Asp-Net-Core-管道VS过滤器
title: Asp.Net Core底层源码剖析(二)过滤器
date: 2022-09-18 10:41:57
categories: 后端
tags:
- .NET
正文
Asp.Net Core中的过滤器有好几种,包括AuthorizationFilter、ActionFilter,ResourceFilter,ExceptionFilter,ResultFilter,平时一般用的多的就是AuthorizationFilter、ActionFilter、ExceptionFilter三个,下面我们写个自定义的ActionFilter,然后debug看一下源码
自定义ActionFilter
我们自定义的ActionFilter可以继承自ActionFilterAttribute,也可以直接实现接口IActionFilter,两者的作用是差不多的,因为ActionFilterAttribute也实现了这个接口,我们看下源码:
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class | AttributeTargets.Method, AllowMultiple = true, Inherited = true)]
public abstract class ActionFilterAttribute :
Attribute, IActionFilter, IAsyncActionFilter, IResultFilter, IAsyncResultFilter, IOrderedFilter
{
// 实现...
}
可以看出,ActionFilterAttribute继承了好几个接口,下面是这几个接口的简单说明

所以我们直接继承ActionFilterAttribute,其实同时实现了好几个方法:
public class MyActionFilterAttribute:ActionFilterAttribute
{
public override void OnActionExecuting(ActionExecutingContext actionExecutingContext)
{
Console.WriteLine("OnActionExecuting");
}
public override void OnActionExecuted(ActionExecutedContext context)
{
base.OnActionExecuted(context);
Console.WriteLine("OnActionExecuted");
}
public override Task OnActionExecutionAsync(ActionExecutingContext context, ActionExecutionDelegate next)
{
return base.OnActionExecutionAsync(context, next);
Console.WriteLine("OnActionExecutionAsync");
}
public override void OnResultExecuting(ResultExecutingContext context)
{
base.OnResultExecuting(context);
Console.WriteLine("OnResultExecuting");
}
public override void OnResultExecuted(ResultExecutedContext context)
{
base.OnResultExecuted(context);
Console.WriteLine("OnResultExecuted");
}
public override Task OnResultExecutionAsync(ResultExecutingContext context, ResultExecutionDelegate next)
{
return base.OnResultExecutionAsync(context, next);
Console.WriteLine("OnResultExecuted");
}
}
下面我们把自己写的过滤器添加到全局的过滤器中,而不是直接用在controller或者方法上
builder.Services.AddMvc(it => it.Filters.Add(typeof(MyActionFilterAttribute)));
然后我们开始debug,给OnActionExecuting函数打个断点,然后查看运行的堆栈,我们可以看到是在EndpointMiddleware中间件内部来调用过滤器的
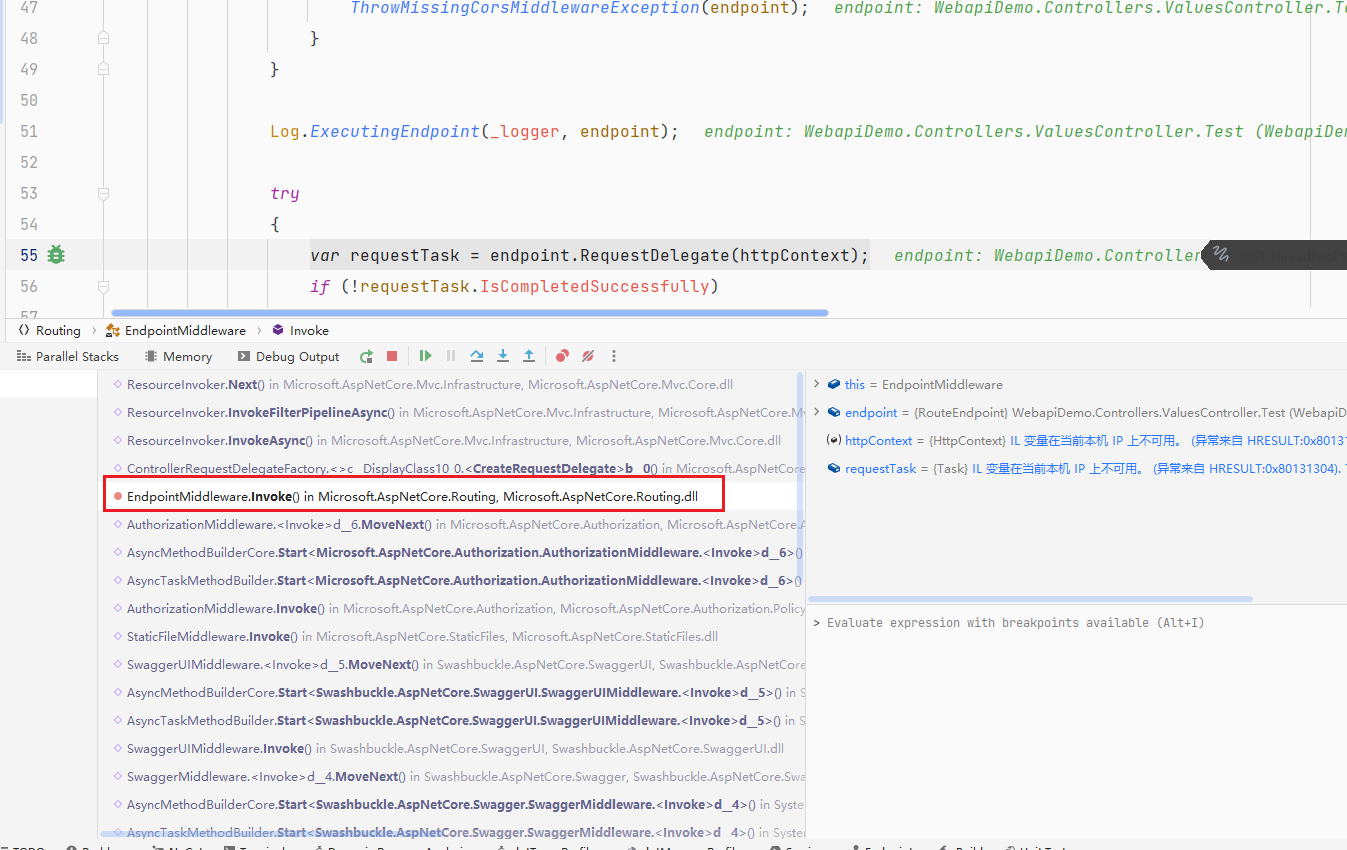
接着我们继续往下,能找到下面这个函数
private Task Next(ref State next, ref Scope scope, ref object? state, ref bool isCompleted)
{
switch (next)
{
case State.InvokeBegin:
{
goto case State.AuthorizationBegin;
}
case State.AuthorizationBegin:
{
_cursor.Reset();
goto case State.AuthorizationNext;
}
