第十六节,卷积神经网络之AlexNet网络实现(六)
上一节内容已经详细介绍了AlexNet的网络结构。这节主要通过Tensorflow来实现AlexNet。
这里做测试我们使用的是CIFAR-10数据集介绍数据集,关于该数据集的具体信息可以通过以下链接查看:
https://blog.csdn.net/davincil/article/details/78793067
下面粗略的介绍一下CIFAR-10数据集。
一 CIFAR-10数据集
CIFAR-10数据集由10类32x32的彩色图片组成,一共包含60000张图片,每一类包含6000图片。其中50000张图片作为训练集,10000张图片作为测试集。
CIFAR-10数据集被划分成了5个训练的batch和1个测试的batch,每个batch均包含10000张图片。测试集batch的图片是从每个类别中随机挑选的1000张图片组成的,训练集batch以随机的顺序包含剩下的50000张图片。不过一些训练集batch可能出现包含某一类图片比其他类的图片数量多的情况。训练集batch包含来自每一类的5000张图片,一共50000张训练图片。
数据集下载地址:http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar-10-python.tar.gz
文件下载后,解压cifar-10-batches-py到我们py问价所在的目录下,打开该文件夹,我们会看到有如下文件:

其中每个文件的作用如下:
batches.meta 程序中不需要使用该文件
data_batch_1 训练集的第一个batch,含有10000张图片
data_batch_2 训练集的第二个batch,含有10000张图片
data_batch_3 训练集的第三个batch,含有10000张图片
data_batch_4 训练集的第四个batch,含有10000张图片
data_batch_5 训练集的第五个batch,含有10000张图片
readme.html 网页文件,程序中不需要使用该文件
test_batch 测试集的batch,含有10000张图片
上述文件结构中,每一个batch文件包含一个python的字典(dict)结构,结构如下:
b'data’ 是一个10000x3072的array,每一行的元素组成了一个32x32的3通道图片,共10000张
b'labels’ 一个长度为10000的list,对应包含data中每一张图片的 label
b'batch_label' 这一份batch的名称
b'filenames' 一个长度为10000的list,对应包含data中每一张图片的名称
由于数据集比较大,在训练的时候如果把所有数据一次性加载到内存训练,会出现内容不足的问题,因此先从batch中读取所有图片的数据,以及每一张图片对应的标签,然后我们创建一个文件夹叫做CIFAR-10-data,在这个文件夹下面创建train和test文件夹,然后在每个文件夹下面创建名称从0-9的文件夹,我们利用OpenCV把每一张图片保存在对应文件夹下面。后面再创建两个文件,一个叫做CIFAR-10-test-label.pkl,另一个叫做CIFAR-10-train-label.pkl,均保存由如下元组:(测试集或训练集的图片路径,以及对应标签)组成的list集合。
save_image()函数执行上面所述的功能:
- 创建一个文件夹 CIFAR-10-data 包含两个子文件夹test,train
- 在子文件夹创建10个文件夹 文件名依次为0-9 对应10个类别
- 训练集数据生成bmp格式文件,存在对应类别的文件下
- 测试集数据生成bmp格式文件,存在对应类别的文件下
- 生成两个文件train_label.pkl,test_label.pkl 分别保存相应的图片文件路径以及对应的标签
执行完save_image()函数,会生成如下文件:




datagenerator.py文件代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Wed Apr 11 14:51:27 2018 @author: Administrator
""" '''
用于加载数据集合
数据集下载地址:http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar-10-python.tar.gz
CIFAR-10数据集介绍:https://blog.csdn.net/davincil/article/details/78793067 一、CIFAR-10
CIFAR-10数据集由10类32x32的彩色图片组成,一共包含60000张图片,每一类包含6000图片。其中50000张图片作为训练集,10000张图片作为测试集。 CIFAR-10数据集被划分成了5个训练的batch和1个测试的batch,每个batch均包含10000张图片。
测试集batch的图片是从每个类别中随机挑选的1000张图片组成的,一共10000张测试图片,
训练集batch包含来自每一类的5000张图片,一共50000张训练图片。
训练集batch以随机的顺序包含剩下的50000张图片。
不过一些训练集batch可能出现包含某一类图片比其他类的图片数量多的情况。 ''' ''' 文件下载之后,解压 主要包括以下文件
名称 作用
batches.meta 程序中不需要使用该文件
data_batch_1 训练集的第一个batch,含有10000张图片
data_batch_2 训练集的第二个batch,含有10000张图片
data_batch_3 训练集的第三个batch,含有10000张图片
data_batch_4 训练集的第四个batch,含有10000张图片
data_batch_5 训练集的第五个batch,含有10000张图片
readme.html 网页文件,程序中不需要使用该文件
test_batch 测试集的batch,含有10000张图片 上述文件结构中,每一个batch文件包含一个python的字典(dict)结构,结构如下:
名称 作用
b'data’ 是一个10000x3072的array,每一行的元素组成了一个32x32的3通道图片,共10000张
b'labels’ 一个长度为10000的list,对应包含data中每一张图片的label
b'batch_label' 这一份batch的名称
b'filenames' 一个长度为10000的list,对应包含data中每一张图片的名称 ''' import pickle
import numpy as np
import cv2
from skimage import io class datagenerator(object):
def __init__(self):
pass def unpickle(self,filename):
'''
batch文件中真正重要的两个关键字是data和labels
反序列化出对象 每一个batch文件包含一个python的字典(dict)结构,结构如下:
名称 作用
b'data’ 是一个10000x3072的array,每一行的元素组成了一个32x32的3通道图片,共10000张
b'labels’ 一个长度为10000的list,对应包含data中每一张图片的label
b'batch_label' 这一份batch的名称
b'filenames' 一个长度为10000的list,对应包含data中每一张图片的名称
'''
with open(filename,'rb') as f:
#默认把字节转换为ASCII编码 这里设置encoding='bytes'直接读取字节数据 因为里面含有图片像素数据 大小从0-255 不能解码为ascii编码,因此先转换成字节类型 后面针对不同项数据再解码,转换为字符串
dic = pickle.load(f,encoding='bytes')
return dic def get_image(self,image):
'''
提取每个通道的数据,进行重新排列,最后返回一张32x32的3通道的图片 在字典结构中,每一张图片是以被展开的形式存储(即一张32x32的3通道图片被展开成了3072长度的list),
每一个数据的格式为uint8,前1024个数据表示红色通道,接下来的1024个数据表示绿色通道,最后的1024
个通道表示蓝色通道。
image:每一张图片的数据 数据按照R,G,B通道依次排列 长度为3072
'''
assert len(image) == 3072
#对list进行切片操作,然后reshape
r = image[:1024].reshape(32,32,1)
g = image[1024:2048].reshape(32,32,1)
b = image[2048:].reshape(32,32,1) #numpy提供了numpy.concatenate((a1,a2,...), axis=0)函数。能够一次完成多个数组的拼接。其中a1,a2,...是数组类型的参数
#沿着某个轴拼接,默认为列方向(axis=0)
img = np.concatenate((r,g,b),-1)
return img def get_data_by_keyword(self,keyword,filelist=[],normalized=False,size=(32,32),one_hot=False):
'''
按照给出的关键字提取batch中的数据(默认是训练集的所有数据) args:
keyword:'data’ 或 'labels’ 或 'batch_label' 或 'filenames' 表示需要返回的项
filelist:list 表示要读取的文件集合
normalized:当keyword = 'data',表示是否需要归一化
size:当keyword = 'data',表示需要返回的图片的尺寸
one_hot:当keyword = 'labels'时,one_hot=Flase,返回实际标签 True时返回二值化后的标签 return:
keyword = 'data' 返回像素数据
keyword = 'labels' 返回标签数据
