详解Python Graphql
前言
很高兴现在接手的项目让我接触到了Python Graphql,百度上对其介绍相对较少也不够全面,几乎没有完整的中文文档,所以这边也借此机会学习一下Graphql。
什么是Graphql呢?
Graphql是一个API查询语言,其数据由服务器上的一个Scheme提供,其查询返回的数据依赖请求的时候用户需要的精确数据。列如用户只需要一个name字段,服务器也只返回name的值。
参考
英文学习文档:https://graphene-python.org/
更多example关注:https://github.com/graphql-python/graphene/tree/master/examples
Hello Word 入门
先看下面一个例子,查询语句为{ hello(name:"gaojiayi") } 定义了要查询的入口,以及传入的参数。
from graphene import ObjectType, String, Schema class Query(ObjectType):
"""定义一个字符串属性域hello 且有一个字符串参数为name,设置name的默认"""
hello = String(name = String(default_value="gaojy",required=True)) # resolve_hello定义了上面hello的实现,并返回查询结果
# 一般resolve需要加上固定前缀resolve_
@staticmethod
def resolve_hello(root,info,name):
return f"hello word -- {name}" schema = Schema(query=Query) if __name__ == '__main__':
query_string = '''{ hello(name:"gaojiayi") }'''
result = schema.execute(query_string)
print(result.data['hello'])
Graphql中的Types
Scheme
下面定义了一个Scheme,其中MyRootQuery,MyRootMutation,MyRootSubscription都是继承了graphene .objectType,但是不同之处在于query定义了查询数据的入口,而mutation用来数据改变或者数据恢复,而subscription是用来实时呈现数据的变化给client。type是用来指定返回数据的精确类型,列如返回的数据是一个interface,但是有多个类型继承了该interface,这时候需要指定一个具体的实现来返回给client。
my_schema = Schema(
query=MyRootQuery,
mutation=MyRootMutation,
subscription=MyRootSubscription,
type=[SomeExtraObjectType,]
)
另外查询字符串默认为驼峰命名,列如
from graphene import ObjectType, String, Schema class Query(ObjectType):
other_name = String(name='_other_Name') @staticmethod
def resolve_other_name(root, info):
return "test CamelCase" schema = Schema(query=Query) if __name__ == '__main__':
# 查询数默认使用otherName,此处用了别名。
result = schema.execute('''{_other_Name}''')
print(result.data['_other_Name'])
如果关闭默认驼峰命名方式,则可以在定义scheme的时候加上auto_camelcase=False
my_schema = Schema(
auto_camelcase=False
)
scalars
scalars type可以理解为用来定义Field,它可以传入以下几种可选参数,例如
other_name = String(name='_other_Name',required=True,description="",deprecation_reason="",defalut_value=Any)
常见的基本saclars type有如下几个:
graphene.String
graphene.Int
graphene.Float
graphene.Boolean
graphene.ID
graphene.types.datetime.Date
graphene.types.datetime.DateTime
graphene.types.datetime.Time
graphene.types.json.JSONString
saclars type的挂载在objectType,interface,Mutation中的field域中。
class Person(graphene.ObjectType):
name = graphene.String() # Is equivalent to:
class Person(graphene.ObjectType):
name = graphene.Field(graphene.String)
Lists and Non-Null
Non-Null
import graphene class Character(graphene.ObjectType):
name = graphene.String(required=True)
#等价于 即返回的数据如果name=null,则会报错
class Character(graphene.ObjectType):
name = graphene.String(required=True)
Lists
import graphene class Character(graphene.ObjectType):
# appears_in表示为一个非null元素的列表
appears_in = graphene.List(graphene.NonNull(graphene.String))
ObjectType
objectType是在scheme中用来定义Fields之间联系以及数据流转的python类,每一个obejctType属性表示一个Field,每个Field定义一个resolve方法用来获取数据,如果没有定义,则使用一个默认的resolver。
接下来看一个例子。
from graphene import ObjectType, String, Schema class Query(ObjectType):
@staticmethod
def resolve_hello(parent,info,name):
return f"hello word -- {name}"
上面的resolve_hello有三个参数,分别是parent,info,name
1 parent通常用来获取objectType内的其他field的值,而在根query中默认为None,看下面的事例,当OjectType的Field为saclar type,则parent不会再向下传递。
class Person(ObjectType):
full_name = String() def resolve_full_name(parent, info):
return f"{parent.first_name} {parent.last_name}" class Query(ObjectType):
me = Field(Person) def resolve_me(parent, info):
# returns an object that represents a Person
# 这里的parent为None
return get_human(name="Luke Skywalker")
当然,根查询的parent也可以初始化值,就是在execute的时候添加root变量