case State.AuthorizationNext:
{
var current = _cursor.GetNextFilter<IAuthorizationFilter, IAsyncAuthorizationFilter>();
if (current.FilterAsync != null)
{
if (_authorizationContext == null)
{
_authorizationContext = new AuthorizationFilterContextSealed(_actionContext, _filters);
}
state = current.FilterAsync;
goto case State.AuthorizationAsyncBegin;
}
else if (current.Filter != null)
{
if (_authorizationContext == null)
{
_authorizationContext = new AuthorizationFilterContextSealed(_actionContext, _filters);
}
state = current.Filter;
goto case State.AuthorizationSync;
}
else
{
goto case State.AuthorizationEnd;
}
}
case State.AuthorizationAsyncBegin:
{
Debug.Assert(state != null);
Debug.Assert(_authorizationContext != null);
var filter = (IAsyncAuthorizationFilter)state;
var authorizationContext = _authorizationContext;
_diagnosticListener.BeforeOnAuthorizationAsync(authorizationContext, filter);
_logger.BeforeExecutingMethodOnFilter(
FilterTypeConstants.AuthorizationFilter,
nameof(IAsyncAuthorizationFilter.OnAuthorizationAsync),
filter);
var task = filter.OnAuthorizationAsync(authorizationContext);
if (!task.IsCompletedSuccessfully)
{
next = State.AuthorizationAsyncEnd;
return task;
}
goto case State.AuthorizationAsyncEnd;
}
case State.AuthorizationAsyncEnd:
{
Debug.Assert(state != null);
Debug.Assert(_authorizationContext != null);
var filter = (IAsyncAuthorizationFilter)state;
var authorizationContext = _authorizationContext;
_diagnosticListener.AfterOnAuthorizationAsync(authorizationContext, filter);
_logger.AfterExecutingMethodOnFilter(
FilterTypeConstants.AuthorizationFilter,
nameof(IAsyncAuthorizationFilter.OnAuthorizationAsync),
filter);
if (authorizationContext.Result != null)
{
goto case State.AuthorizationShortCircuit;
}
goto case State.AuthorizationNext;
}
case State.AuthorizationSync:
{
Debug.Assert(state != null);
Debug.Assert(_authorizationContext != null);
var filter = (IAuthorizationFilter)state;
var authorizationContext = _authorizationContext;
_diagnosticListener.BeforeOnAuthorization(authorizationContext, filter);
_logger.BeforeExecutingMethodOnFilter(
FilterTypeConstants.AuthorizationFilter,
nameof(IAuthorizationFilter.OnAuthorization),
filter);
filter.OnAuthorization(authorizationContext);
_diagnosticListener.AfterOnAuthorization(authorizationContext, filter);
_logger.AfterExecutingMethodOnFilter(
FilterTypeConstants.AuthorizationFilter,