keyword = 'batch_label' 返回batch的名称
keyword = 'filenames' 返回图像文件名 ''' #keyword编码为字节
keyword = keyword.encode('ascii')
assert keyword in [b'data',b'labels',b'batch_label',b'filenames']
assert type(filelist) is list and len(filelist) != 0
assert type(normalized) is bool
assert type(size) is tuple or type(size) is list ret = [] for i in range(len(filelist)):
#反序列化出对象
dic = self.unpickle(filelist[i]) if keyword == b'data':
#b'data’ 是一个10000x3072的array,每一行的元素组成了一个32x32的3通道图片,共10000张
#合并成一个数组
for item in dic[b'data']:
ret.append(item)
print('总长度:',len(ret)) elif keyword == b'labels':
#b'labels’ 一个长度为10000的list,对应包含data中每一张图片的label
#合并成一个数组
for item in dic[b'labels']:
ret.append(item) elif keyword == b'batch_label':
#b'batch_label' 这一份batch的名称
#合并成一个数组
for item in dic[b'batch_label']:
ret.append(item.decode('ascii')) #把数据转换为ascii编码 else:
#b'filenames' 一个长度为10000的list,对应包含data中每一张图片的名称
#合并成一个数组
for item in dic[b'filenames']:
ret.append(item.decode('ascii')) #把数据转换为ascii编码 if keyword == b'data':
if normalized == False:
array = np.ndarray([len(ret),size[0],size[1],3],dtype = np.float32)
#遍历每一张图片数据
for i in range(len(ret)):
#图像进行缩放
array[i] = cv2.resize(self.get_image(ret[i]),size)
return array else:
array = np.ndarray([len(ret),size[0],size[1],3],dtype = np.float32)
#遍历每一张图片数据
for i in range(len(ret)):
array[i] = cv2.resize(self.get_image(ret[i]),size)/255
return array
pass elif keyword == b'labels':
#二值化标签
if one_hot == True:
#类别
depth = 10
m = np.zeros([len(ret),depth])
for i in range(len(ret)):
m[i][ret[i]] = 1
return m
pass
#其它keyword直接返回
return ret import os
import pickle def save_images():
'''
报CIFAR-10数据集图片提取出来保存下来
1.创建一个文件夹 CIFAR-10-data 包含两个子文件夹test,train
2.在文革子文件夹创建10个文件夹 文件名依次为0-9 对应10个类别
3.训练集数据生成bmp格式文件,存在对应类别的文件下
4.测试集数据生成bmp格式文件,存在对应类别的文件下
5 生成两个文件train_label.pkl,test_label.pkl 分别保存相应的图片文件路径以及对应的标签
''' #根目录
root = 'CIFAR-10-data' #如果存在该目录 说明数据存在
if os.path.isdir(root):
print(root+'目录已经存在!')
return '''
如果文件夹不存在 创建文件夹
'''
#'data'目录不存在,创建目录
os.mkdir(root) #创建文件失败
if not os.path.isdir(root):
print(root+'目录创建失败!')
return #创建'test'和'train'目录 以及子文件夹
train = os.path.join(root,'train')
os.mkdir(train)
if os.path.isdir(train):
for i in range(10):
name = os.path.join(train,str(i))
os.mkdir(name) test = os.path.join(root,'test')
os.mkdir(test)
if os.path.isdir(test):
for i in range(10):
name = os.path.join(test,str(i))
os.mkdir(name) '''
把训练集数据转换为图片
'''
data_dir = 'cifar-10-batches-py' #数据所在目录 filelist = []
for i in range(5):
name = os.path.join(data_dir,str('data_batch_%d'%(i+1)))
filelist.append(name) data = datagenerator()
#获取训练集数据
train_x = data.get_data_by_keyword('data',filelist,
normalized=True,size=(32,32)) #标签
train_y = data.get_data_by_keyword('labels',filelist) #读取图片文件名
train_filename = data.get_data_by_keyword('filenames',filelist) #保存训练集的文件名和标签
train_file_labels = [] #保存图片
for i in range(len(train_x)):
#获取图片标签
y = int(train_y[i]) #文件保存目录
dir_name = os.path.join(train,str(y)) #获取文件名
file_name = train_filename[i] #文件的保存路径
file_path = os.path.join(dir_name,file_name) #保存图片
io.imsave(file_path,train_x[i]) #追加第i张图片路径和标签 (文件路径,标签)
train_file_labels.append((file_path,y)) if i % 1000 == 0:
print('训练集完成度{0}/{1}'.format(i,len(train_x))) for i in range(10):
print('训练集前10张图片:',train_file_labels[i]) #保存训练集的文件名和标签
with open('CIFAR-10-train-label.pkl','wb') as f:
pickle.dump(train_file_labels,f) print('训练集图片保存成功!\n') '''
把测试集数据转换为图片
'''
filelist = [os.path.join(data_dir,'test_batch')] #获取训练集数据 数据标准化为0-1之间
test_x = data.get_data_by_keyword('data',filelist,
normalized=True,size=(32,32)) #标签
test_y = data.get_data_by_keyword('labels',filelist) #读取图片文件名
test_filename = data.get_data_by_keyword('filenames',filelist) #保存测试卷的文件名和标签
test_file_labels = [] #保存图片
for i in range(len(test_x)):
#获取图片标签
y = int(test_y[i]) #文件保存目录
dir_name = os.path.join(test,str(y)) #获取文件名
file_name = test_filename[i] #文件的保存路径
file_path = os.path.join(dir_name,file_name) #保存图片 这里要求图片像素值在-1-1之间,所以在获取数据的时候做了标准化
io.imsave(file_path,test_x[i]) #追加第i张图片路径和标签 (文件路径,标签)
test_file_labels.append((file_path,y)) if i % 1000 == 0:
print('测试集完成度{0}/{1}'.format(i,len(test_x))) print('测绘集图片保存成功!\n') #保存测试卷的文件名和标签
with open('CIFAR-10-test-label.pkl','wb') as f:
pickle.dump(test_file_labels,f) for i in range(10):
print('测试集前10张图片:',test_file_labels[i]) def load_data():
'''
加载数据集
返回训练集数据和测试卷数据
training_data 由(x,y)元组组成的list集合
x:图片路径
y:对应标签
'''
#加载使用的训练集文件名和标签 [(文件路径,标签),....]
