Spring框架3--Web
2024-09-18 21:15:35
Spring框架之Web
Javaweb三大组件和四大域

顺便:Javaweb中的四大域,作用范围如下:PageContext<Request<Session<ServletContext(Application)
| 域对象 | 属性的作用范围 |
|---|---|
| PageContext | 仅限于当前jsp页面,在servlet中无法获取该对象 |
| Request | 仅限于同一个请求,主要用于请求转发,服务器跳转有效,客户端跳转无效 |
| Session | 仅限于一次会话,从浏览器打开直到关闭称为一次会话,搭配cookie使用 |
| Application | 限于当前Web应用,是范围最大的属性作用范围,只要在一处设置属性,在其他各处的jsp或servlet中都可以获取到,在servlet中对应于ServletContext对象 |
Spring-Web实现
@WebServlet("/loginServlet")
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");//创建Spring容器
UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService");//获取Bean
User user = userService.login("zhangsan", "123");
System.out.println(user);
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req, resp);
}
}
正常实现的话需要在对应业务的文件中先创建Spring容器,然后再获取对应的Bean对象,业务代码重复。实际上创建容器的过程可以在程序开始执行的时候创建一个单例对象,之后再次使用时只要拿到这个对象直接使用即可,具体实现可以在ServletContext监听器中实现。
Spring整合Servlet:
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" > <!--web.xml文件-->
<web-app>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--指定加载的配置文件--> <listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!--监听器-->
</web-app>
然后将Servlet文件中的内容更改为:
@WebServlet("/loginServlet")
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext servletContext = req.getServletContext();
WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(servletContext);//Spring容器
UserService userService = (UserService) webApplicationContext.getBean("userService");//获取Bean
User user = userService.login("zhangsan", "123");
System.out.println(user);
} @Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req, resp);
}
}
整合Web的痛点
传统的MVC+三层架构:
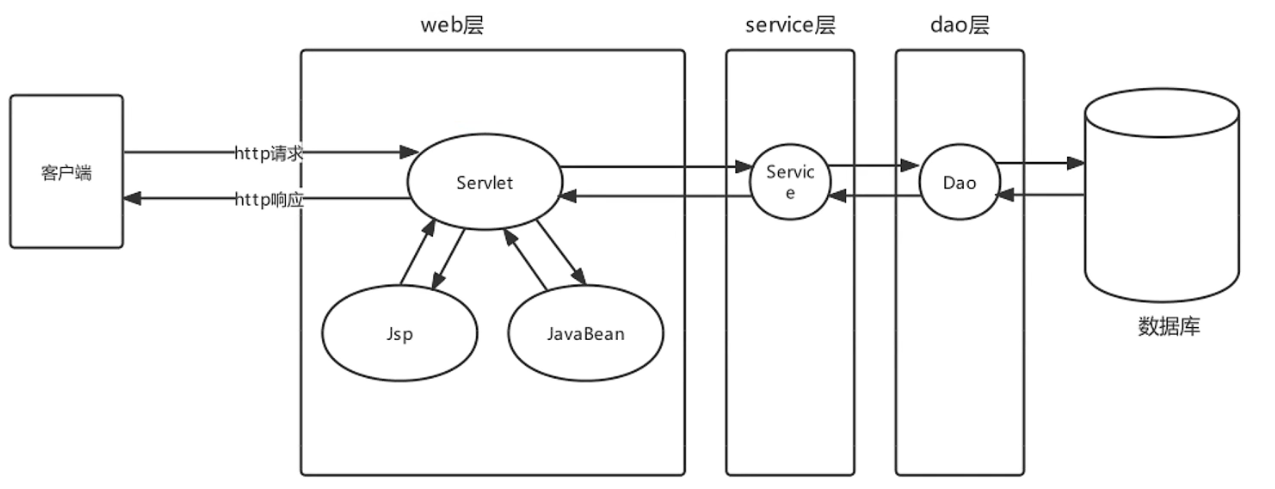
原始Javaweb开发中,Servlet充当Controller的角色, Jsp充当View角色, JavaBean充当模型角色,后期Ajax异
步流行后,在加上现在前后端分离开发模式成熟后, View就被原始HtmI+ Vue替代。原始Javaweb开发中,
Servlet充当Controller有很多弊端,显而易见的有如下几个:
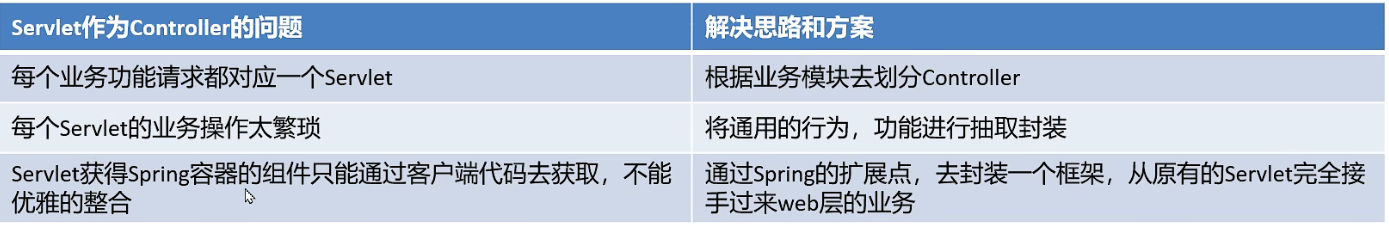
