopGroup (在父类SingleThreadEventExecutor中)
2、selector
3、provider
4、thread (在父类SingleThreadEventExecutor中)
更通俗点就是: NioEventLoopGroup就是一个线程池,NioEventLoop就是一个线程。NioEventLoopGroup线程池中有N个NioEventLoop线程。
ServerBootstrap类分析
本篇博文将分析如下几行代码里面做了些什么。
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new SimpleServerHandler())
.childHandler(new SimpleServerInitializer())
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
ServerBootstrap类的继承结构如下:
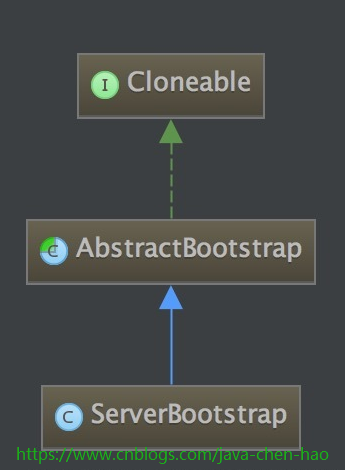
该类的参数,有必要列出:
private final Map<ChannelOption<?>, Object> childOptions = new LinkedHashMap<ChannelOption<?>, Object>();
private final Map<AttributeKey<?>, Object> childAttrs = new LinkedHashMap<AttributeKey<?>, Object>();
private volatile EventLoopGroup childGroup;
private volatile ChannelHandler childHandler;
其父类AbstractBootstrap的参数
private volatile EventLoopGroup group;
private volatile ChannelFactory<? extends C> channelFactory;
private volatile SocketAddress localAddress;
private final Map<ChannelOption<?>, Object> options = new LinkedHashMap<ChannelOption<?>, Object>();
private final Map<AttributeKey<?>, Object> attrs = new LinkedHashMap<AttributeKey<?>, Object>();
private volatile ChannelHandler handler;
下面主要看下这个链式设置相关的参数。
group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
public ServerBootstrap group(EventLoopGroup parentGroup, EventLoopGroup childGroup) {
super.group(parentGroup);
if (childGroup == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("childGroup");
}
if (this.childGroup != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("childGroup set already");
}
this.childGroup = childGroup;
return this;
}
即将workerGroup保存在 ServerBootstrap对象的childGroup属性上。 bossGroup保存在ServerBootstrap对象的group属性上
channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
public B channel(Class<? extends C> channelClass) {
if (channelClass == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("channelClass");
}
return channelFactory(new BootstrapChannelFactory<C>(channelClass));
}
public B channelFactory(ChannelFactory<? extends C> channelFactory) {
if (channelFactory == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("channelFactory");
}
if (this.channelFactory != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("channelFactory set already");
}
this.channelFactory = channelFactory;
return (B) this;
}
函数功能:设置父类属性channelFactory 为: BootstrapChannelFactory类的对象。其中这里BootstrapChannelFactory对象中包括一个clazz属性为:NioServerSocketChannel.class,从如下该类的构造函数中可以明显的得到这一点。
private static final class BootstrapChannelFactory<T extends Channel> implements ChannelFactory<T> {
private final Class<? extends T> clazz;
BootstrapChannelFactory(Class<? extends T> clazz) {
this.clazz = clazz;
}
@Override
public T newChannel() {
try {
return clazz.newInstance();
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new ChannelException("Unable to create Channel from class " + clazz, t);
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return StringUtil.simpleClassName(clazz) + ".class";
}
}
并且BootstrapChannelFactory中提供 newChannel()方法,我们可以看到 clazz.newInstance(),主要是通过反射来实例化NioServerSocketChannel.class
handler(new SimpleServerHandler())
public B handler(ChannelHandler handler) {
if (handler == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("handler");
}
this.handler = handler;
return (B) this;
}
注意:这里的handler函数的入参类是我们自己提供的。如下,后面的博文中将会分析这个handler将会在哪里以及何时被调用,这里只需要记住这一点即可