with open('CIFAR-10-train-label.pkl','rb') as f:
training_data = pickle.load(f) #加载使用的测试集文件名和标签
with open('CIFAR-10-test-label.pkl','rb') as f:
test_data = pickle.load(f) return training_data,test_data def get_one_hot_label(labels,depth):
'''
把标签二值化 返回numpy.array类型 args:
labels:标签的集合
depth:标签总共有多少类
'''
m = np.zeros([len(labels),depth])
for i in range(len(labels)):
m[i][labels[i]] = 1
return m def get_image_data_and_label(value,image_size='NONE',depth=10,one_hot = False):
'''
获取图片数据,以及标签数据 注意每张图片维度为 n_w x n_h x n_c args:
value:由(x,y)元组组成的numpy.array类型
x:图片路径
y:对应标签
image_size:图片大小 'NONE':不改变图片尺寸
one_hot:把标签二值化
depth:数据类别个数
'''
#图片数据集合
x_batch = []
#图片对应的标签集合
y_batch = []
#遍历每一张图片
for image in value:
if image_size == 'NONE':
x_batch.append(cv2.imread(image[0])/255) #标准化0-1之间
else:
x_batch.append(cv2.resize(cv2.imread(image[0]),image_size)/255)
y_batch.append(image[1]) if one_hot == True:
#标签二值化
y_batch = get_one_hot_label(y_batch,depth)
return np.asarray(x_batch,dtype=np.float32),np.asarray(y_batch,dtype=np.float32) '''
测试 保存所有图片
'''
save_images()
二 使用传统神经网络训练
在使用AlexNet网络进行训练之前,我们先使用传统network进行训练,这里我们设置网络为4层,包括输入层在内,每一层神经元个数如下3072,7200,1024,10。
我们在训练的时候,每次随机读取batch_size大小的图片数据进行训练。
传统network的实现,我是通过定义一个单独的类来完成该功能。network.py文件代码如下
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Mon Apr 2 10:32:10 2018 @author: Administrator
""" '''
定义一个network类,实现全连接网络
''' import datagenerator
import os
from tensorflow.python import pywrap_tensorflow def get_one_hot_label(labels,depth):
'''
把标签二值化 args:
labels:标签的集合
depth:标签总共有多少类
'''
m = np.zeros([len(labels),depth])
for i in range(len(labels)):
m[i][labels[i]] = 1
return m import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import random
import pickle class network(object):
'''
全连接神经网络
'''
def __init__(self,sizes,param_path= None):
'''
注意程序中op变量只需要初始化一遍就可以,在fit()中初始化 args:
sizes:list传入每层神经元个数
param_path:是否从指定文件加载模型,None:重新训练 否则指定模型路径 必须指定路径./或者绝对路径
'''
#保存参数
self.__sizes = sizes
#神经网络每一层的神经元个数数组类型
self.sizes = tf.placeholder(tf.int64,shape=[1,len(sizes)])
#计算神经网络层数 包括输入层
self.num_layer = tf.size(self.sizes) #输入样本和输出类别变量
self.x_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=[None,sizes[0]])
self.y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=[None,sizes[-1]]) #设置tensorflow对GPU使用按需分配
config = tf.ConfigProto()
config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
self.sess = tf.InteractiveSession(config=config) file_exist = False
#如果已经存在保存的模型 加载之前保存的w和b
if not param_path is None:
if os.path.isfile(param_path):
with open(param_path,'rb') as f:
dic = pickle.load(f)
weights = dic['weightes']
biases = dic['biases']
file_exist = True if file_exist:
#使用保存的数据初始化 第i层和i+1层之间的权重向量
self.weights = [self.weight_variable(shape=(x,y),value = weights[i]) for x,y,i in zip(sizes[:-1],sizes[1:],range(len(sizes)-1))]
#使用保存的数据初始化 第i层的偏置向量 i=1...num_layers 注意不可以设置shape=(x,1)
self.biases = [self.bias_variable(shape=[x,],value = biases[i]) for x,i in zip(sizes[1:],range(len(sizes)-1))]
print('成功加载参数数据!')
else:
#使用高斯正态分布初始化 第i层和i+1层之间的权重向量
self.weights = [self.weight_variable(shape=(x,y)) for x,y in zip(sizes[:-1],sizes[1:])]
#使用高斯正态分布初始化 第i层的偏置向量 i=1...num_layers 注意不可以设置shape=(x,1)
self.biases = [self.bias_variable(shape=[x,]) for x in sizes[1:]]
print('重新初始化模型参数!') '''这一段代码是使用tensorflow Saver对象保存 但是在取数据时候总是失败,因此不再使用这中方法
#如果已经存在保存的模型 加载之前保存的w和b
if not model_path is None: file = model_path+'.meta'
#print(file)
#文件存在 则直接加载
if os.path.isfile(file):
#加载以前保存的网络 将保存在.meta文件中的图添加到当前的图中
self.new_saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph(file)
#从指定目录下获取最近一次检查点
self.new_saver.restore(self.sess,tf.train.latest_checkpoint(os.path.dirname(file)))
#使用加载的模型
graph = tf.get_default_graph()
#恢复w和b
self.weights = [graph.get_tensor_by_name( 'network_w'+str(i)+':0') for i in range(1,len(sizes))]
self.biases = [graph.get_tensor_by_name( 'network_b'+str(i)+':0') for i in range(1,len(sizes))] print('成功从模型恢复数据!')