nameof(IAuthorizationFilter.OnAuthorization),
filter);
if (authorizationContext.Result != null)
{
goto case State.AuthorizationShortCircuit;
}
goto case State.AuthorizationNext;
}
case State.AuthorizationShortCircuit:
{
Debug.Assert(state != null);
Debug.Assert(_authorizationContext != null);
Debug.Assert(_authorizationContext.Result != null);
_logger.AuthorizationFailure((IFilterMetadata)state);
// This is a short-circuit - execute relevant result filters + result and complete this invocation.
isCompleted = true;
_result = _authorizationContext.Result;
return InvokeAlwaysRunResultFilters();
}
case State.AuthorizationEnd:
{
goto case State.ResourceBegin;
}
case State.ResourceBegin:
{
_cursor.Reset();
goto case State.ResourceNext;
}
case State.ResourceNext:
{
var current = _cursor.GetNextFilter<IResourceFilter, IAsyncResourceFilter>();
if (current.FilterAsync != null)
{
if (_resourceExecutingContext == null)
{
_resourceExecutingContext = new ResourceExecutingContextSealed(
_actionContext,
_filters,
_valueProviderFactories);
}
state = current.FilterAsync;
goto case State.ResourceAsyncBegin;
}
else if (current.Filter != null)
{
if (_resourceExecutingContext == null)
{
_resourceExecutingContext = new ResourceExecutingContextSealed(
_actionContext,
_filters,
_valueProviderFactories);
}
state = current.Filter;
goto case State.ResourceSyncBegin;
}
else
{
// All resource filters are currently on the stack - now execute the 'inside'.
goto case State.ResourceInside;
}
}
case State.ResourceAsyncBegin:
{
Debug.Assert(state != null);
Debug.Assert(_resourceExecutingContext != null);
var filter = (IAsyncResourceFilter)state;
var resourceExecutingContext = _resourceExecutingContext;
_diagnosticListener.BeforeOnResourceExecution(resourceExecutingContext, filter);
_logger.BeforeExecutingMethodOnFilter(
FilterTypeConstants.ResourceFilter,
nameof(IAsyncResourceFilter.OnResourceExecutionAsync),
filter);
var task = filter.OnResourceExecutionAsync(resourceExecutingContext, InvokeNextResourceFilterAwaitedAsync);
if (!task.IsCompletedSuccessfully)
{
next = State.ResourceAsyncEnd;
return task;
}
goto case State.ResourceAsyncEnd;
}
case State.ResourceAsyncEnd:
{
Debug.Assert(state != null);
Debug.Assert(_resourceExecutingContext != null);
var filter = (IAsyncResourceFilter)state;
if (_resourceExecutedContext == null)
{
// If we get here then the filter didn't call 'next' indicating a short circuit.
