Burning widget
This is a widget that we can see in Nero, K3B, or other CD/DVD burning software.
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """
ZetCode PyQt4 tutorial In this example, we create a custom widget. author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
last edited: October 2011
""" import sys
from PyQt4 import QtGui, QtCore class Communicate(QtCore.QObject): updateBW = QtCore.pyqtSignal(int) class BurningWidget(QtGui.QWidget): def __init__(self):
super(BurningWidget, self).__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): self.setMinimumSize(1, 30)
self.value = 75
self.num = [75, 150, 225, 300, 375, 450, 525, 600, 675] def setValue(self, value): self.value = value def paintEvent(self, e): qp = QtGui.QPainter()
qp.begin(self)
self.drawWidget(qp)
qp.end() def drawWidget(self, qp): font = QtGui.QFont('Serif', 7, QtGui.QFont.Light)
qp.setFont(font) size = self.size()
w = size.width()
h = size.height() step = int(round(w / 10.0)) till = int(((w / 750.0) * self.value))
full = int(((w / 750.0) * 700)) if self.value >= 700: qp.setPen(QtGui.QColor(255, 255, 255))
qp.setBrush(QtGui.QColor(255, 255, 184))
qp.drawRect(0, 0, full, h)
qp.setPen(QtGui.QColor(255, 175, 175))
qp.setBrush(QtGui.QColor(255, 175, 175))
qp.drawRect(full, 0, till-full, h) else:
qp.setPen(QtGui.QColor(255, 255, 255))
qp.setBrush(QtGui.QColor(255, 255, 184))
qp.drawRect(0, 0, till, h) pen = QtGui.QPen(QtGui.QColor(20, 20, 20), 1,
QtCore.Qt.SolidLine) qp.setPen(pen)
qp.setBrush(QtCore.Qt.NoBrush)
qp.drawRect(0, 0, w-1, h-1) j = 0 for i in range(step, 10*step, step): qp.drawLine(i, 0, i, 5)
metrics = qp.fontMetrics()
fw = metrics.width(str(self.num[j]))
qp.drawText(i-fw/2, h/2, str(self.num[j]))
j = j + 1 class Example(QtGui.QWidget): def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): sld = QtGui.QSlider(QtCore.Qt.Horizontal, self)
sld.setFocusPolicy(QtCore.Qt.NoFocus)
sld.setRange(1, 750)
sld.setValue(75)
sld.setGeometry(30, 40, 150, 30) self.c = Communicate()
self.wid = BurningWidget()
self.c.updateBW[int].connect(self.wid.setValue) sld.valueChanged[int].connect(self.changeValue)
hbox = QtGui.QHBoxLayout()
hbox.addWidget(self.wid)
vbox = QtGui.QVBoxLayout()
vbox.addStretch(1)
vbox.addLayout(hbox)
self.setLayout(vbox) self.setGeometry(300, 300, 390, 210)
self.setWindowTitle('Burning widget')
self.show() def changeValue(self, value): self.c.updateBW.emit(value)
self.wid.repaint() def main(): app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_()) if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
In our example, we have a QtGui.QSlider and a custom widget. A slider controls the custom widget. This widget shows graphically the total capacity of a medium and the free space available to us. The minimum value of our custom widget is 1, the maximum is 750. If we reach value 700, we begin drawing in red colour. This normally indicates overburning.
The burning widget is placed at the bottom of the window. This is achieved using oneQtGui.QHBoxLayout and one QtGui.QVBoxLayout.
class BurningWidget(QtGui.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(BurningWidget, self).__init__()
The burning widget it based on the QtGui.QWidget widget.
self.setMinimumSize(1, 30)
We change the minimum size (height) of the widget. The default value is a bit small for us.
font = QtGui.QFont('Serif', 7, QtGui.QFont.Light)
qp.setFont(font)
We use a smaller font than the default one. This better suits our needs.
size = self.size()
w = size.width()
h = size.height() step = int(round(w / 10.0)) till = int(((w / 750.0) * self.value))
full = int(((w / 750.0) * 700))
We draw the widget dynamically. The greater is the window, the greater is the burning widget and vice versa. That is why we must calculate the size of the widget onto which we draw the custom widget. The till parameter determines the total size to be drawn. This value comes from the slider widget. It is a proportion of the whole area. The full parameter determines the point where we begin to draw in red colour. Notice the use of floating point arithmetics to achieve greater precision in drawing.
The actual drawing consists of three steps. We draw the yellow or the red and yellow rectangle. Then we draw the vertical lines which divide the widget into several parts. Finally, we draw the numbers which indicate the capacity of the medium.
metrics = qp.fontMetrics()
fw = metrics.width(str(self.num[j]))
qp.drawText(i-fw/2, h/2, str(self.num[j]))
We use font metrics to draw the text. We must know the width of the text in order to center it around the vertical line.
def changeValue(self, value):
self.c.updateBW.emit(value)
self.wid.repaint()
When we move the slider, the changeValue() method is called. Inside the method, we send a customupdateBW signal with a parameter. The parameter is the current value of the slider. The value is later used to calculate the capacity of the Burning widget to be drawn. The custom widget is then repainted.
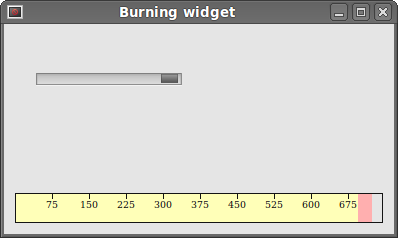 Figure: The burning widget
Figure: The burning widget
最新文章
- jQuery 菜单
- scala 学习笔记(06) OOP(下)多重继承 及 AOP
- JavaWeb学习总结(三)——Tomcat服务器学习和使用(二) 包含https 非对称秘钥 NB
- 利用COPYDATASTRUCT传递命令行参数给驻留内存的进程(SendMessage应用)
- CentOS7安装Docker时的异常报错与解决方法
- Miles per gallon to kilometers per liter
- NOIP2006 作业调度方案
- 了解SQL Server锁争用:NOLOCK 和 ROWLOCK 的秘密
- ASP.NET页面生命周期总结(1)
- Js动态设置Img大小
- SUN SERVER X3-2 服务器数据写入缓慢
- 【20171025中】alert(1) to win 脚本渲染自建
- StarSpace是用于高效学习实体向量的通用神经模型
- 博三F5第一次站立会议(2019-03-09)
- GLog 初始化说明
- Go基础系列:Go slice详解
- 网络嗅探与欺骗(FTP部分)——P201421410029
- 解决打开bootstrap模态框抖动问题
- C#使用PriorityQueue
- BZOJ5315 [JSOI2018]防御网络 【仙人掌 + dp】
热门文章
- luoguP4320 道路相遇 圆方树
- Arab Collegiate Programming Contest 2012 J- Math Homework
- hdu 3435 图回路分割
- <摘录>Gson对Java嵌套对象和JSON字符串之间的转换
- IOS上传图片方法类
- Visual Studio 2015创建Shared Project时出错
- Druid 常见问题
- 測试oracle 11g cluster 中OLR的重要性
- Assembly.Load()方法,Assembly.LoadFrom()方法,Assembly.LoadFile()方法的区别!
- Unity 国际化 多语言设置