sh = [self.sess.run(i).shape for i in self.weights]
print('权重维度:',sh) file_exist = True #不存在 再新创建
if not file_exist:
#随机初始化权重 第i层和i+1层之间的权重向量
self.weights = [self.weight_variable(shape=(x,y),name='network_w'+str(i)) for x,y,i in zip(sizes[:-1],sizes[1:],range(1,len(sizes)))]
#随机初始化偏置 第i层的偏置向量 i=1...num_layers 注意不可以设置shape=(x,1)
self.biases = [self.bias_variable(shape=[x,],name='network_b'+str(i)) for x,i in zip(sizes[1:],range(1,len(sizes)))]
print('重新初始化模型参数!') #创建Saver op用于保存新的训练参数 指定保存哪些变量,如果全部保存,在恢复时,会有错误 主要是由于偏置和权重我保存在了一个dict中引起的
param =[w for w in self.weights]
for i in self.biases:
param.append(i)
self.saver = tf.train.Saver(param)''' def weight_variable(self,shape,value=None,name=None):
'''
初始化权值
'''
if value is None:
#使用截断式正太分布初始化权值 截断式即在正态分布基础上加以限制,以使生产的数据在一定范围上
value = tf.truncated_normal(shape,mean=0.0,stddev= 1.0/shape[0]) #方差为1/nin if name is None:
return tf.Variable(value)
else:
return tf.Variable(value,name=name) def bias_variable(self,shape,value=None,name=None):
'''
#初始化偏重
'''
if value is None:
value = tf.truncated_normal(shape,mean=0.0,stddev= 1.0/shape[0]) #方差为1/nin if name is None:
return tf.Variable(value)
else:
return tf.Variable(value,name=name) def feedforward(self,x):
'''
构建阶段:前向反馈
x:变量op,tf.placeholder()类型变量
返回一个op
'''
#计算隐藏层
output = x
for i in range(len(self.__sizes)-1):
b = self.biases[i]
w = self.weights[i]
if i != len(self.__sizes)-2 :
output = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(output,w) + b)
else:
output = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(output,w) + b)
return output def fit(self,training_data,learning_rate=0.001,batch_size=64,epoches=10):
'''
训练神经网络
training_data (x,y)元祖组成的list
x:训练集图片数据路径
y:训练集样本对应的标签
learning_rate:学习率
batch_size:批量大小
epoches:迭代轮数
'''
#计算输出层
output = self.feedforward(self.x_) #代价函数 J =-(Σy.logaL)/n .表示逐元素乘
cost = tf.reduce_mean( -tf.reduce_sum(self.y_*tf.log(output),axis = 1)) #求解
train = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost) #使用会话执行图 #初始化变量 必须在train之后 变量出事后化之后才可以显示相关属性
self.sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
sh = [self.sess.run(i).shape for i in self.weights]
print('权重维度:',sh) #训练集长度
n_train =len(training_data) #开始迭代
for i in range(epoches):
#打乱训练集
random.shuffle(training_data)
#分组
mini_batchs = [training_data[k:k+batch_size] for k in range(0,n_train,batch_size)] #遍历每一个mini_batch
for mini_batch in mini_batchs:
x_batch,y_batch = datagenerator.get_image_data_and_label(mini_batch,one_hot=True)
#每张图片数据展开正一列
x_batch = x_batch.reshape(len(mini_batch),-1)
train.run(feed_dict={self.x_:x_batch,self.y_:y_batch}) '''
#计算每一轮迭代后在整个训练集的误差 并打印
'''
train_cost_sum = []
train_accuracy_sum = []
#遍历每一个mini_batch
for mini_batch in mini_batchs:
train_cost = cost.eval(feed_dict={self.x_:x_batch,self.y_:y_batch})
train_cost_sum.append(train_cost)
train_accuracy = self.accuracy(x_batch,y_batch)
train_accuracy_sum.append(train_accuracy)
print('Epoch {0} Training set cost {1} accuracy {2}:'.format(i,np.mean(train_cost),np.mean(train_accuracy))) def predict(self,test_x):
'''
对输入test_x样本进行预测(图片数据) nxm维 n为样本个数 m为数据长度
'''
output = self.feedforward(self.x_)
#使用会话执行图
return output.eval(feed_dict={self.x_:test_x}) def accuracy(self,x,y):
'''
返回值准确率
x:测试样本集合(图片数据) nxm维 n为样本个数 m为数据长度
y:测试类别集合 也是二值化的标签
'''
output = self.feedforward(self.x_)
correct = tf.equal(tf.argmax(output,1),tf.argmax(self.y_,1)) #返回一个数组 表示统计预测正确或者错误
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct,tf.float32)) #求准确率
#使用会话执行图
return accuracy.eval(feed_dict={self.x_:x,self.y_:y}) def cost(self,x,y):
'''
计算代价值
x:样本集合(图片数据) nxm维 n为样本个数 m为数据长度
y:类别集合 也是二值化的标签
'''
#计算输出层
output = self.feedforward(self.x_)
#代价函数 J =-(Σy.logaL)/n .表示逐元素乘
cost = tf.reduce_mean( -tf.reduce_sum(self.y_*tf.log(output),axis = 1))
#使用会话执行图
return cost.eval(feed_dict={self.x_:x,self.y_:y}) def remove_model_file(self,file):
'''
删除保存的模型文件
删除成功返回True 否则返回 False args:
file:模型文件名
