Codeforces Round #370 (Div. 2) A B C 水 模拟 贪心
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
There are n integers b1, b2, ..., bn written in a row. For all i from 1 to n, values ai are defined by the crows performing the following procedure:
- The crow sets ai initially 0.
- The crow then adds bi to ai, subtracts bi + 1, adds the bi + 2 number, and so on until the n'th number. Thus,ai = bi - bi + 1 + bi + 2 - bi + 3....
Memory gives you the values a1, a2, ..., an, and he now wants you to find the initial numbers b1, b2, ..., bn written in the row? Can you do it?
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the number of integers written in the row.
The next line contains n, the i'th of which is ai ( - 109 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — the value of the i'th number.
Print n integers corresponding to the sequence b1, b2, ..., bn. It's guaranteed that the answer is unique and fits in 32-bit integer type.
5
6 -4 8 -2 3
2 4 6 1 3
5
3 -2 -1 5 6
1 -3 4 11 6
In the first sample test, the crows report the numbers 6, - 4, 8, - 2, and 3 when he starts at indices 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 respectively. It is easy to check that the sequence 2 4 6 1 3 satisfies the reports. For example, 6 = 2 - 4 + 6 - 1 + 3, and - 4 = 4 - 6 + 1 - 3.
In the second sample test, the sequence 1, - 3, 4, 11, 6 satisfies the reports. For example, 5 = 11 - 6 and 6 = 6.
题意:a,b序列满足ai = bi - b(i + 1) + b(i + 2) - b(i + 3)....
给你a序列 输出b序列
题解:观察样咧很容易得出b[i]=a[i]+a[i+1];
/******************************
code by drizzle
blog: www.cnblogs.com/hsd-/
^ ^ ^ ^
O O
******************************/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
int n;
ll a[];
ll b[];
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%I64d",&a[i]);
b[n]=a[n];
for(int i=n-;i>=;i--)
b[i]=a[i]+a[i+];
cout<<b[];
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
cout<<" "<<b[i];
cout<<endl;
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Memory is performing a walk on the two-dimensional plane, starting at the origin. He is given a string s with his directions for motion:
- An 'L' indicates he should move one unit left.
- An 'R' indicates he should move one unit right.
- A 'U' indicates he should move one unit up.
- A 'D' indicates he should move one unit down.
But now Memory wants to end at the origin. To do this, he has a special trident. This trident can replace any character in s with any of 'L', 'R', 'U', or 'D'. However, because he doesn't want to wear out the trident, he wants to make the minimum number of edits possible. Please tell Memory what is the minimum number of changes he needs to make to produce a string that, when walked, will end at the origin, or if there is no such string.
The first and only line contains the string s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 100 000) — the instructions Memory is given.
If there is a string satisfying the conditions, output a single integer — the minimum number of edits required. In case it's not possible to change the sequence in such a way that it will bring Memory to to the origin, output -1.
RRU
-1
UDUR
1
RUUR
2
In the first sample test, Memory is told to walk right, then right, then up. It is easy to see that it is impossible to edit these instructions to form a valid walk.
In the second sample test, Memory is told to walk up, then down, then up, then right. One possible solution is to change s to "LDUR". This string uses 1 edit, which is the minimum possible. It also ends at the origin.
题意:给你一个串4个方向用4个字母表示 形成路径 要求要从起点最终回到起点 问你最少需要更改多少字母(某次的方向)
使得满足条件 回到起点。
题解:对于当前路径 判断起点与终点间的曼哈顿距离为dis
dis%2!=0则无论怎么更改都不能回到起点 (每更改一次方向都会使得距离变化2)
/******************************
code by drizzle
blog: www.cnblogs.com/hsd-/
^ ^ ^ ^
O O
******************************/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
char s[];
int main()
{
cin>>s;
int len=strlen(s);
int xx=,yy=;
for(int i=; i<len; i++)
{
if(s[i]=='L')
xx--;
if(s[i]=='R')
xx++;
if(s[i]=='U')
yy++;
if(s[i]=='D')
yy--;
}
if((abs(xx)+abs(yy))%)
cout<<"-1"<<endl;
else
cout<<(abs(xx)+abs(yy))/<<endl;
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Memory is now interested in the de-evolution of objects, specifically triangles. He starts with an equilateral triangle of side length x, and he wishes to perform operations to obtain an equilateral triangle of side length y.
In a single second, he can modify the length of a single side of the current triangle such that it remains a non-degenerate triangle (triangle of positive area). At any moment of time, the length of each side should be integer.
What is the minimum number of seconds required for Memory to obtain the equilateral triangle of side length y?
The first and only line contains two integers x and y (3 ≤ y < x ≤ 100 000) — the starting and ending equilateral triangle side lengths respectively.
Print a single integer — the minimum number of seconds required for Memory to obtain the equilateral triangle of side length y if he starts with the equilateral triangle of side length x.
6 3
4
8 5
3
22 4
6
In the first sample test, Memory starts with an equilateral triangle of side length 6 and wants one of side length 3. Denote a triangle with sides a, b, and c as (a, b, c). Then, Memory can do 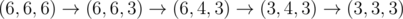 .
.
In the second sample test, Memory can do 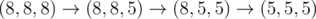 .
.
In the third sample test, Memory can do: 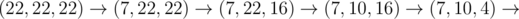
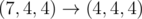 .
.
题意:给你x,y分别为初始等边三角形的边长和目标等边三角形的边长(x>y) 每次只能变化一条边,并且中间三角形为非退化三角形也就是必须是合法的三角形
问你最少的变化次数
题解:逆向思维 由y变到x 贪心使得 某条边增量尽可能大 并且能行成三角形 统计次数
/******************************
code by drizzle
blog: www.cnblogs.com/hsd-/
^ ^ ^ ^
O O
******************************/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
int x,y;
int a[];
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d",&x,&y);
a[]=y;a[]=y;a[]=y;
int ans=;
while(a[]!=x||a[]!=x||a[]!=x)
{
sort(a,a+);
if(a[]+a[]->=x)
a[]=x;
else
a[]=a[]+a[]-;
ans++;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return ;
}
最新文章
- 【2016-11-5】【坚持学习】【Day20】【Linq where in 语句】
- MVC:上传文件时限制文件类型
- linuxlcd驱动程序编写 mini2440(w35)
- springboot 学习笔记(一)
- Vue多元素过渡
- 最常用前端框架BootStrap——栅格系统
- Java中进制的转换函数
- [BZOJ1657] [Usaco2006 Mar] Mooo 奶牛的歌声 (单调栈)
- Win10系统盘制作及安装流程
- 自己写的一个用js把select换成div与span与ul的东西
- Nginx 配置文件优化
- day07数据类型的相互转化,字符编码
- C# Directory.Exists() 文件存在但返回一直为false
- 窥探ASP.Net MVC底层原理 实现跨越Session的分布式TempData
- 09-babel
- 【BZOJ2823】[AHOI2012]信号塔(最小圆覆盖)
- Spring.Net配置
- [转载]Linux目录说明
- 使用patroni 构建高可用的pg 数据库
- git中的ssh和https方式的使用(gitee为例)