伤透了心的pytorch的cuda容器版
公司GPU的机器版本本比较低,找了好多不同的镜像都不行,
自己从anaconda开始制作也没有搞定(因为公司机器不可以直接上网),
哎,官网只有使用最新的NVIDIA驱动,安装起来才顺利。
最后,找到一个暂时可用的镜像:
https://linux.ctolib.com/anibali-docker-pytorch.html
其间遇到两个问题:
1, 安装全没出错,但torch.cuda.is_available()为False,这表示torch还是不能使用GPU。
2,在跑例程时,显示RuntimeError: CUDA error: out of memory,这表示运行的时候使用CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES限制一下使用的GPU。
PyTorch Docker image
Ubuntu + PyTorch + CUDA (optional)
Requirements
In order to use this image you must have Docker Engine installed. Instructions for setting up Docker Engine are available on the Docker website.
CUDA requirements
If you have a CUDA-compatible NVIDIA graphics card, you can use a CUDA-enabled version of the PyTorch image to enable hardware acceleration. I have only tested this in Ubuntu Linux.
Firstly, ensure that you install the appropriate NVIDIA drivers and libraries. If you are running Ubuntu, you can install proprietary NVIDIA drivers from the PPA and CUDA from the NVIDIA website.
You will also need to install nvidia-docker2 to enable GPU device access within Docker containers. This can be found at NVIDIA/nvidia-docker.
Prebuilt images
Pre-built images are available on Docker Hub under the name anibali/pytorch. For example, you can pull the CUDA 10.0 version with:
$ docker pull anibali/pytorch:cuda-10.0
The table below lists software versions for each of the currently supported Docker image tags available for anibali/pytorch.
| Image tag | CUDA | PyTorch |
|---|---|---|
no-cuda |
None | 1.0.0 |
cuda-10.0 |
10.0 | 1.0.0 |
cuda-9.0 |
9.0 | 1.0.0 |
cuda-8.0 |
8.0 | 1.0.0 |
The following images are also available, but are deprecated.
| Image tag | CUDA | PyTorch |
|---|---|---|
cuda-9.2 |
9.2 | 0.4.1 |
cuda-9.1 |
9.1 | 0.4.0 |
cuda-7.5 |
7.5 | 0.3.0 |
Usage
Running PyTorch scripts
It is possible to run PyTorch programs inside a container using the python3 command. For example, if you are within a directory containing some PyTorch project with entrypoint main.py, you could run it with the following command:
docker run --rm -it --init \ --runtime=nvidia \ --ipc=host \ --user="$(id -u):$(id -g)" \ --volume="$PWD:/app" \ -e NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 \ anibali/pytorch python3 main.py
Here's a description of the Docker command-line options shown above:
--runtime=nvidia: Required if using CUDA, optional otherwise. Passes the graphics card from the host to the container.--ipc=host: Required if using multiprocessing, as explained at https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch#docker-image.--user="$(id -u):$(id -g)": Sets the user inside the container to match your user and group ID. Optional, but is useful for writing files with correct ownership.--volume="$PWD:/app": Mounts the current working directory into the container. The default working directory inside the container is/app. Optional.-e NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0: Sets an environment variable to restrict which graphics cards are seen by programs running inside the container. Set toallto enable all cards. Optional, defaults to all.
You may wish to consider using Docker Compose to make running containers with many options easier. At the time of writing, only version 2.3 of Docker Compose configuration files supports the runtimeoption.
Running graphical applications
If you are running on a Linux host, you can get code running inside the Docker container to display graphics using the host X server (this allows you to use OpenCV's imshow, for example). Here we describe a quick-and-dirty (but INSECURE) way of doing this. For a more comprehensive guide on GUIs and Docker check out http://wiki.ros.org/docker/Tutorials/GUI.
On the host run:
sudo xhost +local:root
You can revoke these access permissions later with sudo xhost -local:root. Now when you run a container make sure you add the options -e "DISPLAY" and --volume="/tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix:rw". This will provide the container with your X11 socket for communication and your display ID. Here's an example:
docker run --rm -it --init \ --runtime=nvidia \ -e "DISPLAY" --volume="/tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix:rw" \ anibali/pytorch python3 -c "import tkinter; tkinter.Tk().mainloop()"
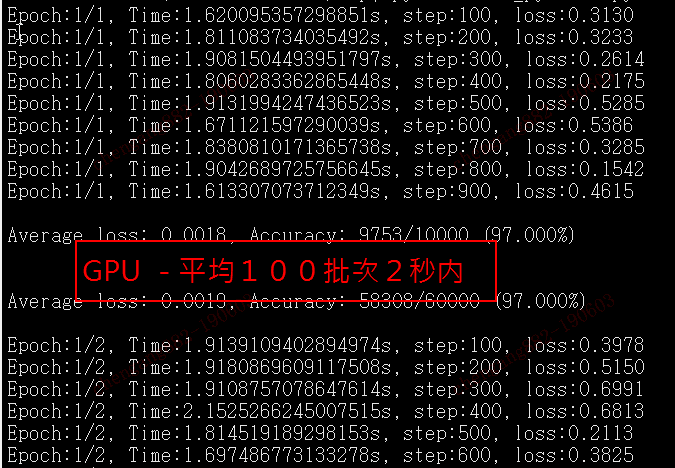
十倍的时间差距:

最新文章
- C# 基于json通讯中的中文的处理
- HDU 4888 Redraw Beautiful Drawings(2014 Multi-University Training Contest 3)
- cshell学习
- WebView 获取网页点击事件
- linux 病毒 sfewfesfs
- linux scp 服务器远程拷贝
- PHP开发套件
- JNA入门实例
- 初识google多语言通信框架gRPC系列(二)编译gRPC
- 关于JavaScript简单描述
- SQL之trigger(触发器)
- Modbus库开发笔记之四:Modbus TCP Client开发
- 论文阅读笔记三十八:Deformable Convolutional Networks(ECCV2017)
- 过滤器(Filter)与拦截器(Interceptor)区别
- (三)MongoDB数据库注意
- 【BZOJ】【2626】JZPFAR
- driver.get()和driver.navigate().to()到底有什么不同?-----Selenium快速入门(四)
- 关于hashcode 里面 使用31 系数的问题
- python学习 (三十) python的函数
- [国家集训队]最长双回文串 manacher