'''
path = [file+item for item in ('.index','.meta')]
path.append(os.path.join( os.path.dirname(path[0]),'checkpoint'))
for f in path:
if os.path.isfile(f):
os.remove(f)
ret = True
#检查文件是否存在
for f in path:
if os.path.isfile(f):
ret = False
return ret def save_model(self,file):
'''
保存模型 args:
file:保存文件名
'''
'''
#先删除之前的模型数据
if self.remove_model_file(file) == True:
self.saver.save(self.sess,file)
print('模型保存成功!')''' #把参数序列化并保存
weights = [item.eval() for item in self.weights]
biases = [item.eval() for item in self.biases]
dic = {'weightes':weights,'biases':biases}
with open(file,'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(dic,f)
print('模型参数保存成功!') def global_variables_initializer(self):
'''
全局张量初始化,由于全局变量只在fit()训练时进行初始化,如果我们直接加载已经训练好的数据
就不需要调用fit()函数,因此只有收到调用这个函数就行初始化权重和偏置以及其他张量
然后才可以执行图 如accuracy()等等
'''
self.sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
然后我们使用该网络进行测试,并且把测试后的权重和偏置保存在指定文件,下次可以使用该数据初始化,然后继续训练
- 我们先读取CIFAR-10-train-label.pkl,获取每张的训练图片路径以及标签组成的元组,保存在一个字典中
- 我们先把该字典打乱,然后选择batch_size张图片,读取图片,以及one_hot(二值化)标签,组成一个mini_batch
- 使用mini_batch进行训练
- 迭代字典中的所有数据,迭代完一轮,我们继续迭代,直至到我们设置的迭代轮数
在这里有个地方需要注意:由于我们每次都是从指定路径读取图片,因此速度比较慢,其实我们可以利用get_data_by_keyword()函数一次性读取所有数据和标签,然后保存在内存中,然后每次选择batch_size数据进行训练。这样就避免了每次从硬盘读取图片数据。这里我们取数据的时候可以先设置一个训练集大小的索引字典,然后打乱该字典,我们每次把batch_size个字典元素,传给数据,这样我们就可以达到随机取数据的目的。
# 生成并打乱训练集的顺序。
indices = np.arange(50000)
random.shuffle(indices)
测试代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Wed Apr 11 16:42:09 2018
@author: Administrator
"""
'''
用于训练network网络
由于内存有限,不能一次读取所有的数据,因此采用每次读取小批量的图片
1.在datagenerator.py文件中 把所有图片保存成bmp格式文件
2.存储一个dict字典,每个元素为 (图片的相对路径,标签),将这个字典序列化保存到文件
3.读取该文件,把元组顺序打乱,分成多组,每次加载mini_batch个图片进行训练
''' import tensorflow as tf
from alexnet import alexnet
import datagenerator
import numpy as np
#import cv2
import random
import network
import os
def remove_model_file(file):
'''
删除保存的模型文件
删除成功返回True 否则返回 False args:
file:模型文件名
'''
path = [file+item for item in ('.index','.meta')]
path.append(os.path.join( os.path.dirname(path[0]),'checkpoint'))
for f in path:
if os.path.isfile(f):
os.remove(f)
ret = True
#检查文件是否存在
for f in path:
if os.path.isfile(f):
ret = False
return ret def network_main():
'''
使用network网络测试
由于数据量比较大,图片不能一次全部加载进来,因此采用分批读取图片数据
''' '''
一 加载数据
'''
training_data,test_data = datagenerator.load_data()
param_path = './network_param/network_param.pkl' #模型参数保存所在文件
learning_rate = 1e-4 #学习率
training_epoches = 10 #训练轮数
batch_size = 256 #小批量大小 '''
二 创建网络
'''
#如果已经存在训练好的数据,直接加载初始化
nn = network.network([3072,7200,1024,10],param_path=param_path) '''
三 开始训练
'''
nn.fit(training_data,learning_rate=learning_rate,batch_size=batch_size,epoches=training_epoches) nn.save_model(param_path) #保存参数 '''
四 校验
'''
mini_batchs = [test_data[k:k+batch_size] for k in range(0,len(test_data),batch_size)]
test_accuracy_sum = [] #如果不训练网络,需要手动初始化张量
#nn.global_variables_initializer() for mini_batch in mini_batchs:
x_batch,y_batch = datagenerator.get_image_data_and_label(mini_batch,one_hot=True)
#每张图片数据展开正一列
x_batch = x_batch.reshape(len(mini_batch),-1)
test_accuracy_sum.append(nn.accuracy(x_batch,y_batch)) print('准确率:',np.mean(test_accuracy_sum))
'''
测试
'''
if __name__ == '__main__':
network_main()
运行结果如下,我们可以看到迭代10次后,在测试集的准确率大概为52%,如果我们使用卷积神经网络的话或者迭代次数更多一些的话,准确率可能会更高,你也可以尝试使用LeNet进行训练,详情可以参考:Tensorflow深度学习之二十一:LeNet的实现(CIFAR-10数据集)https://blog.csdn.net/davincil/article/details/78794044

三 使用AlexNet网络训练
按照上一节讲的内容定义,alexnet网络结构,alexnet.py文件代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Wed Apr 11 10:48:31 2018 @author: Administrator
""" '''
自己实现一个标准的AlexNet网络
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/OliverkingLi/article/details/73849228
https://blog.csdn.net/DaVinciL/article/details/78888605
'''
import tensorflow as tf def conv(x,filter_height,filter_width,out_channels,stride_y, stride_x, name,
padding='SAME'):
'''
定义一个卷积层
Create a convolution layer.
