Useful NumPy functions: Reshape, Argpartition, Clip, Extract, Setdiff1d
In everyday data processing for Machine Learning and Data Science projects, we encounter unique situations, those require boilerplate code to solve the problem. Over the period some of those are converted into base features provided by the core language or the package itself as per need and usage from the community. Here I am sharing 5 elegant python Numpy functions, which can be used for efficient and neat data manipulation.
1) Use of -1 in Reshape
Numpy allows us to reshape a matrix provided new shape should be compatible with the original shape. One interesting aspect of this new shape is, we can give one of the shape parameter as -1. It simply means that it is an unknown dimension and we want Numpy to figure it out. Numpy will figure this by looking at the ‘length of the array and remaining dimensions’ and making sure it satisfies the above mentioned criteria. Let's see one example now.

Pictorial representation of different reshape with one dimension as -1
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8]])
a.shape
(2, 4)
Suppose we give row as 1 and -1 as column then Numpy will able to find column as 8.
a.reshape(1,-1)
array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]])
Suppose we give row as -1 and 1 as column then Numpy will able to find row as 8.
a.reshape(-1,1)
array([[1],
[2],
[3],
[4],
[5],
[6],
[7],
[8]])
Similarly below are possible.
a.reshape(-1,4)
array([[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8]])a.reshape(-1,2)
array([[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[5, 6],
[7, 8]])a.reshape(2,-1)
array([[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8]])a.reshape(4,-1)
array([[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[5, 6],
[7, 8]])
This is also applicable to any higher level tensor reshape as well but only one dimension can be given -1.
a.reshape(2,2,-1)
array([[[1, 2],
[3, 4]], [[5, 6],
[7, 8]]])a.reshape(2,-1,1)
array([[[1],
[2],
[3],
[4]], [[5],
[6],
[7],
[8]]])
If we try to reshape a non-compatible shape or more than one unknown shape then there will be an error message.
a.reshape(-1,-1)
ValueError: can only specify one unknown dimensiona.reshape(3,-1)
ValueError: cannot reshape array of size 8 into shape (3,newaxis)
To summarize, when reshaping an array, the new shape must contain the same number of elements as the old shape, meaning the products of the two shapes’ dimensions must be equal. When using a -1, the dimension corresponding to the -1 will be the product of the dimensions of the original array divided by the product of the dimensions given to reshape so as to maintain the same number of elements.
2) Argpartition : Find N maximum values in an array
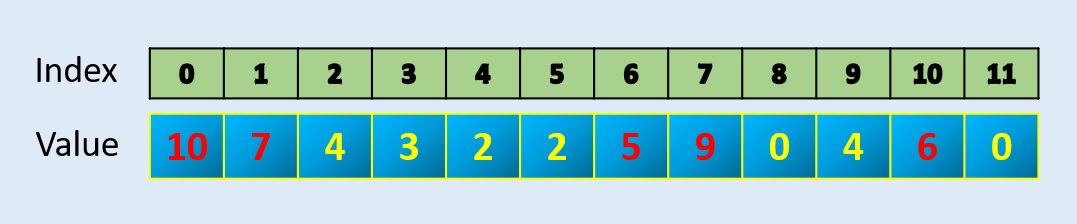
Numpy has a function called argpartition which can efficiently find largest of N values index and in-turn N values. It gives index and then you can sort if you need sorted values.
array = np.array([10, 7, 4, 3, 2, 2, 5, 9, 0, 4, 6, 0])index = np.argpartition(array, -5)[-5:]
index
array([ 6, 1, 10, 7, 0], dtype=int64)np.sort(array[index])
array([ 5, 6, 7, 9, 10])
3) Clip : How to keep values in an array within an interval
In many data problem or algorithm (like PPO in Reinforcement Learning) we need to keep all values within an upper and lower limit. Numpy has a built in function called Clip that can be used for such purpose. Numpy clip() function is used to Clip (limit) the values in an array. Given an interval, values outside the interval are clipped to the interval edges. For example, if an interval of [-1, 1] is specified, values smaller than -1 become -1, and values larger than 1 become 1.

Clip example with min value 2 and maximum value 6
#Example-1
array = np.array([10, 7, 4, 3, 2, 2, 5, 9, 0, 4, 6, 0])
print (np.clip(array,2,6))[6 6 4 3 2 2 5 6 2 4 6 2]#Example-2
array = np.array([10, -1, 4, -3, 2, 2, 5, 9, 0, 4, 6, 0])
print (np.clip(array,2,5))[5 2 4 2 2 2 5 5 2 4 5 2]
4) Extract: To extract specific elements from an array based on condition
We can use Numpy extract() function to extract specific elements from an array that matches the condition.
