postgresql高可用集群部署
2024-08-30 19:46:39
一、概况
1、概念
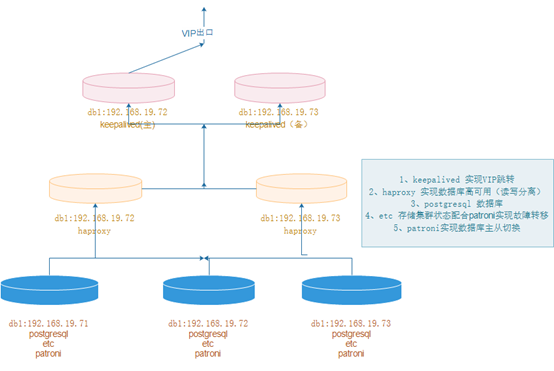
pgsql高可用集群采用postgresql+etcd+patroni+haproxy+keepalived等软件实现,以postgresql做数据库,etcd存储集群状态,patroni与etcd结合实现数据库集群故障切换,
haproxy实现数据库高可用(读读写分离),keepalived实现VIP跳转。
2、拓扑图
二、postgresql部署(三个节点)
1、下载解压
https://www.enterprisedb.com/download-postgresql-binaries
mkdir -p /data/pg_data
tar xf postgresql-10.18-1-linux-x64-binaries.tar.gz -C /data/
2、创建用户并授权
useradd postgres
passwd postgres
chown -R postgres.postgres /data/
3、初始化数据库(postgres用户下)
切换目录
[root@centos7 ~]# su – postgres
初始化目录
[postgres@centos7 ~]$ /data/pgsql/bin/initdb -D /data/pg_data/
4、配置变量
su – postgres
vim .bash_profile
PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin export PATH
export PATH
export PGHOME=/data/pgsql
export PATH=$PATH:$PGHOME/bin
export PGDATA=/data/pg_data
export PGLOG=/data/pg_log/pg.log source .bash_profile
mkdir -p /data/pg_log
chown postgres.postgres /data/pg_data
chown postgres.postgres /data/pg_log
5、配置postgresql启动脚本
vim /etc/systemd/system/postgresql.service
[Unit]
Description=PostgreSQL database server
After=network.target [Service]
Type=forking
User=postgres
Group=postgres
ExecStart= /data/pgsql/bin/pg_ctl -D /data/pg_data/ start
ExecReload= /data/pgsql/bin/pg_ctl -D /data/pg_data/ restart
ExecStop= /data/pgsql/bin/pg_ctl -D /data/pg_data/ stop
PrivateTmp=true [Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
6、启动与关闭
systemctl daemon-reload
开启
systemctl start postgresql
关闭
systemctl stop postgresql
重启
systemctl restart postgresql
7、数据库添加密码
[postgres@pgsql-19 ~]$ psql -U postgres -h localhost
postgres=# alter user postgres with password 'P@sswrd';
8、允许远程连接
vim /data/pg_data/pg_hba.conf
host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5

vim /data/pg_data/postgresql.conf
listen_addresses = '*'
password_encryption = on
重启数据库
systemctl restart postgresql
三、etcd部署(三个节点)
1、下载解压
tar xf etcd-v3.1.20-linux-amd64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/
ln -s /usr/local/etcd-v3.1.20-linux-amd64 /usr/local/etcd
2、文件配置
mkdir -p /usr/local/etcd/data/etcd
vim /usr/local/etcd/conf.yml
name: pgsql_1971
data-dir: /usr/local/etcd/data/etcd
listen-client-urls: http://192.168.19.71:2379,http://127.0.0.1:2379
advertise-client-urls: http://192.168.19.71:2379,http://127.0.0.1:2379
listen-peer-urls: http://192.168.19.71:2380
initial-advertise-peer-urls: http://192.168.19.71:2380
initial-cluster: pgsql_1971=http://192.168.19.71:2380,pgsql_1972=http://192.168.19.72:2380,pgsql_1973=http://192.168.19.73:2380
initial-cluster-token: etcd-cluster-token
initial-cluster-state: new mkdir -p /usr/local/etcd/data/etc
vim /usr/local/etcd/conf.yml
name: pgsql_1972
data-dir: /usr/local/etcd/data/etcd
listen-client-urls: http://192.168.19.72:2379,http://127.0.0.1:2379
advertise-client-urls: http://192.168.19.72:2379,http://127.0.0.1:2379
listen-peer-urls: http://192.168.19.72:2380
initial-advertise-peer-urls: http://192.168.19.72:2380
initial-cluster: pgsql_1971=http://192.168.19.71:2380,pgsql_1972=http://192.168.19.72:2380,pgsql_1973=http://192.168.19.73:2380
initial-cluster-token: etcd-cluster-token
initial-cluster-state: new mkdir -p /usr/local/etcd/data/etc
vim /usr/local/etcd/conf.yml
name: pgsql_1973