Adapted from: https://github.com/ethereon/caffe-tensorflow Args:
x:输入图片集合 维度为[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels]
weights:共享权重[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels]
filter_height : 过滤器高度
filter_width: 过滤器宽度
in_channels: 输入通道数
out_channels 过滤器个数
biases:共享偏置 [out_channels]
stride_x: x轴步长
stride_y: y轴步长
name: 卷积层名字
padding: 卷基层填充方式 'VALID'或者'SAME'
'''
#获取输入通道数
in_channels = int(x.get_shape()[-1]) with tf.name_scope(name) as scope:
#搜索变量没有就创建,有会报错 get_variable创建的变量不受name_scope的影响
weights = tf.get_variable(scope+'w', shape=[filter_height,
filter_width,
in_channels,
out_channels],
dtype = tf.float32,
initializer = tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer_conv2d()) '''
或者写成
shape=[filter_height,filter_width,in_channels,out_channels]
weights = tf.get_variable(scope+'w', shape=shape,dtype = tf.float32)
'''
#Variable创建变量,自动检测有没有重命名,有就自行处理
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[out_channels]),dtype=tf.float32,trainable=True,name=scope+'b') #注意这里的strides每个元素分别与[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels]对应
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(x, weights,strides=[1, stride_y, stride_x, 1],
padding=padding)
# Add biases
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) # Apply relu function
relu = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
return relu def max_pool(x, filter_height, filter_width, stride_y, stride_x, name,
padding='SAME'):
'''
定义一个池化层 最大下采样操作 Args:
x:输入图片集合 维度为[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels]
filter_height : 滑动窗口高度
filter_width: 滑动窗口宽度
stride_x: x轴步长
stride_y: y轴步长
name: 池化层名字
padding: 填充方式 'SAME'或者'VALID'
'''
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, filter_height, filter_width, 1],
strides=[1, stride_y, stride_x, 1],
padding=padding, name=name) def fc(x, num_out,name, relu=True):
'''
全连接网络
'''
num_in = int(x.get_shape()[-1])
with tf.name_scope(name) as scope: # Create tf variables for the weights and biases
weights = tf.get_variable(scope+'w', shape=[num_in, num_out],
dtype = tf.float32,
initializer = tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer_conv2d())
'''
或者写成
shape=[num_in, num_out]
weights = tf.get_variable(scope+'w', shape=shape,dtype = tf.float32) ''' biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[num_out]),dtype=tf.float32,trainable=True,name=scope+'b') if relu:
act = tf.nn.xw_plus_b(x, weights, biases)
# Apply ReLu non linearity
relu = tf.nn.relu(act, name=scope)
return relu
else:
act = tf.nn.xw_plus_b(x, weights, biases, name=scope)
return act def lrn(x, radius, alpha, beta, name, bias=1.0):
'''
局部相应归一化操作
参考论文:http://papers.nips.cc/paper/4824-imagenet-classification-with-deep-convolutional-neural-networks.pdf
Create a local response normalization layer. Args:
depth_radius:归一化窗口的半径长度 一般设置为5 也是 论文中的n/2的值
alpha:超参数 一般设置为1e-4
beta:指数 一般设置为0.5
bias:偏置 一般设置为1.0
name:lrn层名字
'''
return tf.nn.local_response_normalization(x, depth_radius=radius,
alpha=alpha, beta=beta,
bias=bias, name=name) def dropout(x, keep_prob):
'''
弃权操作 Args:
x:激活函数之后的输出
keep_prob:弃权概率 即每个神经元被保留的概率
'''
return tf.nn.dropout(x, keep_prob) '''
初始化权值和偏重
为了创建这个模型,我们需要创建大量的权重和偏置项。这个模型中的权重在初始化时应该加入少量的噪声来
打破对称性以及避免0梯度。由于我们使用的是ReLU神经元,因此比较好的做法是用一个较小的正数来初始化
偏置项,以避免神经元节点输出恒为0的问题(dead neurons)。为了不在建立模型的时候反复做初始化操作
,我们定义两个函数用于初始化。
'''
def weight_variable(shape):
#使用正太分布初始化权值
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape,dtype=tf.float32,mean=0,stddev=0.1) #标准差为0.1
return tf.Variable(initial) def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.0,shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial,dtype=tf.float32) def print_dimension(t):
'''
输出指定张量的维度
'''
print(t.op.name,'',t.get_shape().as_list()) class alexnet(object):
'''
定义一个类 实现AlexNet网络
''' def __init__(self, n_classes):
'''
Create the graph of the AlexNet model. Args:
x: 输入张量的占位符 Placeholder for the input tensor.
keep_prob: 占位符 每个神经元保留的概率 Dropout probability.
'''
# 初始化参数
#占位符输入
self.input_x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=[None,227,227,3],name='input_x')
self.input_y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=[None,n_classes],name='input_y')
self.keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,name='keep_prob')
self.n_classes = n_classes self.out = self.create() def initial_weights_biases(self):
'''
初始化权重和偏置 '''
#标砖AlexNet参数
weights = {
'wc1': weight_variable([11,11,3,96]),
'wc2': weight_variable([5,5,96,256]),
'wc3': weight_variable([3,3,256,384]),
'wc4': weight_variable([3,3,384,384]),
'wc5': weight_variable([3,3,384,256]),
'wfc6': weight_variable([6*6*256,4096]),
'wfc7': weight_variable([4096,4096]),
'wfc8': weight_variable([4096,10]),
}
biases = {
'bc1':bias_variable([96]),
'bc2':bias_variable([256]),
'bc3':bias_variable([384]),
'bc4':bias_variable([384]),
'bc5':bias_variable([256]),
'bfc6':bias_variable([4096]),
'bfc7':bias_variable([4096]),
'bfc8':bias_variable([10]),
}
'''
#为了加快训练速度 简化网络
weights = {
'wc1': weight_variable([11,11,3,64]),
'wc2': weight_variable([5,5,64,192]),
'wc3': weight_variable([3,3,192,384]),
'wc4': weight_variable([3,3,384,384]),
'wc5': weight_variable([3,3,384,256]),
'wfc6': weight_variable([6*6*256,4096]),
'wfc7': weight_variable([4096,4096]),
'wfc8': weight_variable([4096,10]),
}
biases = {
'bc1':bias_variable([64]),
'bc2':bias_variable([192]),
'bc3':bias_variable([384]),
'bc4':bias_variable([384]),
'bc5':bias_variable([256]),
'bfc6':bias_variable([4096]),
'bfc7':bias_variable([4096]),
'bfc8':bias_variable([10]),
}
'''
return weights,biases def create(self):
'''
Create the network graph.
