HashMap中的散列函数、冲突解决机制和rehash
一、概述
散列算法有两个主要的实现方式:开散列和闭散列,HashMap采用开散列实现。
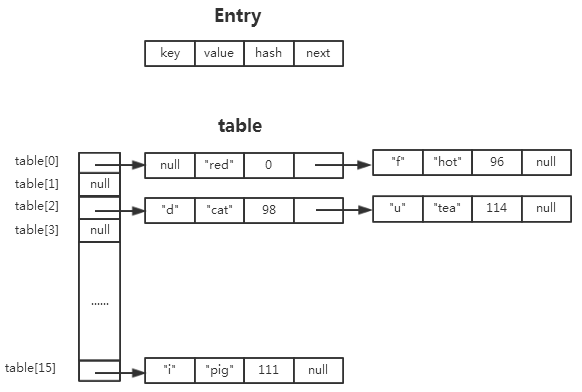
HashMap中,键值对(key-value)在内部是以Entry(HashMap中的静态内部类)实例的方式存储,散列表table是一个Entry数组,保存Entry实例。
对于冲突的情况,在开散列中,如果若干个entry计算得到相同散列地址(具体是由indexFor(hash(key.hashCode()),length)求得),这些entry被组织成一个链表,并以table[i]为头指针。
HashMap的数据结构大致可以用下图表示(以HashMap<String,String>的实例为例):
二、散列函数
HashMap采用简单的除法散列,其散列公式可表示为:

一般来讲,采用除法散列,m的值应该尽量避免某些特殊值,例如m不应该为2的幂。
如果m=2^p,那么h(k)的结果就是k的p个最低位,这样就会与k的比特位产生关联,更容易产生冲突,不能很好的保证散列函数的结果在[0...m-1]之间均匀分布。所以除非已知各种最低p为排列是等可能的,否则m选择应该考虑到关键字的所有位。
但是HashMap中提供了hash(int h)函数,这个函数以key.hashCode为参数,对其做进一步的处理,处理过程中较好的解决了以上的因素的影响。大致保证了每一个hashCode具有有限的冲突次数(通过移位运算和异或操作具体怎么达到这个目的?我也没有在深入去挖,感兴趣的同学可以来一起探讨学习下。。。)。
这样一来,某个key散列地址计算过程实际就是:
indexFor(hash(key.hashCode()),length)
可见,这里的hash(key.hashCode())结果相当于上面的散列公式中的k,lenght相当于m。
以下为hash(int h)和indexFor(int h, int length)源代码,更能说明问题:
/**
* Applies a supplemental hash function to a given hashCode, which
* defends against poor quality hash functions. This is critical
* because HashMap uses power-of-two length hash tables, that
* otherwise encounter collisions for hashCodes that do not differ
* in lower bits. Note: Null keys always map to hash 0, thus index 0.
*/
static int hash(int h) {
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
} /**
* Returns index for hash code h.
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
}
注意indexFor(int h, int length)的处理方式:
在length为2的幂的情况下,h & (length-1) 等效于h%length。这里length为table的长度,HashMap保证了无论是在初始化时还是在后续resize操作过程中,length都是2的幂。
三、冲突解决机制
在需要插入<key,value>键值对(内部对应插入Entry实例)时,执行put操作。
两个相同的key必然计算出相同的散列地址(相同的indexFor(hash, table.length)结果),HashMap中不接受相同的key,对原有的key进行put操作实际上是进行覆盖value的操作。
两个不同的key仍有可能计算出相同的散列地址(例如前例中key为"d"和"u"),此时产生冲突。
HashMap中的冲突解决机制比较简单,将这些冲突的entry节点以链表的方式挂靠到table[i]处。插入时以参数(hash, key, value, e)创建新的Entry实例,e就是位于table[i]处的链表的第一个entry节点,e作为新创建的entry的next元素,所以新创建的entry直接插入到了链表的头部充当新的头结点。
从源代码层面分析来看,put操作调用addEntry()方法,后者继续调用HashMap中静态内部类Entry<K,V>的构造函数。
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
if (size++ >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
...
/**
* Creates new entry.
*/
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
...
}
四、rehash
当键值对的数量>=设定的阀值(capacity * load factor(0.75))时,为保证HashMap的性能,会进行重散列(rehash)。
HashMap中,重散列主要有两步:1、扩充table长度。2、转移table中的entry,从旧table转移到新的table。
table长度以2倍的方式扩充,一直到最大长度2^30。
entry转移的过程是真正意义上的重散列,在此过程中,对原来的每个entry的key重新计算新的散列地址,旧table中相同位置的entry极有可能会被散列到新table中不同的位置,这主要是因为table的length变化的原因。
在源代码中主要涉及resize()和transfer()两个方法。
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
transfer(newTable);
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
}
/**
* Transfers all entries from current table to newTable.
*/
void transfer(Entry[] newTable) {
Entry[] src = table;
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (int j = 0; j < src.length; j++) {
Entry<K,V> e = src[j];
if (e != null) {
src[j] = null;
do {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
} while (e != null);
}
}
}
五、一些总结
1、capacity(table数组长度)必须为2的幂,初始容量(initial capacity)默认为16。即使是以传入参数initialCapacity的方式构造实例(HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)),构造过程中内部也会将capacity修整为与initialCapacity最接近并且不小于它的2的幂的数作为capacity来实例化。
2、装填因子loadFactor默认为0.75。
3、如果key为null,这始终会被散列到table[0]的桶中,即使是rehash的过程也是一样。非null的key也有可能会被散列到table[0]的位置,例如上图中key=“f”,而且相同的key在在不同的时间可能会被散列到不同的位置,这与rehash有关。
4、HashMap以链表的方式解决冲突,插入键值对(put操作)时,新增的entry会被插入到链表的头部,也就是会插入到table[i]的位置。
5、与其他集合类一样,由于fail-fast特性的存在,利用遍历器(Iterator)进行遍历操作时应该采用遍历器自身的方法进行结构化的修改(例如remove操作),不应采用其他方式对其数据内容进行修改。
最新文章
- spoj 839 Optimal Marks(二进制位,最小割)
- 第十一篇:web之Django之Form组件
- javascript 函数参数
- 局部更新 java web 的文件
- 【并查集+拓扑排序】【HDU1811】【Rank of Tetris】
- UVALive - 3263 That Nice Euler Circuit (几何)
- js中style的属性
- SQL优化及注意事项
- jQuery 初识 筛选器 属性选择器
- Android Studio中解决jar包重复依赖导致的代码编译错误
- 部署DTCMS到Jexus遇到的问题及解决思路---部署
- centos环境无法安装paramiko的问题解决
- Codeforces Round #341 (Div. 2) E - Wet Shark and Blocks
- SQL基本练习
- mysql如何让自增id从某个位置开始设置方法
- centos6.5 安装PHP7.0支持nginx
- Android计时器和倒计时
- [转载]How To Install Nginx And PHP-FPM On CentOS 6 Via Yum
- 转:关于 OGRE 与 OSG 的简单比较
- 架构师养成记--25.linux用户管理