一致性检验评价方法kappa
最近在做眼底图像的无监督分类,使用的数据集辣子kaggle的Diabetic Retinopathy,简称DR,中文称糖尿病型眼底疾病。
最后的评估方法是二次加权kappa。以前没接触过,网上也没有具体的介绍,在这里简单谈谈我的理解,如有错误欢迎指出。
简介
Kappa指数用来衡量两个模型对同一张图片进行判断时,判断结果一致的程度,结果范围从0~1,1表示评价完全相同,0表示评价完全相反。
一般用模型获得相同评价的数量与基于可能性的期望是否有差别来分析,当两个模型相同评价的数量和基于可能性期望的数量基本一样时,kappa的值就接近于1。
举个栗子,模型A和基准的kappa:
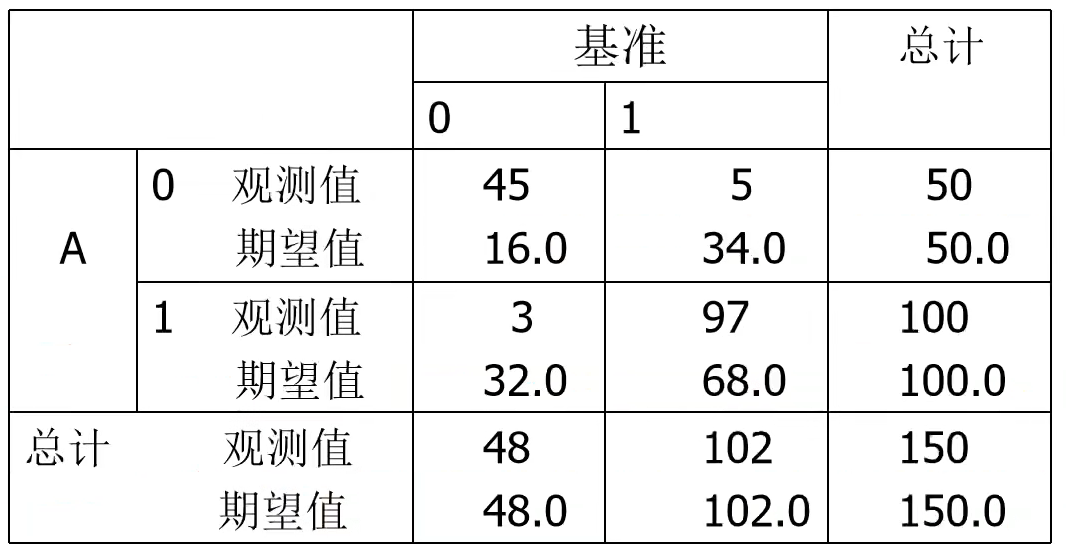
kappa = (p0-pe) / (n-pe)
其中,P0 = 对角线单元中观测值的总和;pe = 对角线单元中期望值的总和。
根据kappa的计算方法分为简单kappa(simple kappa)和加权kappa(weighted kappa),加权kappa又分为linear weighted kappa和quadratic weighted kappa。
weighted kappa
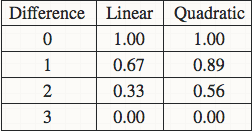
关于linear还是quadratic weighted kappa的选择,取决于你的数据集中不同class之间差异的意义。比如对于眼底图像识别的数据,class=0为健康,class=4为疾病晚期非常严重,所以对于把class=0预测成4的行为所造成的惩罚应该远远大于把class=0预测成class=1的行为,使用quadratic的话0->4所造成的惩罚就等于16倍的0->1的惩罚。如下图是一个四分类的两个计算方法的比较。
Python实现
参考:https://github.com/benhamner/Metrics/blob/master/Python/ml_metrics/quadratic_weighted_kappa.py
#! /usr/bin/env python2.7
import numpy as np
def confusion_matrix(rater_a, rater_b, min_rating=None, max_rating=None):
"""
Returns the confusion matrix between rater's ratings
"""
assert(len(rater_a) == len(rater_b))
if min_rating is None:
min_rating = min(rater_a + rater_b)
if max_rating is None:
max_rating = max(rater_a + rater_b)
num_ratings = int(max_rating - min_rating + 1)
conf_mat = [[0 for i in range(num_ratings)]
for j in range(num_ratings)]
for a, b in zip(rater_a, rater_b):
conf_mat[a - min_rating][b - min_rating] += 1
return conf_mat
def histogram(ratings, min_rating=None, max_rating=None):
"""
Returns the counts of each type of rating that a rater made
"""
if min_rating is None:
min_rating = min(ratings)
if max_rating is None:
max_rating = max(ratings)
num_ratings = int(max_rating - min_rating + 1)
hist_ratings = [0 for x in range(num_ratings)]
for r in ratings:
hist_ratings[r - min_rating] += 1
return hist_ratings
def quadratic_weighted_kappa(rater_a, rater_b, min_rating=None, max_rating=None):
"""
Calculates the quadratic weighted kappa
quadratic_weighted_kappa calculates the quadratic weighted kappa
value, which is a measure of inter-rater agreement between two raters
that provide discrete numeric ratings. Potential values range from -1
(representing complete disagreement) to 1 (representing complete
agreement). A kappa value of 0 is expected if all agreement is due to
chance.