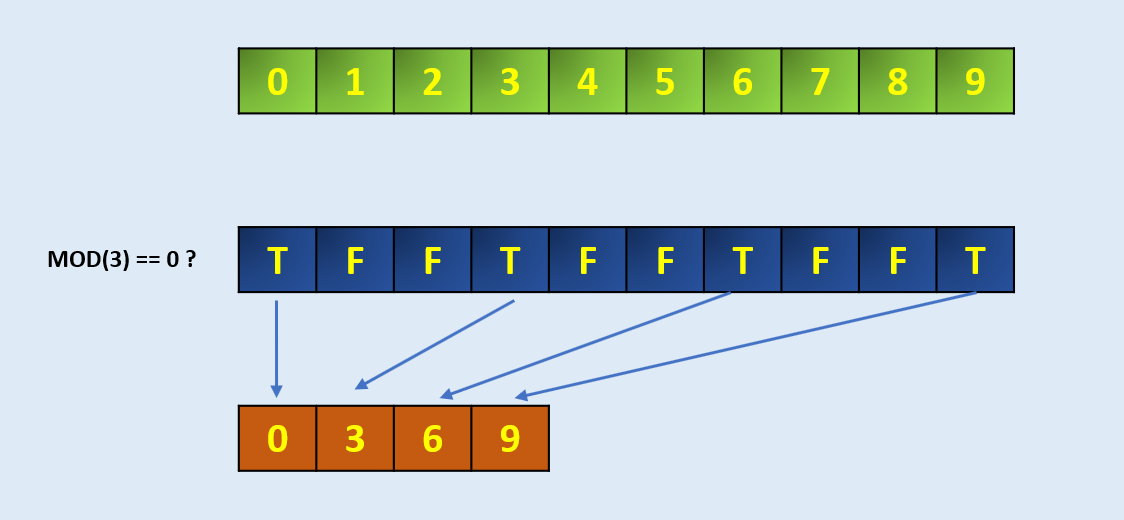
arr = np.arange(10)
arrarray([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])# Define the codition, here we take MOD 3 if zero
condition = np.mod(arr, 3)==0
conditionarray([ True, False, False, True, False, False, True, False, False,True])np.extract(condition, arr)
array([0, 3, 6, 9])
Similarly, we can use direct condition with combination of AND and OR if required like
np.extract(((arr > 2) & (arr < 8)), arr)array([3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
5) setdiff1d : How to find unique values in an array compared to another
Return the unique values in an array that are not in present in another array. This is equivalent to set difference of two arrays.
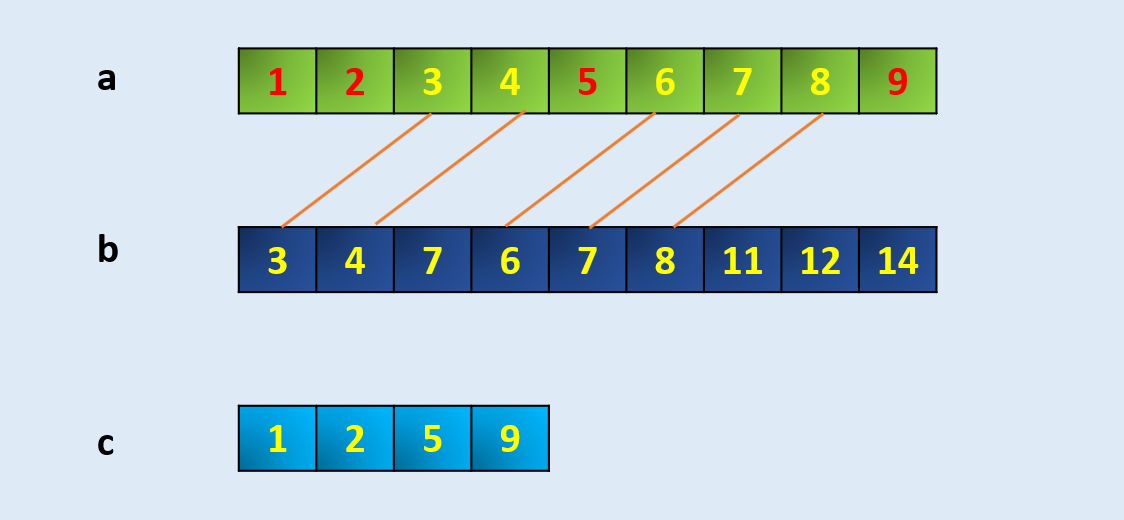
a = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
b = np.array([3,4,7,6,7,8,11,12,14])
c = np.setdiff1d(a,b)
carray([1, 2, 5, 9])
Final Note :
These are 5 Numpy functions which are not used frequently by the community but they are neat and elegant. In my view, we should use them whenever there is similar situation as these provide not just less code but mostly smart way of achieving a solution for a complex problem.
最新文章
- Spring MVC返回Map格式JSON数据
- @Controller和@RestController的区别?
- C#语言——类
- bootstrap-datepicker带中文的js文件
- solr6安装部署
- bzoj3130
- 获取设备mac地址和md5加密
- 元素重叠及position定位的z-index顺序
- python3 获取阿里云ECS 实例及监控的方法
- 如何将mysql数据导入Hadoop之Sqoop安装
- css基础语法三
- python列表中的pop函数
- MYSQL 总结——2
- vue脚手架 构建豆瓣App 第一天
- Linux init进程学习 转
- JUC集合之 CopyOnWriteArraySet
- eclipse插件开发常见的问题及解决办法
- Flink实例-Wordcount详细步骤
- Delphi实现在数据库中存取图像
- lightoj1234调和级数+欧拉常数