_resourceExecutedContext = new ResourceExecutedContextSealed(_resourceExecutingContext, _filters)
{
Canceled = true,
Result = _resourceExecutingContext.Result,
};
_diagnosticListener.AfterOnResourceExecution(_resourceExecutedContext, filter);
_logger.AfterExecutingMethodOnFilter(
FilterTypeConstants.ResourceFilter,
nameof(IAsyncResourceFilter.OnResourceExecutionAsync),
filter);
// A filter could complete a Task without setting a result
if (_resourceExecutingContext.Result != null)
{
goto case State.ResourceShortCircuit;
}
}
goto case State.ResourceEnd;
}
case State.ResourceSyncBegin:
{
Debug.Assert(state != null);
Debug.Assert(_resourceExecutingContext != null);
var filter = (IResourceFilter)state;
var resourceExecutingContext = _resourceExecutingContext;
_diagnosticListener.BeforeOnResourceExecuting(resourceExecutingContext, filter);
_logger.BeforeExecutingMethodOnFilter(
FilterTypeConstants.ResourceFilter,
nameof(IResourceFilter.OnResourceExecuting),
filter);
filter.OnResourceExecuting(resourceExecutingContext);
_diagnosticListener.AfterOnResourceExecuting(resourceExecutingContext, filter);
_logger.AfterExecutingMethodOnFilter(
FilterTypeConstants.ResourceFilter,
nameof(IResourceFilter.OnResourceExecuting),
filter);
if (resourceExecutingContext.Result != null)
{
_resourceExecutedContext = new ResourceExecutedContextSealed(resourceExecutingContext, _filters)
{
Canceled = true,
Result = _resourceExecutingContext.Result,
};
goto case State.ResourceShortCircuit;
}
var task = InvokeNextResourceFilter();
if (!task.IsCompletedSuccessfully)
{
next = State.ResourceSyncEnd;
return task;
}
goto case State.ResourceSyncEnd;
}
case State.ResourceSyncEnd:
{
Debug.Assert(state != null);
Debug.Assert(_resourceExecutingContext != null);
Debug.Assert(_resourceExecutedContext != null);
var filter = (IResourceFilter)state;
var resourceExecutedContext = _resourceExecutedContext;
_diagnosticListener.BeforeOnResourceExecuted(resourceExecutedContext, filter);
_logger.BeforeExecutingMethodOnFilter(
FilterTypeConstants.ResourceFilter,
nameof(IResourceFilter.OnResourceExecuted),
filter);
filter.OnResourceExecuted(resourceExecutedContext);
_diagnosticListener.AfterOnResourceExecuted(resourceExecutedContext, filter);
_logger.AfterExecutingMethodOnFilter(
FilterTypeConstants.ResourceFilter,
nameof(IResourceFilter.OnResourceExecuted),
filter);
goto case State.ResourceEnd;
}
case State.ResourceShortCircuit:
{
Debug.Assert(state != null);
Debug.Assert(_resourceExecutingContext != null);
Debug.Assert(_resourceExecutedContext != null);
_logger.ResourceFilterShortCircuited((IFilterMetadata)state);
_result = _resourceExecutingContext.Result;
var task = InvokeAlwaysRunResultFilters();
if (!task.IsCompletedSuccessfully)
{
next = State.ResourceEnd;
return task;
}
goto case State.ResourceEnd;
}
case State.ResourceInside:
{
goto case State.ExceptionBegin;
}
case State.ExceptionBegin:
{
_cursor.Reset();
goto case State.ExceptionNext;
}
case State.ExceptionNext:
{
var current = _cursor.GetNextFilter<IExceptionFilter, IAsyncExceptionFilter>();
if (current.FilterAsync != null)
{
state = current.FilterAsync;
goto case State.ExceptionAsyncBegin;
}
else if (current.Filter != null)
{
state = current.Filter;
goto case State.ExceptionSyncBegin;
}
else if (scope == Scope.Exception)
{
// All exception filters are on the stack already - so execute the 'inside'.
goto case State.ExceptionInside;
}
else
{
// There are no exception filters - so jump right to the action.