利用一个Servlet负责共有行为,JavaBean负责对应的业务行为:
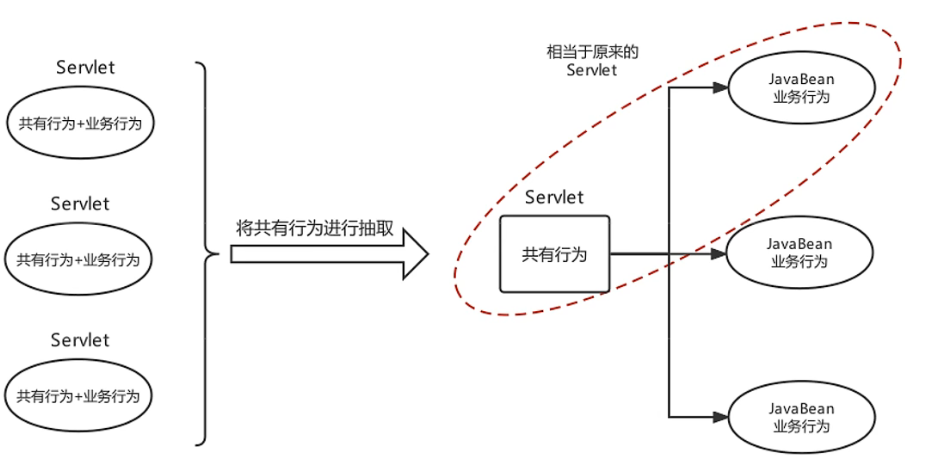
负责共有行为的Servlet称为前端控制器,应具有以下作用:
- 具备可以映射到业务Bean的能力
- 具备可以解析请求参数、封装实体等共有功能
- 具备响应视图及响应其他数据的功能
SpringMVC
- 配置过程

<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<servlet>
<!--前端控制器DispatchServlet-->
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring_mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param> <!--加载的配置文件-->
<load-on-startup>2</load-on-startup>
<!--启动时加载 大于0生效,数字越小优先级越高-->
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.azy.web.controller"/>
<!--交给Spring容器-->
</beans>
@Controller
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/show")
public String show(){
System.out.println("show ...");
return "index.jsp"
}
}
SpringMVC的工作原理
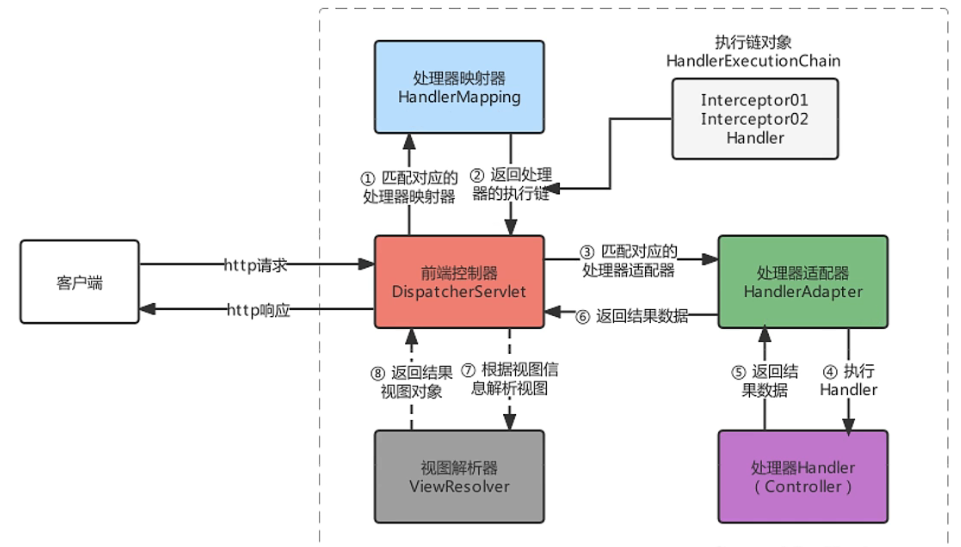
- 客户端发出一个http请求给web服务器,web服务器对http请求进行解析,如果匹配
DispatcherServlet的请求映射路径(在web.xml中指定),web容器将请求转交给DispatcherServlet. DipatcherServlet接收到这个请求之后将根据请求的信息(包括URL、Http方法、请求报文头和请求参数Cookie等)以及HandlerMapping的配置找到处理请求的处理器(Handler)DispatcherServlet根据HandlerMapping找到对应的Handler,将处理权交给Handler(Handler将具体的处理进行封装),再由具体的HandlerAdapter对Handler进行具体的调用。Handler对数据处理完成以后将返回一个ModelAndView对象给DispatcherServlet。Handler返回的ModelAndView是一个逻辑视图并不是一个正式的视图,DispatcherSevlet通过ViewResolver将逻辑视图转化为真正的视图View。Dispatcher通过model解析出ModelAndView中的参数进行解析最终展现出完整的view并返回给客户端。
- 客户端发出一个http请求给web服务器,web服务器对http请求进行解析,如果匹配
在文件DispatcherServlet.properties中包含默认的各部分组件:
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.RouterFunctionMapping
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.function.support.HandlerFunctionAdapter
org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver
可以自定义各个组件,在spring_mvc.xml文件中进行配置即可:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.azy.web.controller"/>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter"> <!--配置HandlerAdapter-->
<property name="messageConverters">
<list>