@staticmethod
def resolve_hello(parent, info, name):
# 打印结果 man ,parent默认为root的值
print(parent['sex'])
return f"hello word -- {name}" schema = Schema(query=Query, mutation=MyMutations) if __name__ == '__main__':
query_string = '''{ hello(name:"gaojiayi") }'''
# 指定root的值
result = schema.execute(query_string, root={'sex': 'man'})
print(result.data['hello'])
当查询语句存在多个的时候,可指定执行那一条语句
schema = Schema(Query)
query_string = '''
query getUserWithFirstName {
user {
id
firstName
lastName
}
}
query getUserWithFullName {
user {
id
fullName
}
}
'''
result = schema.execute(
query_string,
# 指定执行第二条语句
operation_name='getUserWithFullName'
)
2 info表示请求的上下文,可以在查询语中添加context,列如
class Query(ObjectType):
hello = String(name=String(default_value="gaojy", required=True))
@staticmethod
def resolve_hello(root, info, name):
# 通过info可获取上下文内容
print(info.context.get('company'))
return f"hello word -- {name}" schema = Schema(query=Query, mutation=MyMutations) if __name__ == '__main__':
query_string = '''{ hello(name:"gaojiayi") }'''
# 1 execute中添加context
result = schema.execute(query_string, context={'company': 'baidu'})
print(result.data['hello'])
3 name表示请求时带的参数,可以参考hello word事例,如有多个参数可形参**kwargs
from graphene import ObjectType, String class Query(ObjectType):
hello = String(required=True, name=String()) def resolve_hello(parent, info, **kwargs):
# name 为None 则name = World
name = kwargs.get('name', 'World')
return f'Hello, {name}!'
4 默认resolver:列如一个objectType的field都没有指定队友的resolve,那么对象默认会序列化一个字典。
PersonValueObject = namedtuple('Person', 'first_name', 'last_name')
class Person(ObjectType):
first_name = String()
last_name = String()
class Query(ObjectType):
me = Field(Person)
my_best_friend = Field(Person)
def resolve_me(parent, info):
# always pass an object for `me` field
# {"firstName": "Luke", "lastName": "Skywalker"}
return PersonValueObject(first_name='Luke', last_name='Skywalker')
5 meta 类:用于objectType的配置
Enum
class Episode(graphene.Enum):
NEWHOPE = 4
EMPIRE = 5
JEDI = 6 @property
def description(self):
if self == Episode.NEWHOPE:
return 'New Hope Episode'
return 'Other episode' class Query(ObjectType):
desc1 = String(
v=Argument(Episode, default_value=Episode.NEWHOPE.value),
description='default value in schema is `4`, which is not valid. Also, awkward to write.') @staticmethod
def resolve_desc1(parent, info,v):
return f'argument: {v!r}' # 使用下面的方式可以将python类型的enum转化成saclars类型
graphene.Enum.from_enum(
AlreadyExistingPyEnum,
description=lambda v: return 'foo' if v == AlreadyExistingPyEnum.Foo else 'bar')
Interfaces
顾名思义,接口,其他的obectType可以继承接口,示例如下
import graphene class Character(graphene.Interface):
id = graphene.ID(required=True)
name = graphene.String(required=True)
friends = graphene.List(lambda: Character) #继承Character
class Human(graphene.ObjectType):
class Meta:
interfaces = (Character, ) starships = graphene.List(Starship)
home_planet = graphene.String() #继承Character
class Droid(graphene.ObjectType):
class Meta:
interfaces = (Character, ) primary_function = graphene.String() class Query(graphene.ObjectType):
# 返回的类型是Character
hero = graphene.Field(
Character,
required=True,
episode=graphene.Int(required=True)
) def resolve_hero(root, info, episode):
# Luke is the hero of Episode V
if episode == 5:
return get_human(name='Luke Skywalker')
return get_droid(name='R2-D2') #对于返回数据具体类型,可以在type属性中列举
schema = graphene.Schema(query=Query, types=[Human, Droid])
另外scheme中如果没有指定type,会报错
"Abstract type Character must resolve to an Object type at runtime for field Query.hero ..."