Debug.Assert(scope == Scope.Invoker || scope == Scope.Resource);
goto case State.ActionBegin;
}
}
case State.ExceptionAsyncBegin:
{
var task = InvokeNextExceptionFilterAsync();
if (!task.IsCompletedSuccessfully)
{
next = State.ExceptionAsyncResume;
return task;
}
goto case State.ExceptionAsyncResume;
}
case State.ExceptionAsyncResume:
{
Debug.Assert(state != null);
var filter = (IAsyncExceptionFilter)state;
var exceptionContext = _exceptionContext;
// When we get here we're 'unwinding' the stack of exception filters. If we have an unhandled exception,
// we'll call the filter. Otherwise there's nothing to do.
if (exceptionContext?.Exception != null && !exceptionContext.ExceptionHandled)
{
_diagnosticListener.BeforeOnExceptionAsync(exceptionContext, filter);
_logger.BeforeExecutingMethodOnFilter(
FilterTypeConstants.ExceptionFilter,
nameof(IAsyncExceptionFilter.OnExceptionAsync),
filter);
var task = filter.OnExceptionAsync(exceptionContext);
if (!task.IsCompletedSuccessfully)
{
next = State.ExceptionAsyncEnd;
return task;
}
goto case State.ExceptionAsyncEnd;
}
goto case State.ExceptionEnd;
}
case State.ExceptionAsyncEnd:
{
Debug.Assert(state != null);
Debug.Assert(_exceptionContext != null);
var filter = (IAsyncExceptionFilter)state;
var exceptionContext = _exceptionContext;
_diagnosticListener.AfterOnExceptionAsync(exceptionContext, filter);
_logger.AfterExecutingMethodOnFilter(
FilterTypeConstants.ExceptionFilter,
nameof(IAsyncExceptionFilter.OnExceptionAsync),
filter);
if (exceptionContext.Exception == null || exceptionContext.ExceptionHandled)
{
// We don't need to do anything to trigger a short circuit. If there's another
// exception filter on the stack it will check the same set of conditions
// and then just skip itself.
_logger.ExceptionFilterShortCircuited(filter);
}
goto case State.ExceptionEnd;
}
case State.ExceptionSyncBegin:
{
var task = InvokeNextExceptionFilterAsync();
if (!task.IsCompletedSuccessfully)
{
next = State.ExceptionSyncEnd;
return task;
}
goto case State.ExceptionSyncEnd;
}
case State.ExceptionSyncEnd:
{
Debug.Assert(state != null);
var filter = (IExceptionFilter)state;
var exceptionContext = _exceptionContext;
// When we get here we're 'unwinding' the stack of exception filters. If we have an unhandled exception,
// we'll call the filter. Otherwise there's nothing to do.
if (exceptionContext?.Exception != null && !exceptionContext.ExceptionHandled)
{
_diagnosticListener.BeforeOnException(exceptionContext, filter);
_logger.BeforeExecutingMethodOnFilter(
FilterTypeConstants.ExceptionFilter,
nameof(IExceptionFilter.OnException),
filter);
filter.OnException(exceptionContext);
_diagnosticListener.AfterOnException(exceptionContext, filter);
_logger.AfterExecutingMethodOnFilter(
FilterTypeConstants.ExceptionFilter,
nameof(IExceptionFilter.OnException),
filter);
if (exceptionContext.Exception == null || exceptionContext.ExceptionHandled)
{
// We don't need to do anything to trigger a short circuit. If there's another
// exception filter on the stack it will check the same set of conditions
// and then just skip itself.
