十二、java_网络编程
2024-08-26 13:21:22
目录:
一、网络基础
什么是计算机网络:
把分布在不同地理区域的计算机与专门的外部设备用通信线路互连成一个规模大、功能强的网络系统,从而使众多的计算机可以方便地相互传递信息,共享硬件、软件、数据信息等资源
计算机网络的主要功能:
- 资源共享
- 信息传输与集中处理
- 均衡负荷与分布处理
- 综合信息服务(www/综合业务数字网络ISDN)
什么是网络通信协议:
计算机网络中实现通信必需有一些约定即通信协议,对速率、传输代码、代码结构、传输步骤控制、出错控制等指定标准
网络通信接口:
为了使两个节点之间能够进行对话,必需在他们之间建立通信工具(即接口),使彼此之间能进行信息交换。接口包括两部分:
- 硬件装置:实现节点之间的信息传送
- 软件装置:规定双方进行通信的约定协议
通信协议分层的思想:
由于节点之间的联系很复杂,在指定协议时,把复杂成分分解城一些简单的成分,再将他们复合起来。最常用的复合方式是层次的方式,即同层间可以通信、上一层可以调用下一层,再而与下一层不发生关系。各层互不影响,利于系统的开发和扩展
通信协议的分层规定:
把用户应用程序作为最高层,把物理通信路线作为最底层,将其间的协议处理分为若干层,规定每层处理的任务,也规定每层的接口标准

分层参考模型:
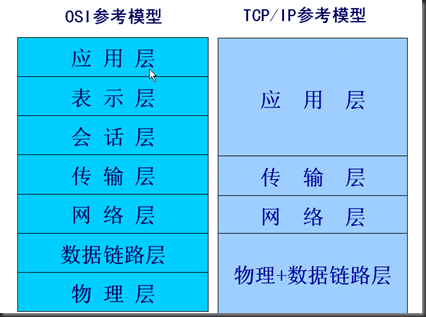
二、TCP/IP协议
IP协议
IP(Internet Protlcol)协议是网际层的主要协议,支持网间互联的数据通信。他提供的主要功能有:
- 无链接数据报传送
- 数据报路由选择和差错控制
TCP协议和UDP协议:
- TCP(transmission control protolcol)是专门用于在不可靠的因特网上提供可靠的、端到端的字节流通信的协议。他是一种面向链接的协议。TCP链接是字节流而非报文流(首先建立虚拟通道,然后发一个包后再收一个包,同时一定要收了一个包后才能收另外一个包)可靠,但是执行效率慢
- UDP(user data protocol)向应用程序提供了一种发送封装的原始IP数据报的方法、并且发送时无需简历链接。是一种不可靠的链接(就像发电报一样,不管对方是否收到了,只管发了就行)不可靠但是执行效率快
- 一般登录都是TCP,游戏中的战斗(比如cs等)都是UDP
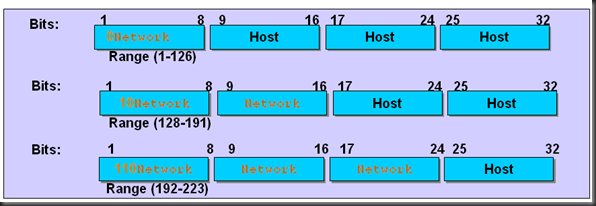
三、IP地址
提供了独一无二的IP地址
四、Socket通信
- 两个java应用程序可通过一个双向的网络通信链接实现数据交换,这个双向链路的一端成为一个socket
- socket通常用来实现client-server链接
- java.net包中定义的两个类socket和ServerSocket,分别用来实现双向链接的client和server端
- 建立链接时所需要的寻址信息为远程计算机的IP地址和端口号(port number),其中端口号又分为TCP端口和UDP端口
TCP的编程:
Socket通信模型:
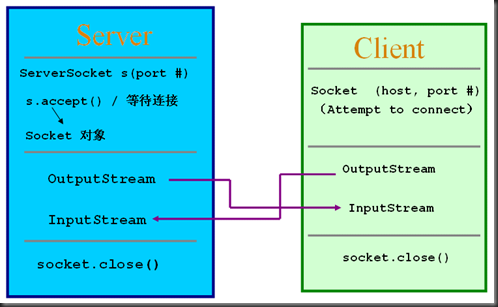
看一个例子:
public class TCPServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//new一个serverSocket占用8888端口
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(8888);
while(true) {
Socket s = ss.accept();//接收client申请链接的时候accept一下,使用wile循环可以一直接受
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(s.getInputStream());//接受client的对话
System.out.println(dis.readUTF());//打印client发过来的对话
dis.close();
s.close();
}
}
}
public class TCPClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException, IOException {
//new一个请求本机8888端口的链接
Socket s = new Socket("127.0.0.1",8888);
//开始跟server对话
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();//IO
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);//套接
dos.writeUTF("hello server !");
dos.flush();
dos.close();
s.close();
}
}
启动的时候要注意首先启动server,然后启动client。
如上的例子属于阻塞式(同步)的交互方式
再看一个例子:
public class TestServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//new一个server占用8888端口
ServerSocket s = new ServerSocket(8888);
while(true) {
Socket s1 = s.accept();
OutputStream os = s1.getOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
//getInetAddress()拿到client的IP地址。getPort()拿到client的端口
dos.writeUTF("Hello , "+s1.getInetAddress() + " port# " +s1.getPort()+" bye-bye!");
dos.close();
s1.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("程序运行出错" + e);
}
}
}
public class TestClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//new一个socket链接到8888端口
Socket s1 = new Socket("127.0.0.1",8888);
InputStream is = s1.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);
System.out.println(dis.readUTF());
dis.close();
s1.close();
} catch(ConnectException connExc) {
connExc.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("服务器连接失败!");
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
再看一个例子:
public class TestSocketServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream in = null;
OutputStream out = null;
try {
//new 一个新端口占用8888
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(8888);
//允许一个客户端链接
Socket socket = ss.accept();
//输入输出管道包装好,先读后写
in = socket.getInputStream();
out = socket.getOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(out);
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(in);
//打印
String s = null;
if ((s=dis.readUTF()) != null) {
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println("from: "+socket.getInetAddress());
System.out.println("Port: "+socket.getPort());
}
dos.writeUTF("hi, hello");
dis.close();
dos.close();