创建AlexNet网络 返回网络输出的张量(没有经过正激函数)
共有8层网络 5层卷积测,3个全连接网络
'''
# 1st Layer: Conv (w ReLu) -> Lrn -> Pool
self.conv1 = conv(self.input_x,filter_height=11,filter_width=11,out_channels=96,stride_y=4, stride_x=4, padding='VALID', name='conv1')
print_dimension(self.conv1)
self.norm1 = lrn(self.conv1, radius=4, alpha=1e-4, beta=0.75, name='norm1')
self.pool1 = max_pool(self.norm1, filter_height=3, filter_width=3, stride_y=2, stride_x=2, padding='VALID', name='pool1')
print_dimension(self.pool1) # 2nd Layer: Conv (w ReLu) -> Lrn -> Pool with 2 groups
self.conv2 = conv(self.pool1,5,5,256, 1, 1, name='conv2')
print_dimension(self.conv2)
self.norm2 = lrn(self.conv2, radius=4, alpha=1e-4, beta=0.75, name='norm2')
self.pool2 = max_pool(self.norm2, 3, 3, 2, 2, padding='VALID', name='pool2')
print_dimension(self.pool2) # 3rd Layer: Conv (w ReLu)
self.conv3 = conv(self.pool2,3,3,384, 1, 1, name='conv3')
print_dimension(self.conv3) # 4th Layer: Conv (w ReLu) splitted into two groups
self.conv4 = conv(self.conv3,3,3,384, 1, 1, name='conv4')
print_dimension(self.conv4) # 5th Layer: Conv (w ReLu) -> Pool splitted into two groups
self.conv5 = conv(self.conv4,3,3,256, 1, 1, name='conv5')
print_dimension(self.conv5)
self.pool5 = max_pool(self.conv5, 3, 3, 2, 2, padding='VALID', name='pool5')
print_dimension(self.pool5) # 6th Layer: Flatten -> FC (w ReLu) -> Dropout
flattened = tf.reshape(self.pool5, [-1, 6*6*256])
self.fc6 = fc(flattened, 4096, name='fc6')
print_dimension(self.fc6)
self.dropout6 = dropout(self.fc6, self.keep_prob) # 7th Layer: FC (w ReLu) -> Dropout
self.fc7 = fc(self.dropout6,4096, name='fc7')
print_dimension(self.fc7)
self.dropout7 = dropout(self.fc7, self.keep_prob) # 8th Layer: FC and return unscaled activations
self.out = fc(self.dropout7,self.n_classes, relu=False, name='out')
print_dimension(self.out) #计算交叉熵损失函数
with tf.name_scope('cost'):
self.cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits = self.out,labels = self.input_y)) #准确率
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
#tf.argmax(output,1) 按行统计最大值得索引
self.correct = tf.equal(tf.argmax(self.out,1),tf.argmax(self.input_y,1)) #返回一个数组 表示统计预测正确或者错误
self.accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(self.correct,tf.float32)) #求准确率 #use softmax activations
#self.out = tf.nn.softmax(fc8)
return self.out
定义好网络结构之后,我们需要进行测试:这里在读取数据时我采用两种方式,代码中会有解释:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Wed Apr 11 16:42:09 2018
@author: Administrator
"""
'''
用于训练AlexNet网络
由于内存有限,不能一次读取所有的数据,因此采用每次读取小批量的图片
1.在datagenerator.py文件中 把所有图片保存成bmp格式文件
2.存储一个dict字典 每个元素为 (图片的相对路径,标签) 将这个字典序列化保存到文件
3.读取该文件,把文件名顺序打乱,分成多组,每次加载mini_batch个图片进行训练
4.在加载图片时,需要把图片放大为227*227的 这是由于AlexNet网络输入的维度
''' import tensorflow as tf
from alexnet import alexnet
import datagenerator
import numpy as np
import cv2
import random
import network
import os def remove_model_file(file):
'''
删除保存的模型文件
删除成功返回True 否则返回 False args:
file:模型文件名
'''
path = [file+item for item in ('.index','.meta')]
path.append(os.path.join( os.path.dirname(path[0]),'checkpoint'))
for f in path:
if os.path.isfile(f):
os.remove(f)
ret = True
#检查文件是否存在
for f in path:
if os.path.isfile(f):
ret = False
return ret
def alexnet_main():
'''
使用AlexNet测试
由于数据量比较大,图片不能一次全部加载进来,因此采用分批读取图片数据 由于这里每次从硬盘读取batch_size大小的图片,速度较慢
''' '''
一 加载数据 '''
training_data,test_data = datagenerator.load_data() '''
二 定义网络参数
'''
model_name = './alexnet_param/alexnet_model.ckpt' #模型保存所在文件
#定义网络超参数
learning_rate = 1e-4 #学习率
training_epoches = 40 #训练轮数
batch_size = 256 #小批量大小 #定义网络参数
n_classes = 10 #标签的维度
pdropout = 0.5 #弃权的概率
n_train = len(training_data) #训练集数据长度
n_test = len(test_data) #测试卷数据长度
image_size = (227,227) #图片大小 #如果目录不存在创建目录
if not os.path.isdir(os.path.dirname(model_name)):
os.mkdir(os.path.dirname(model_name)) '''
三 求解 构建模型 开始测试
''' alex = alexnet(n_classes) #创建Saver op用于保存和恢复所有变量
saver = tf.train.Saver() #定义学习步骤
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate)
train = optimizer.minimize(alex.cost)
#train = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost) with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) #初始化变量 #如果该文件存在,恢复模型数据
if os.path.isfile(model_name+'.meta'):
saver.restore(sess,model_name) count = 0
#开始迭代
for i in range(training_epoches):
#打乱训练集
random.shuffle(training_data)
#分组
mini_batchs = [training_data[k:k+batch_size] for k in range(0,n_train,batch_size)] #遍历每一个mini_batch
for mini_batch in mini_batchs:
print('输出',mini_batch[0])
x_batch,y_batch = datagenerator.get_image_data_and_label(mini_batch,image_size=image_size,one_hot=True)
#开始训练
train.run(feed_dict={alex.input_x:x_batch,alex.input_y:y_batch,alex.keep_prob:pdropout}) #每次训练一批后,输出训练集准确率
training_accuracy,training_cost = sess.run([alex.accuracy,alex.cost],feed_dict={alex.input_x:x_batch,alex.input_y:y_batch,alex.keep_prob:pdropout})
count +=1
print('Iteration {0}:Training set accuracy {1},cost {2}.'.format(count,np.mean(training_accuracy),np.mean(training_cost))) '''
每一轮训练完成做测试
#输出测试集准确率 如果一次性全部做测试,内容不够用会出现OOM错误。所以测试时选取比较小的mini_batch来测试
'''
#分组
mini_batchs = [test_data[k:k+batch_size] for k in range(0,n_test,batch_size)] test_accuracy_sum = []
test_cost_sum = []