data-dir: /usr/local/etcd/data/etcd
listen-client-urls: http://192.168.19.73:2379,http://127.0.0.1:2379
advertise-client-urls: http://192.168.19.73:2379,http://127.0.0.1:2379
listen-peer-urls: http://192.168.19.73:2380
initial-advertise-peer-urls: http://192.168.19.73:2380
initial-cluster: pgsql_1971=http://192.168.19.71:2380,pgsql_1972=http://192.168.19.72:2380,pgsql_1973=http://192.168.19.73:2380
initial-cluster-token: etcd-cluster-token
initial-cluster-state: new
3、启动并加入到开机自启中
加入开机自启里边
nohup /usr/local/etcd/etcd --config-file=/usr/local/etcd/conf.yml &
4、集群检查
netstat -lntup|grep etcd
/usr/local/etcd/etcdctl member list
四、patroni部署(三个节点)
1、更新postgresql.conf文件
postgresql.conf配置如下 max_connections = '500'
max_wal_senders = '10'
port = '5432'
listen_addresses = '*'
synchronous_commit = on
full_page_writes = on
wal_log_hints = on
synchronous_standby_names = '*'
max_replication_slots = 10
wal_level = replica
注:这两个参数会导致数据库执行呆滞,后来者欢迎留言看是怎么回事儿
2、更新pg_hba.conf文件
vim /data/pg_data/pg_hba.conf
清理最后配置的配置,新增以下
local all all peer
host all all 127.0.0.1/32 md5
host all postgres 127.0.0.1/32 md5
host all all 192.168.19.0/24 md5
host all all ::1/128 md5
local replication replicator peer
host replication replicator 127.0.0.1/32 md5
host replication replicator ::1/128 md5
host replication replicator 192.168.19.71/32 md5
host replication replicator 192.168.19.72/32 md5
host replication replicator 192.168.19.73/32 md5
以上配置完成后,重启数据库
3、在主节点上创建复制槽,很重要,patroni会用到
postgres=# create user replicator replication login encrypted password '1qaz2wsx';
4、配置stream replication(在两个从节点操作)
systemctl stop postgresql
su - postgres
cd /data/ && rm -rf pg_data
/data/pgsql/bin/pg_basebackup -h 192.168.19.71 -D /data/pg_data -U replicator -v -P -R
启动数据库
systemctl start postgresql
5、安装patroni(三个节点)
yum install -y python3 python-psycopg2 python3-devel
pip3 install --upgrade pip
pip3 install psycopg2-binary -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple/ --trusted-host pypi.douban.com
pip3 install patroni[etcd] -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple/ --trusted-host pypi.douban.com 验证是否安装成功 which patroni
patronictl --help
6、创建patroni配置文件
mkdir -p /usr/patroni/conf
cd /usr/patroni/conf/
node1 scope: batman
namespace: /service/
name: postgresql1 restapi:
listen: 192.168.19.71:8008
connect_address: 192.168.19.71:8008
# certfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
# keyfile: /etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key
# authentication:
# username: username
# password: password # ctl:
# insecure: false # Allow connections to SSL sites without certs
# certfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
# cacert: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cacert-snakeoil.pem etcd:
#Provide host to do the initial discovery of the cluster topology:
host: 192.168.19.71:2379
#Or use "hosts" to provide multiple endpoints
#Could be a comma separated string:
#hosts: host1:port1,host2:port2
#host: 192.168.19.71:2379,192.168.19.71:2379,192.168.19.73:2379
#or an actual yaml list:
#hosts:
#- host1:port1
#- host2:port2
#Once discovery is complete Patroni will use the list of advertised clientURLs
#It is possible to change this behavior through by setting:
#use_proxies: true #raft:
# data_dir: .
# self_addr: 192.168.19.71:2222
# partner_addrs:
# - 192.168.19.71:2223
# - 192.168.19.71:2224 bootstrap:
# this section will be written into Etcd:/<namespace>/<scope>/config after initializing new cluster
# and all other cluster members will use it as a `global configuration`
dcs:
ttl: 30
loop_wait: 10
retry_timeout: 10
maximum_lag_on_failover: 1048576
# master_start_timeout: 300
# synchronous_mode: false
#standby_cluster:
#host: 192.168.19.71
#port: 1111
#primary_slot_name: patroni
postgresql:
use_pg_rewind: true
# use_slots: true
parameters:
# wal_level: hot_standby
# hot_standby: "on"
# max_connections: 100
# max_worker_processes: 8
# wal_keep_segments: 8
# max_wal_senders: 10
# max_replication_slots: 10
# max_prepared_transactions: 0
# max_locks_per_transaction: 64
# wal_log_hints: "on"
# track_commit_timestamp: "off"
# archive_mode: "on"
# archive_timeout: 1800s
# archive_command: mkdir -p ../wal_archive && test ! -f ../wal_archive/%f && cp %p ../wal_archive/%f
# recovery_conf:
# restore_command: cp ../wal_archive/%f %p # some desired options for 'initdb'
initdb: # Note: It needs to be a list (some options need values, others are switches)
- encoding: UTF8
- data-checksums pg_hba: # Add following lines to pg_hba.conf after running 'initdb'
# For kerberos gss based connectivity (discard @.*$)
#- host replication replicator 192.168.19.71/32 gss include_realm=0
#- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 gss include_realm=0
- host replication replicator 192.168.19.71/32 md5
- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
# - hostssl all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5 # Additional script to be launched after initial cluster creation (will be passed the connection URL as parameter)
# post_init: /usr/local/bin/setup_cluster.sh # Some additional users users which needs to be created after initializing new cluster
users:
admin:
password: admin
options:
- createrole
- createdb postgresql:
listen: 192.168.19.71:5432
connect_address: 192.168.19.71:5432
data_dir: /data/pg_data
bin_dir: /data/pgsql/bin
# config_dir:
pgpass: /tmp/pgpass0
authentication:
replication:
username: replicator
password: 1qaz2wsx
superuser:
username: postgres
password: P@sswrd
rewind: # Has no effect on postgres 10 and lower
username: postgres
password: P@sswrd
# Server side kerberos spn
# krbsrvname: postgres
parameters:
# Fully qualified kerberos ticket file for the running user
# same as KRB5CCNAME used by the GSS
# krb_server_keyfile: /var/spool/keytabs/postgres
unix_socket_directories: '.'
# Additional fencing script executed after acquiring the leader lock but before promoting the replica
#pre_promote: /path/to/pre_promote.sh #watchdog:
# mode: automatic # Allowed values: off, automatic, required
# device: /dev/watchdog
# safety_margin: 5 tags:
nofailover: false
noloadbalance: false
clonefrom: false
nosync: false
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
node2 scope: batman
namespace: /service/
name: postgresql2 restapi:
listen: 192.168.19.72:8008
connect_address: 192.168.19.72:8008
# certfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
# keyfile: /etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key
# authentication:
# username: username
# password: password # ctl:
# insecure: false # Allow connections to SSL sites without certs
# certfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
# cacert: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cacert-snakeoil.pem etcd:
#Provide host to do the initial discovery of the cluster topology:
host: 192.168.19.72:2379
#Or use "hosts" to provide multiple endpoints
#Could be a comma separated string:
#hosts: host1:port1,host2:port2
#host: 192.168.19.71:2379,192.168.19.72:2379,192.168.19.73:2379
#or an actual yaml list:
#hosts:
#- host1:port1
#- host2:port2
#Once discovery is complete Patroni will use the list of advertised clientURLs
#It is possible to change this behavior through by setting:
#use_proxies: true #raft:
# data_dir: .
# self_addr: 192.168.19.72:2222
# partner_addrs:
# - 192.168.19.72:2223
# - 192.168.19.72:2224 bootstrap:
# this section will be written into Etcd:/<namespace>/<scope>/config after initializing new cluster
# and all other cluster members will use it as a `global configuration`
dcs:
ttl: 30
loop_wait: 10
retry_timeout: 10
maximum_lag_on_failover: 1048576
# master_start_timeout: 300
# synchronous_mode: false
#standby_cluster:
#host: 192.168.19.72
#port: 1111
#primary_slot_name: patroni
postgresql:
use_pg_rewind: true
# use_slots: true
parameters:
# wal_level: hot_standby
# hot_standby: "on"
# max_connections: 100
# max_worker_processes: 8
# wal_keep_segments: 8
# max_wal_senders: 10
# max_replication_slots: 10
# max_prepared_transactions: 0
# max_locks_per_transaction: 64
# wal_log_hints: "on"
# track_commit_timestamp: "off"
# archive_mode: "on"
# archive_timeout: 1800s
# archive_command: mkdir -p ../wal_archive && test ! -f ../wal_archive/%f && cp %p ../wal_archive/%f
# recovery_conf:
# restore_command: cp ../wal_archive/%f %p # some desired options for 'initdb'
initdb: # Note: It needs to be a list (some options need values, others are switches)
- encoding: UTF8
- data-checksums pg_hba: # Add following lines to pg_hba.conf after running 'initdb'
# For kerberos gss based connectivity (discard @.*$)
#- host replication replicator 192.168.19.72/32 gss include_realm=0
#- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 gss include_realm=0
- host replication replicator 192.168.19.72/32 md5
- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
# - hostssl all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5 # Additional script to be launched after initial cluster creation (will be passed the connection URL as parameter)
# post_init: /usr/local/bin/setup_cluster.sh # Some additional users users which needs to be created after initializing new cluster
users:
admin:
password: admin
options:
- createrole
- createdb postgresql:
listen: 192.168.19.72:5432
connect_address: 192.168.19.72:5432
data_dir: /data/pg_data
bin_dir: /data/pgsql/bin
# config_dir:
pgpass: /tmp/pgpass0
authentication:
replication:
username: replicator
password: 1qaz2wsx
superuser:
username: postgres
password: P@sswrd
rewind: # Has no effect on postgres 10 and lower
username: postgres
password: P@sswrd
# Server side kerberos spn
# krbsrvname: postgres
parameters:
# Fully qualified kerberos ticket file for the running user
# same as KRB5CCNAME used by the GSS
# krb_server_keyfile: /var/spool/keytabs/postgres
unix_socket_directories: '.'
# Additional fencing script executed after acquiring the leader lock but before promoting the replica
#pre_promote: /path/to/pre_promote.sh #watchdog:
# mode: automatic # Allowed values: off, automatic, required
# device: /dev/watchdog
# safety_margin: 5 tags:
nofailover: false
noloadbalance: false
clonefrom: false
nosync: false ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
node3 scope: batman
namespace: /service/
name: postgresql3 restapi:
listen: 192.168.19.73:8008
connect_address: 192.168.19.73:8008
# certfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
# keyfile: /etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key
# authentication:
# username: username
# password: password # ctl:
# insecure: false # Allow connections to SSL sites without certs
# certfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
# cacert: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cacert-snakeoil.pem etcd:
#Provide host to do the initial discovery of the cluster topology:
host: 192.168.19.73:2379
#Or use "hosts" to provide multiple endpoints
#Could be a comma separated string:
#hosts: host1:port1,host2:port2
#host: 192.168.19.73:2379,192.168.19.73:2379,192.168.19.73:2379
#or an actual yaml list:
#hosts:
#- host1:port1
#- host2:port2
#Once discovery is complete Patroni will use the list of advertised clientURLs
#It is possible to change this behavior through by setting:
#use_proxies: true #raft:
# data_dir: .
# self_addr: 192.168.19.73:2222
# partner_addrs:
# - 192.168.19.73:2223
# - 192.168.19.73:2224 bootstrap:
# this section will be written into Etcd:/<namespace>/<scope>/config after initializing new cluster
# and all other cluster members will use it as a `global configuration`
dcs:
ttl: 30
loop_wait: 10
retry_timeout: 10
maximum_lag_on_failover: 1048576
# master_start_timeout: 300
# synchronous_mode: false
#standby_cluster:
#host: 192.168.19.73
#port: 1111
#primary_slot_name: patroni
postgresql:
use_pg_rewind: true
# use_slots: true
parameters:
# wal_level: hot_standby
# hot_standby: "on"
# max_connections: 100
# max_worker_processes: 8
# wal_keep_segments: 8
# max_wal_senders: 10
# max_replication_slots: 10
# max_prepared_transactions: 0
# max_locks_per_transaction: 64
# wal_log_hints: "on"
# track_commit_timestamp: "off"
# archive_mode: "on"
# archive_timeout: 1800s
# archive_command: mkdir -p ../wal_archive && test ! -f ../wal_archive/%f && cp %p ../wal_archive/%f
# recovery_conf:
# restore_command: cp ../wal_archive/%f %p # some desired options for 'initdb'
initdb: # Note: It needs to be a list (some options need values, others are switches)
- encoding: UTF8
- data-checksums pg_hba: # Add following lines to pg_hba.conf after running 'initdb'
# For kerberos gss based connectivity (discard @.*$)
#- host replication replicator 192.168.19.73/32 gss include_realm=0
#- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 gss include_realm=0
- host replication replicator 192.168.19.73/32 md5
- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
# - hostssl all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5 # Additional script to be launched after initial cluster creation (will be passed the connection URL as parameter)
# post_init: /usr/local/bin/setup_cluster.sh # Some additional users users which needs to be created after initializing new cluster
users:
admin:
password: admin
options:
- createrole
- createdb postgresql:
listen: 192.168.19.73:5432
connect_address: 192.168.19.73:5432
data_dir: /data/pg_data
bin_dir: /data/pgsql/bin
# config_dir:
pgpass: /tmp/pgpass0
authentication:
replication:
username: replicator
password: 1qaz2wsx
superuser:
username: postgres
password: P@sswrd
rewind: # Has no effect on postgres 10 and lower
username: postgres
password: P@sswrd
# Server side kerberos spn
# krbsrvname: postgres
parameters:
# Fully qualified kerberos ticket file for the running user
# same as KRB5CCNAME used by the GSS
# krb_server_keyfile: /var/spool/keytabs/postgres
unix_socket_directories: '.'
# Additional fencing script executed after acquiring the leader lock but before promoting the replica
#pre_promote: /path/to/pre_promote.sh #watchdog:
# mode: automatic # Allowed values: off, automatic, required
# device: /dev/watchdog
# safety_margin: 5 tags:
nofailover: false
noloadbalance: false
clonefrom: false
nosync: false
7、依次启动patroni服务
Postgres用户下启动
nohup patroni /usr/patroni/conf/patroni_postgresql.yml &
8、patroni配置启动脚本
为了方便开机自启,故配置成 patroni.service,3个node都需要进行配置,配置好patroni.service后就可以直接在root用户下切换Leader以及重启postgres节点等操作
[root@pgsql_1971 ~]$ vim /etc/systemd/system/patroni.service
[Unit]
Description=patroni - a high-availability PostgreSQL
Documentation=https://patroni.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html
After=syslog.target network.target etcd.target
Wants=network-online.target [Service]
Type=simple
User=postgres
Group=postgres
PermissionsStartOnly=true
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/patroni /usr/patroni/conf/patroni_postgresql.yml
ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID
LimitNOFILE=65536
KillMode=process
KillSignal=SIGINT
Restart=on-abnormal
RestartSec=30s
TimeoutSec=0 [Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
9、禁用postgresql脚本采用patroni服务启动数据库
禁止 postgresql 的自启动,通过 patroni 来管理 postgresql systemctl stop postgresql
systemctl status postgresql
systemctl disable postgresql systemctl status patroni
systemctl start patroni
systemctl enable patroni
五、集群检查
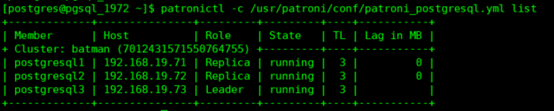
1、数据库集群检查
patronictl -c /usr/patroni/conf/patroni_postgresql.yml list
2、etcd检查
root@pgsql_1971 ~]# /usr/local/etcd/etcdctl ls /service/batman
root@pgsql_1971 ~]# /usr/local/etcd/etcdctl get /service/batman/members/postgresql1
六、haproxy部署(两个从节点)
七、keepalived部署(两个从节点)
最新文章
- Cesium应用篇:3控件(4)Geocoder
- 循序渐进Python3(六) -- 初识内置变量、反射、递归
- Why Deep Learning Works – Key Insights and Saddle Points
- MyBatis传入参数为集合 list 数组 map写法
- 2D客户端+微端技术总结
- 使用feof()函数判断文件是否结束
- Spring3之MVC
- 深入浅出理解iOS经常使用的正則表達式—基础篇[Foundation]
- Math对象中比较常用的计算数学相关的三个方法
- stm32位操作详解
- 【转】python 退出程序的方式
- iTerm2连接远程-中文乱码问题
- \r\n 如何转换成utf-8格式的,在jsp页面中正常显示换行
- Java 基础总结--反射的基本操作
- 什么是Kali Linux?
- js前台加密,java后端解密
- go环境安装
- jquery toggle()设置
- git log 常用选项
- CF 447A(DZY Loves Hash-简单判重)