_logger.ExceptionFilterShortCircuited(filter);
}
}
goto case State.ExceptionEnd;
}
case State.ExceptionInside:
{
goto case State.ActionBegin;
}
case State.ExceptionHandled:
{
// We arrive in this state when an exception happened, but was handled by exception filters
// either by setting ExceptionHandled, or nulling out the Exception or setting a result
// on the ExceptionContext.
//
// We need to execute the result (if any) and then exit gracefully which unwinding Resource
// filters.
Debug.Assert(state != null);
Debug.Assert(_exceptionContext != null);
if (_exceptionContext.Result == null)
{
_exceptionContext.Result = new EmptyResult();
}
_result = _exceptionContext.Result;
var task = InvokeAlwaysRunResultFilters();
if (!task.IsCompletedSuccessfully)
{
next = State.ResourceInsideEnd;
return task;
}
goto case State.ResourceInsideEnd;
}
case State.ExceptionEnd:
{
var exceptionContext = _exceptionContext;
if (scope == Scope.Exception)
{
isCompleted = true;
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
if (exceptionContext != null)
{
if (exceptionContext.Result != null ||
exceptionContext.Exception == null ||
exceptionContext.ExceptionHandled)
{
goto case State.ExceptionHandled;
}
Rethrow(exceptionContext);
Debug.Fail("unreachable");
}
var task = InvokeResultFilters();
if (!task.IsCompletedSuccessfully)
{
next = State.ResourceInsideEnd;
return task;
}
goto case State.ResourceInsideEnd;
}
case State.ActionBegin:
{
var task = InvokeInnerFilterAsync();
if (!task.IsCompletedSuccessfully)
{
next = State.ActionEnd;
return task;
}
goto case State.ActionEnd;
}
case State.ActionEnd:
{
if (scope == Scope.Exception)
{
// If we're inside an exception filter, let's allow those filters to 'unwind' before
// the result.
isCompleted = true;
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
Debug.Assert(scope == Scope.Invoker || scope == Scope.Resource);
var task = InvokeResultFilters();
if (!task.IsCompletedSuccessfully)
{
next = State.ResourceInsideEnd;
return task;
}
goto case State.ResourceInsideEnd;
}
case State.ResourceInsideEnd:
{
if (scope == Scope.Resource)
{
_resourceExecutedContext = new ResourceExecutedContextSealed(_actionContext, _filters)
{
Result = _result,
};
goto case State.ResourceEnd;
}
goto case State.InvokeEnd;
}
case State.ResourceEnd:
{
if (scope == Scope.Resource)
{
isCompleted = true;
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
Debug.Assert(scope == Scope.Invoker);
Rethrow(_resourceExecutedContext!);
goto case State.InvokeEnd;
}
case State.InvokeEnd:
{
isCompleted = true;
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
default:
throw new InvalidOperationException();
}
}
上面这段就是过滤器的核心代码了,其实很简单,就是在一个switch里面不停地根据条件跳转,下面是官网上不同过滤器的执行顺序图

那么过滤器和管道之间的执行顺序又是什么样的呢?直接看官方文档内的图:

其实从刚开始的单步调试我们就已经知道了,是在EndpointMiddleware管道内执行的,也就是说先执行了一些我们自己添加的中间件,到最后和Action交互的时候才会执行相关的过滤器
过滤器和管道的重要区别
中间件可以处理所有的请求,而过滤器只能针对到达
EndpointMiddlewareApi的请求进行处理过滤器处理的是
ActionExecutingContext、ResultExecutedContext等,而中间件处理的是HttpContext,相较于HttpContext,ActionExecutingContext拥有了更多的信息,比如执行的方法,对应的参数等
以异常处理来举例,我们可以在中间件的级别来处理异常,也可以在过滤器的级别来处理异常,那一般情况下我们应该怎么选择呢?