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.
MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter"/>
</list><!--注入JSON数据转换为实体类的转换器-->
</property>
</bean>
配置好JSON转换器后,在使用JSON数据传输时就可以自动转换为实体类对象。
Spring整合SpringMVC
- xml方式:
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<!--Spring加载-->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<servlet>
<!--前端控制器DispatchServlet-->
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring_mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param> <!--加载的配置文件-->
<load-on-startup>2</load-on-startup>
<!--启动时加载 大于0生效,数字越小优先级越高-->
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
<!--spring_mvc.xml-->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.azy.web.controller"/>
<!--交给Spring容器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter"> <!--配置HandlerAdapter-->
<property name="messageConverters">
<list>
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.
MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter"/>
</list><!--注入JSON数据转换为实体类的转换器-->
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
<!--applicationContext.xml-->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.azy.web.service"/>
</beans>
@Controller
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("/show")
public String show(@RequestBody User user){//JSON可以自动转换
System.out.println(user);
return "/index.jsp";
}
}
最新文章
- 在Qt Creator 和在 vs2012 里添加信号和槽
- maven:用appassembler-maven-plugin打包含有自定义目录的JAVA程序
- jquery时间轴幻灯展示源代码
- FZU 2193 So Hard (有限小数转换最简分数)(想法题)
- iOS仿京东分类菜单实例实现
- 图片格式转换之ImageMagick
- 淘宝初始化css代码
- (1)搭建opencv-android环境
- 【阿里云产品公测】云引擎ACE -discuz安装
- 整理收藏一份PHP高级工程师的笔试题
- JMS的作用
- javascript的语法作用域你真的懂了吗
- C++内存布局详解
- JDBC+Servlet+jsp(增删查改)
- linux系统调用之进程控制
- vue axios拦截器 + 自编写插件 实现全局 loading 效果;
- Linux的磁盘系统和文件系统显示的文件大小为什么不一样(du指令和ls指令的区别)
- Bitnami Redmine 中文附件名 报错修复
- ubuntu密码正确,却不能登录图形界面
- 编程开发之--Oracle数据库--存储过程和存储函数(2)