private static class SimpleServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("channelActive");
}
@Override
public void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("channelRegistered");
}
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("handlerAdded");
}
}
childHandler(new SimpleServerInitializer())
public ServerBootstrap childHandler(ChannelHandler childHandler) {
if (childHandler == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("childHandler");
}
this.childHandler = childHandler;
return this;
}
由最后一句可知,其实就是讲传入的childHandler赋值给ServerBootstrap的childHandler属性。
该函数的主要作用是设置channelHandler来处理客户端的请求的channel的IO。 这里我们一般都用ChannelInitializer这个类的实例或则继承自这个类的实例
这里我是通过新建类SimpleChatServerInitializer继承自ChannelInitializer。具体的代码如下:
public class SimpleChatServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>{
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("framer", new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(8192, Delimiters.lineDelimiter()));
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
pipeline.addLast("handler", new SimpleChatServerHandler());
System.out.println("SimpleChatClient:" + ch.remoteAddress()+"连接上");
}
}
我们再看看ChannelInitializer这个类的继承图可知ChannelInitializer其实就是继承自ChannelHandler的
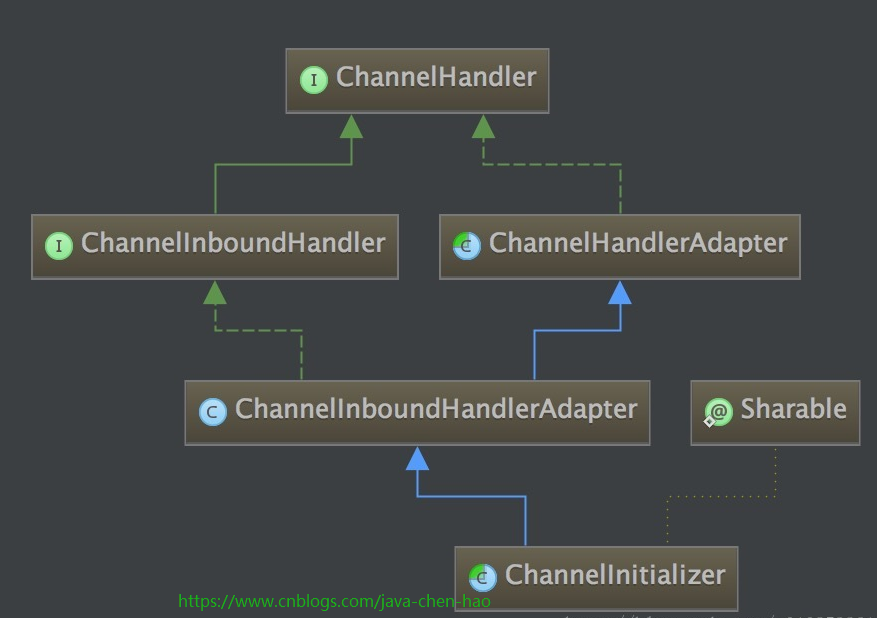
可知,这个类其实就是往pipeline中添加了很多的channelHandler。
配置ServerBootstrap的option
这里调用的是父类的AbstractBootstrap的option()方法,源码如下:
public <T> B option(ChannelOption<T> option, T value) {
if (option == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("option");
}
if (value == null) {
synchronized (options) {
options.remove(option);
}
} else {
synchronized (options) {
options.put(option, value);
}
}
return (B) this;
}
其中最重要的一行代码就是:
options.put(option, value);
这里用到了options这个参数,在AbstractBootstrap的定义如下:
private final Map<ChannelOption<?>, Object> options = new LinkedHashMap<ChannelOption<?>, Object>();
可知是私有变量,而且是一个Map集合。这个变量主要是设置TCP连接中的一些可选项,而且这些属性是作用于每一个连接到服务器被创建的channel。
配置ServerBootstrap的childOption
这里调用的是父类的ServerBootstrap的childOption()方法,源码如下:
public <T> ServerBootstrap childOption(ChannelOption<T> childOption, T value) {
if (childOption == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("childOption");
}
if (value == null) {
synchronized (childOptions) {
childOptions.remove(childOption);
}
} else {
synchronized (childOptions) {
childOptions.put(childOption, value);
}
}
return this;
}
这个函数功能与option()函数几乎一样,唯一的区别是该属性设定只作用于被acceptor(也就是boss EventLoopGroup)接收之后的channel。
总结
比较简单哈,主要是将我们提供的参数设置到其相应的对象属性中去了。 因为后面会用到如下的几个属性,因此最好知道下,这些属性是何时以及在那里赋值的。
1、group:workerGroup保存在 ServerBootstrap对象的childGroup属性上。 bossGroup保存在ServerBootstrap对象的group属性上
2、channelFactory:BootstrapChannelFactory类的对象(clazz属性为:NioServerSocketChannel.class)
3、handler:SimpleServerHandler
4、childHandler
5、option
6、childOption
最新文章
- BZOJ 3110 [Zjoi2013]K大数查询 ——整体二分
- ngui中 代码调用按钮事件(后来改成了按钮绑定键盘..)
- 字节对齐导致的iOS EXC_ARM_DA_ALIGN崩溃
- [iOS翻译]Cocoa编码规范
- 【TYVJ】1338 QQ农场(最大流+最大权闭合图)
- Python的交互式界面 编写 .
- jruby中的异常
- setTimeout setInterval 区别 javascript线程解释
- html template
- 转自:Tsihang 三层网络设备对于IP报文的分片和重组处理原理
- hdu1698(线段树)
- UVA - 11090 - Going in Cycle!!(二分+差分约束系统)
- 高斯消元(Gauss消元)
- 7、TypeScript数据类型
- Windows 查看端口占用情况
- Incorrect username or password ( access token )解决
- JavaSE学习总结(十八)—— 多线程
- Ajax - 汇总
- 原生js实现ajax用于简单的签到或登录
- eclipse中整合ejb和web工程