- 如果我们需要处理Asp.Net Core框架内部的错误,比如管道中处理出现了一些异常,我们需要使用
中间件处理异常,并且位于管道的开始位置 - 如果我们只关心自己的业务代码是否出现异常,比如controller中的action抛出了异常,我们可以使用
过滤器,这样有个好处就是我们更方便获取对应抛出异常方法的信息 - 如果我们又想处理Asp.Net Core框架内部的异常,又想处理业务逻辑的异常,那么我们可以两者都同时使用
过滤器执行顺序
过滤器的执行是有顺序的,官方文档提供了一个表格我们可以参考一下:
| Sequence | Filter scope | Filter method |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Global | OnActionExecuting |
| 2 | Controller | OnActionExecuting |
| 3 | Action | OnActionExecuting |
| 4 | Action | OnActionExecuted |
| 5 | Controller | OnActionExecuted |
| 6 | Global | OnActionExecuted |
看得出来顺序是这样的:
- 全局级别
- Controller级别
- Action级别
返回时执行顺序相反,这个顺序也不是写死的,我们可以通过配置一个字段来设置顺序:
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class | AttributeTargets.Method, AllowMultiple = true, Inherited = true)]
public abstract class ActionFilterAttribute :
Attribute, IActionFilter, IAsyncActionFilter, IResultFilter, IAsyncResultFilter, IOrderedFilter
{
/// <inheritdoc />
public int Order { get; set; }
}
实现了IOrderedFilter接口的过滤器都可以通过Order字段设置执行顺序,这个Order的默认值都是0,我们可以在自定义的过滤器上添加下面的代码来测试是否是这样的:
public int Level { get; set; } = 0;
public override void OnActionExecuting(ActionExecutingContext actionExecutingContext)
{
Console.WriteLine($"OnActionExecuting {Order} {Level}");
}
在全局、Controller和Action级别都添加一个:
[MyActionFilter(Level = 100)]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class ValuesController : ControllerBase
{
public ValuesController()
{
}
[MyActionFilter(Level = 99)]
[HttpGet("test")]
public string Test()
{
return "123";
}
}
最后调用这个接口,输出的结果为:
OnActionExecuting 0 0
OnActionExecuting 0 100
OnActionExecuting 0 99
可以看出,默认的Order都是0,如果我们想要将某个过滤器在其它过滤器前执行,则可以手动设置Order的顺序,Order越小优先级越高
这里有个问题,如果我们设置某一个过滤器的执行顺序在全局和Controller之间,那我们也必须设置Controller级别的过滤器的Order属性,比如Action级别的过滤器Order为1,那么Controller级别的过滤器Orde必须大于1,如果涉及到很多个过滤器的话这里会比较复杂,而且不直观,所以一般情况下都不会对这个字段进行修改
参考
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/42582758/asp-net-core-middleware-vs-filters
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/mvc/controllers/filters?view=aspnetcore-6.0
https://www.yogihosting.com/advanced-filters-topics-aspnet-core/#execution-order
https://www.dotnettricks.com/learn/aspnetcore/mvc-core-filters-real-world-exmaple
最新文章
- 对jquery分页的升级
- AnguarJS测试的实施步骤整理
- linux tar order
- sql server 之函数小技巧 && 整数类型为空是用空字符串替代实现
- poj 2342 Anniversary party
- javascript RegExp类型 学习小记
- 学会使用git
- QF——iOS的单例模式
- ssh远程登录不上的处理
- SDWebImage之工具类
- app v2界面
- djbc
- 通过jdbc获取数据库中的表结构 主键 各个表字段类型及应用生成实体类
- 2014年最佳的10款 PHP 开发框架
- js鼠标自定移入输入框文本框光标自动定位到文本框
- 恶补java基础 位运算符
- [SoapUI] EndPoint不需要在配置文件中设置不同环境的值,SoapUI自带此参数的设置
- HTTP-java模拟Post请求小栗子
- Oracle18c创建不带C##的用户
- ASP.NET Core项目中新增和删除的内容