quadratic_weighted_kappa(rater_a, rater_b), where rater_a and rater_b
each correspond to a list of integer ratings. These lists must have the
same length.
The ratings should be integers, and it is assumed that they contain
the complete range of possible ratings.
quadratic_weighted_kappa(X, min_rating, max_rating), where min_rating
is the minimum possible rating, and max_rating is the maximum possible
rating
"""
rater_a = np.array(rater_a, dtype=int)
rater_b = np.array(rater_b, dtype=int)
assert(len(rater_a) == len(rater_b))
if min_rating is None:
min_rating = min(min(rater_a), min(rater_b))
if max_rating is None:
max_rating = max(max(rater_a), max(rater_b))
conf_mat = confusion_matrix(rater_a, rater_b,
min_rating, max_rating)
num_ratings = len(conf_mat)
num_scored_items = float(len(rater_a))
hist_rater_a = histogram(rater_a, min_rating, max_rating)
hist_rater_b = histogram(rater_b, min_rating, max_rating)
numerator = 0.0
denominator = 0.0
for i in range(num_ratings):
for j in range(num_ratings):
expected_count = (hist_rater_a[i] * hist_rater_b[j]
/ num_scored_items)
d = pow(i - j, 2.0) / pow(num_ratings - 1, 2.0)
numerator += d * conf_mat[i][j] / num_scored_items
denominator += d * expected_count / num_scored_items
return 1.0 - numerator / denominator
def linear_weighted_kappa(rater_a, rater_b, min_rating=None, max_rating=None):
"""
Calculates the linear weighted kappa
linear_weighted_kappa calculates the linear weighted kappa
value, which is a measure of inter-rater agreement between two raters
that provide discrete numeric ratings. Potential values range from -1
(representing complete disagreement) to 1 (representing complete
agreement). A kappa value of 0 is expected if all agreement is due to
chance.
linear_weighted_kappa(rater_a, rater_b), where rater_a and rater_b
each correspond to a list of integer ratings. These lists must have the
same length.
The ratings should be integers, and it is assumed that they contain
the complete range of possible ratings.
linear_weighted_kappa(X, min_rating, max_rating), where min_rating
is the minimum possible rating, and max_rating is the maximum possible
rating
"""
assert(len(rater_a) == len(rater_b))
if min_rating is None:
min_rating = min(rater_a + rater_b)
if max_rating is None:
max_rating = max(rater_a + rater_b)
conf_mat = confusion_matrix(rater_a, rater_b,
min_rating, max_rating)
num_ratings = len(conf_mat)
num_scored_items = float(len(rater_a))
hist_rater_a = histogram(rater_a, min_rating, max_rating)
hist_rater_b = histogram(rater_b, min_rating, max_rating)
numerator = 0.0
denominator = 0.0
for i in range(num_ratings):
for j in range(num_ratings):
expected_count = (hist_rater_a[i] * hist_rater_b[j]
/ num_scored_items)
d = abs(i - j) / float(num_ratings - 1)
numerator += d * conf_mat[i][j] / num_scored_items
denominator += d * expected_count / num_scored_items
return 1.0 - numerator / denominator
def kappa(rater_a, rater_b, min_rating=None, max_rating=None):
"""
Calculates the kappa
kappa calculates the kappa
value, which is a measure of inter-rater agreement between two raters
that provide discrete numeric ratings. Potential values range from -1
(representing complete disagreement) to 1 (representing complete
agreement). A kappa value of 0 is expected if all agreement is due to
chance.
kappa(rater_a, rater_b), where rater_a and rater_b
each correspond to a list of integer ratings. These lists must have the
same length.