可以在interface中重写resolve_type方法
class Character(graphene.Interface):
id = graphene.ID(required=True)
name = graphene.String(required=True)
#返回数据的时候,可以转换成具体的数据类型
@classmethod
def resolve_type(cls, instance, info):
if instance.type == 'DROID':
return Droid
return Human
Union
该scalars type用来组合多个ObjectType,列如
import graphene class Human(graphene.ObjectType):
name = graphene.String()
born_in = graphene.String() class Droid(graphene.ObjectType):
name = graphene.String()
primary_function = graphene.String() class Starship(graphene.ObjectType):
name = graphene.String()
length = graphene.Int()
# SearchResult组合了Human Droid Starship所有的Fields
class SearchResult(graphene.Union):
class Meta:
types = (Human, Droid, Starship)
Mutations
如果说query是一个http get请求,那么Mutations可以看做是一个http post put请求。
def Mutate作为一个特殊的resover,当被调用的时候意在改变Mutation内的数据。
看下面一个操作示例
#具体的操作类
class CreatePerson(graphene.Mutation):
# 请求提交的参数,同样需要传递到mutate中
class Arguments:
name = graphene.String() ok = graphene.Boolean()
person = graphene.Field(Person) def mutate(root, info, name):
person = Person(name=name)
ok = True
#可执行具体的业务逻辑 包括写表 发消息等等
return CreatePerson(person=person, ok=ok) # Mutation
class MyMutations(graphene.ObjectType):
create_person = CreatePerson.Field()
#指定mutation MyMutations
schema = Schema(query=Query,mutation=MyMutations)
执行结果如下:
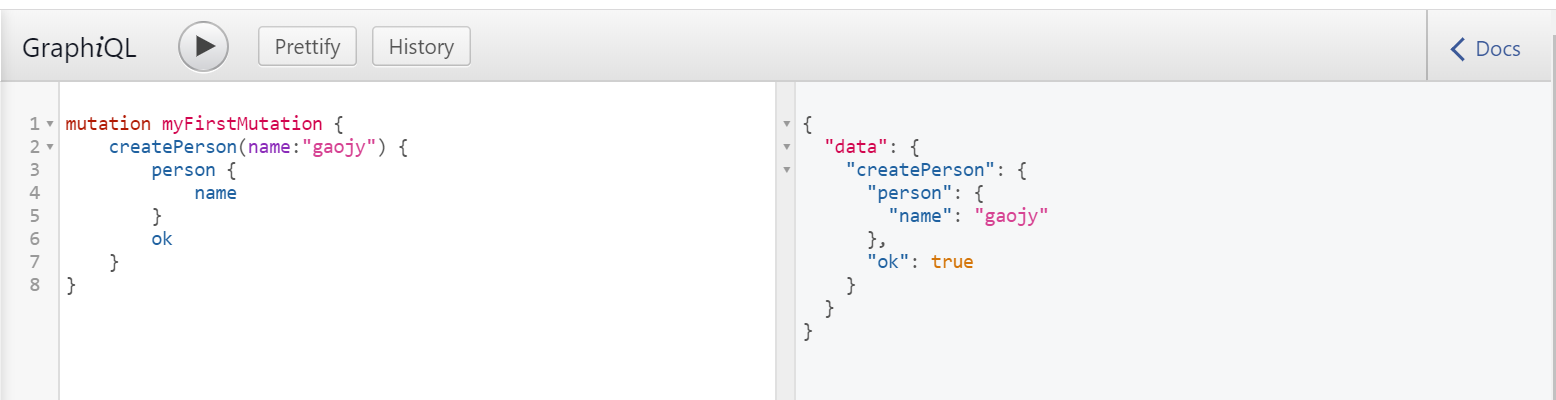
Mutation下可申明InputFields 和InputObjectTypes类型的出入参,其中InputFields可以定义复合型入参,Output可指定复合型出参。
例1:InputFields
class DataInput(graphene.InputObjectType):
user_name = String()
basic_age = Int() class Person(graphene.ObjectType):
name = graphene.String()
age = graphene.Int() # 具体的操作类
class CreatePerson(graphene.Mutation):
# 请求提交的参数,同样需要传递到mutate中
class Arguments:
data = DataInput(required=True) ok = graphene.Boolean()
person = graphene.Field(Person) def mutate(root, info, data):
person = Person(name=data.user_name, age=data.basic_age * 10)
ok = True
return CreatePerson(person=person, ok=ok)
执行结果:
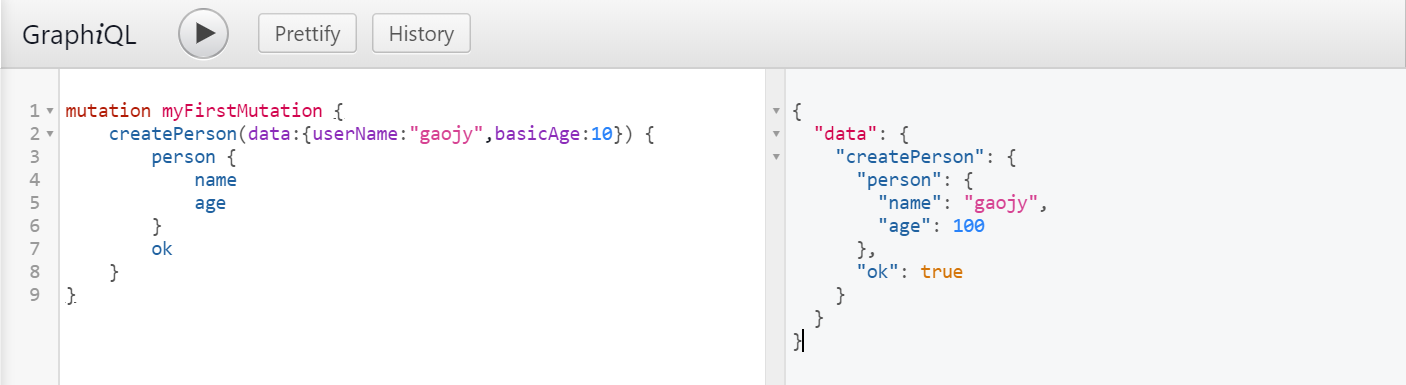
例2:InputObjectTypes
class DataInput(graphene.InputObjectType):
user_name = String()
basic_age = Int() class Person(graphene.ObjectType):
name = graphene.String()
age = graphene.Int() # 具体的操作类
class CreatePerson(graphene.Mutation):
# 请求提交的参数,同样需要传递到mutate中
class Arguments:
data = DataInput(required=True)
# 定义一个Output 且指定class ,在mutate方法中返回实例
Output = Person
def mutate(root, info, data):
person = Person(name=data.user_name, age=data.basic_age * 10)
return person
运行结果:
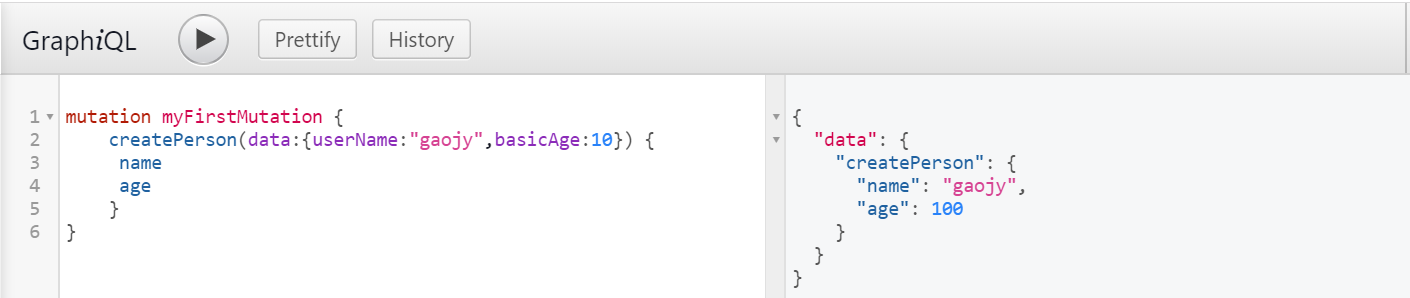
relay
relay类似于react js中的redux,VUE中的vuex,可以缓存server端数据,加快查询并提供更新机制。example可参考前言中的example。
小结
技术本身就是为业务服务,读者会问Graphql究竟可以使用在哪些业务场景呢?
官方有这么一句话ask exactly what you want.如果一个前端的接口只需要返回部分数据,而另一个前端接口也只需要返回部分数据,这两份数据有可能有交集,也可能没有。传统的做法可能需要开发两个接口或者一个接口内不断的if else来根据前端的具体场景去过滤某些数据。使用Graphql能够根据client指定需要哪些参数,后端scheme返回哪些参数,而后端只需要一个API可以查询到数据全集,Graphql可以自动完成数据解析,封装,过滤操作。
最新文章
- iOS学习23之事件处理
- elasticsearch Java API汇总
- jdk分析工具:jps和jstack
- iOS中 @synthesize 和 @dynamic 区别
- IE6和IE7的line-height和现代浏览器不一致的问题
- 兼容IE,Firefox,Opera等浏览器的添加到收藏夹js代码实现
- UI/UE对个性化推荐的影响
- sersync做实时同步(第二步)
- easyui combobox赋值
- flex-linkbutton
- SuperMapPy 批量拼接 GeoTiff影像
- PHP资源类型
- Caused by: java.io.FileNotFoundException: class path resource [applicationContext.xml] cannot be ope
- python datetime 与 time模块
- 关于datagrid中数据条件颜色问题
- 应用调试(四)系统调用SWI
- ide phpStorm更换主题
- 002-MVC布局页
- sdk(输入驱动物体 驱动属性 被驱动物体 被驱动属性 驱动数值 一键搞定驱动),当你的目标体很多展开会卡的时候使用这个
- vue源码分析—数据绑定