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class TestSocketClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream is = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost",8888);
//输入输出管道包装好,先写后读
is = socket.getInputStream();
os = socket.getOutputStream();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
dos.writeUTF("hey");
String s = null;
if ((s=dis.readUTF()) != null) {
System.out.println(s);
}
dos.close();
dos.close();
socket.close();
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
熟悉上面两个例子之后再来看个例子:这是一个阻塞式的server和client之间相互对话的小程序,服务器说一句话后等待客户端说一句话,客户端说一句话后等待服务器说一句话
public class TalkServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ServerSocket server = null;
try {
server = new ServerSocket(8888);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("can not listen to: " + e);
}
Socket socket = null;
try {
socket = server.accept();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Error:"+ e);
}
String line;
BufferedReader is = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
PrintWriter os = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream());
BufferedReader sin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("Client" + is.readLine());
line = sin.readLine();
while(!line.equals("bye")) {
os.println(line);
os.flush();
System.out.println("Server: "+line);
System.out.println("Client: "+is.readLine());
line = sin.readLine();
}
is.close();
os.close();
socket.close();
server.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Error: "+e);
}
}
}
public class TalkClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1",8888);
BufferedReader sin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter os = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream());
BufferedReader is = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
String readline;
readline = sin.readLine();
while(!readline.equals("bye")) {
os.println(readline);
os.flush();
System.out.println("Client: "+readline);
System.out.println("Server: " +is.readLine());
readline = sin.readLine();
}
os.close();
is.close();
socket.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Error: "+ e);
}
}
}
UDP的编程:
看一个例子:
public class TestUDPServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//new一个数据包来接受对方UDP发过来的数据,接过来的数据存在buf[]中
byte buf[] = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length);
//监听5678端口
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(5678);
while (true) {
ds.receive(dp);//接收数据
/*接收并打印UDPClient传过来的long类型的数据
ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(buf);
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(bais);
System.out.print(dis.readLong());
*/
System.out.println(new String(buf,0,dp.getLength()));//打印
}
}
}
public class TestUDPClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
/*把一个long类型的数值解析为一个字节类型的数组
long n = 10000L;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(baos);
dos.writeLong(n);
byte[] buf1 = baos.toByteArray();
*/
//把一个字符串"hello"解析为一个字节类型的数组
byte[] buf = (new String("Hello")).getBytes();
//把字节数组放到一个包袱里才能发出去,注:InetSocketAddress就是ip地址
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length, new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 5678));
//客户端本身占据的是9999端口向5678这个端口发送数据
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(9999);
ds.send(dp);//发送数据
ds.close();
}
}
最新文章
- 自定义UserProvider,更改验证方法
- Android获取手机制作商,系统版本等
- 【转载】Spring中的applicationContext.xml与SpringMVC的xxx-servlet.xml的区别
- Linux系统Load average负载详细解释
- SQLserver 数据库
- [置顶] Ajax程序:处理异步调用中的异常(使用Asp.Net Ajax内建的异常处理方法)
- Unable to resolve target 'android-XX'解决办法
- 201521123091 《Java程序设计》第11周学习总结
- (原)怎样解决python dataframe loc,iloc循环处理速度很慢的问题
- requests 获取token
- SOCKET.IO 的用法 系统API,
- 1259 整数划分 V2
- python自动化开发-9 进程 线程
- window有哪些属性?
- Mybatis中的jdbcType的作用
- Hibernate利用纯sql
- PHP简单利用 token 防止表单重复提交
- LayoutInflater的动态增加控件
- sql语句的group by 与 inner join
- 三年同行,质造未来,腾讯WeTest五大服务免费体验