The ratings should be integers, and it is assumed that they contain
the complete range of possible ratings.
kappa(X, min_rating, max_rating), where min_rating
is the minimum possible rating, and max_rating is the maximum possible
rating
"""
assert(len(rater_a) == len(rater_b))
if min_rating is None:
min_rating = min(rater_a + rater_b)
if max_rating is None:
max_rating = max(rater_a + rater_b)
conf_mat = confusion_matrix(rater_a, rater_b,
min_rating, max_rating)
num_ratings = len(conf_mat)
num_scored_items = float(len(rater_a))
hist_rater_a = histogram(rater_a, min_rating, max_rating)
hist_rater_b = histogram(rater_b, min_rating, max_rating)
numerator = 0.0
denominator = 0.0
for i in range(num_ratings):
for j in range(num_ratings):
expected_count = (hist_rater_a[i] * hist_rater_b[j]
/ num_scored_items)
if i == j:
d = 0.0
else:
d = 1.0
numerator += d * conf_mat[i][j] / num_scored_items
denominator += d * expected_count / num_scored_items
return 1.0 - numerator / denominator
def mean_quadratic_weighted_kappa(kappas, weights=None):
"""
Calculates the mean of the quadratic
weighted kappas after applying Fisher's r-to-z transform, which is
approximately a variance-stabilizing transformation. This
transformation is undefined if one of the kappas is 1.0, so all kappa
values are capped in the range (-0.999, 0.999). The reverse
transformation is then applied before returning the result.
mean_quadratic_weighted_kappa(kappas), where kappas is a vector of
kappa values
mean_quadratic_weighted_kappa(kappas, weights), where weights is a vector
of weights that is the same size as kappas. Weights are applied in the
z-space
"""
kappas = np.array(kappas, dtype=float)
if weights is None:
weights = np.ones(np.shape(kappas))
else:
weights = weights / np.mean(weights)
# ensure that kappas are in the range [-.999, .999]
kappas = np.array([min(x, .999) for x in kappas])
kappas = np.array([max(x, -.999) for x in kappas])
z = 0.5 * np.log((1 + kappas) / (1 - kappas)) * weights
z = np.mean(z)
return (np.exp(2 * z) - 1) / (np.exp(2 * z) + 1)
def weighted_mean_quadratic_weighted_kappa(solution, submission):
predicted_score = submission[submission.columns[-1]].copy()
predicted_score.name = "predicted_score"
if predicted_score.index[0] == 0:
predicted_score = predicted_score[:len(solution)]
predicted_score.index = solution.index
combined = solution.join(predicted_score, how="left")
groups = combined.groupby(by="essay_set")
kappas = [quadratic_weighted_kappa(group[1]["essay_score"], group[1]["predicted_score"]) for group in groups]
weights = [group[1]["essay_weight"].irow(0) for group in groups]
return mean_quadratic_weighted_kappa(kappas, weights=weights)
最新文章
- 《CLR.via.C#第三版》第二部分第13章节 接口 读书笔记(七)
- C#并行编程-Parallel
- android 中layer-list的用法
- DBHelper (支持事务与数据库变更)
- ng-bind,ng-cloak优化数据显示
- BIEE从底层表结构向上更新
- HTML中解决双击会选中文本的问题
- php加了命名空间没引入初始化文件:类的命名空间要与文件夹名一致namespace Business\Event;缺少了Event
- 向SharePoint页面添加后台代码
- ueditor之ruby on rails 版
- myeclipse 8.5打开文件Could not open the editor: Invalid thread access 异常
- Flink资料(2)-- 数据流容错机制
- OC中@class的使用
- 小白的Python之路 day4 迭代器
- junit4X系列--Builder、Request与JUnitCore
- pytest进阶之配置文件
- opencv使用总结
- 【评分】BETA 版冲刺前准备
- python 获取列表中次大的数值.
- linux 强制删除杀死进程 sudo pkill uwsgi -9 杀死uwsgi 关闭防火墙 iptables -F