#遍历每一个mini_batch
for mini_batch in mini_batchs: x_batch,y_batch = datagenerator.get_image_data_and_label(mini_batch,image_size=image_size,one_hot=True) #校验
test_accuracy,test_cost = sess.run([alex.accuracy,alex.cost],feed_dict={alex.input_x:x_batch,alex.input_y:y_batch,alex.keep_prob:pdropout})
test_accuracy_sum.append(test_accuracy)
test_cost_sum.append(test_cost)
#迭代完一轮测试集,求平均
print('Epoch {0}: Test set accuracy {1},cost {2}.'.format(i,np.mean(test_accuracy_sum),np.mean(test_cost_sum))) #tensorflow的saver,用于保存模型
if remove_model_file(model_name) == True: #删除原先模型文件
saver.save(sess,model_name)
print('模型保存成功!') def alexnet_improve_main():
'''
使用AlexNet测试
这里采用一次获取所有的图片数据和标签,然后每次训练时从这些数据中随机选取batch_size去训练
''' '''
一 加载数据 '''
data_dir = 'cifar-10-batches-py' #数据所在目录 filelist = []
for i in range(5):
name = os.path.join(data_dir,str('data_batch_%d'%(i+1)))
filelist.append(name)
data = datagenerator.datagenerator()
#获取训练集数据
train_x = data.get_data_by_keyword('data',filelist,
normalized=True,size=(32,32))
#标签
train_y = data.get_data_by_keyword('labels',filelist) filelist = [os.path.join(data_dir,'test_batch')] #获取训练集数据 数据标准化为0-1之间
test_x = data.get_data_by_keyword('data',filelist,
normalized=True,size=(32,32)) #标签
test_y = data.get_data_by_keyword('labels',filelist) '''
二 定义网络参数
'''
tf.reset_default_graph() tf.flags.DEFINE_string('model_file_name','./alexnet_improve_param/alexnet_model.ckpt','model file name (default:./alexnet_improve_param/alexnet_model.ckpt) ')
#定义网络超参数
tf.flags.DEFINE_float('learning_rate', 0.0001,'learning rate (default:0.0001)')
tf.flags.DEFINE_float('pdropout' , 0.5,'Dropout keep probability (default:0.5)') #定义网络参数
tf.flags.DEFINE_integer('training_epoches',5,'Number of training epochs (default:20)')
tf.flags.DEFINE_integer('batch_size', 512,'Batch size (default:256)') n_classes = 10 #标签的维度
n_train = len(train_y) #训练集数据长度
n_test = len(test_y) #测试卷数据长度
image_size = (227,227) #图片大小 FLAGS = tf.flags.FLAGS
FLAGS._parse_flags() print('网络参数')
for attr,value in sorted(FLAGS.__flags.items()):
print('{0}:{1}'.format(attr.upper(),value)) #如果目录不存在创建目录
if not os.path.isdir(os.path.dirname(FLAGS.model_file_name)):
os.mkdir(os.path.dirname(FLAGS.model_file_name)) '''
三 求解 构建模型 开始测试
'''
#构建alexnet网络
alex = alexnet(n_classes) #创建Saver op用于保存和恢复所有变量
saver = tf.train.Saver() #定义学习步骤
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(FLAGS.learning_rate)
train = optimizer.minimize(alex.cost)
#train = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost) #设置tensorflow对GPU使用按需分配
config = tf.ConfigProto()
config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True with tf.Session(config=config) as sess:
#初始化变量
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) #如果该文件存在,恢复模型数据
if os.path.isfile(FLAGS.model_file_name + '.meta'):
saver.restore(sess, FLAGS.model_file_name) #开始迭代
for epoch in range(FLAGS.training_epoches):
indices = np.arange(n_train)
#打乱训练集
random.shuffle(indices) #这里取n_train-batch_size+1 是为了防止indices[i+j]溢出
for i in range(0, n_train - FLAGS.batch_size + 1, FLAGS.batch_size):
x_batch = []
y_batch = [] for j in range(FLAGS.batch_size):
x_batch.append(cv2.resize(train_x[indices[i+j]], image_size)/255)
y_batch.append(train_y[indices[i+j]]) #转换为one_hot格式
y_batch = datagenerator.get_one_hot_label(y_batch,n_classes)
#开始训练
train.run(feed_dict={alex.input_x:x_batch,alex.input_y:y_batch,alex.keep_prob:FLAGS.pdropout})
#training_accuracy,training_cost = sess.run([alex.accuracy,alex.cost],feed_dict={alex.input_x:x_batch,alex.input_y:y_batch,alex.keep_prob:FLAGS.pdropout})
#print('Iteration {0}:Training set accuracy {1},cost {2}.'.format(int((i+epoch * n_train)/FLAGS.batch_size) ,np.mean(training_accuracy),np.mean(training_cost))) #迭代完一轮后 输出训练集准确率
training_accuracy_sum = []
training_cost_sum = []
for i in range(0,n_train-FLAGS.batch_size+1,FLAGS.batch_size):
x_batch = []
y_batch = [] for j in range(FLAGS.batch_size):
x_batch.append(cv2.resize(train_x[i+j],image_size)/255)
y_batch.append(train_y[i+j]) #转换为one_hot格式
y_batch = datagenerator.get_one_hot_label(y_batch,n_classes) training_accuracy,training_cost = sess.run([alex.accuracy,alex.cost],feed_dict={alex.input_x:x_batch,alex.input_y:y_batch,alex.keep_prob:FLAGS.pdropout})
training_accuracy_sum.append(training_accuracy)
training_cost_sum.append(training_cost)
print('Epoch {0}:Training set accuracy {1},cost {2}.'.format(epoch,np.mean(training_accuracy_sum),np.mean(training_cost_sum))) '''
每一轮训练完成做测试
#输出测试集准确率 如果一次性全部做测试,内容不够用会出现OOM错误。所以测试时选取比较小的mini_batch来测试
'''
test_accuracy_sum = []
test_cost_sum = []
for i in range(0,n_test-FLAGS.batch_size+1,FLAGS.batch_size):
x_batch = []
y_batch = [] for j in range(FLAGS.batch_size):
x_batch.append(cv2.resize(test_x[i+j],image_size)/255)
y_batch.append(test_y[i+j]) #转换为one_hot格式
y_batch = datagenerator.get_one_hot_label(y_batch,n_classes) #校验
test_accuracy,test_cost = sess.run([alex.accuracy,alex.cost],feed_dict={alex.input_x:x_batch,alex.input_y:y_batch,alex.keep_prob:FLAGS.pdropout})
test_accuracy_sum.append(test_accuracy)
test_cost_sum.append(test_cost)
#迭代完一轮测试集,求平均
print('Epoch {0}: Test set accuracy {1},cost {2}.'.format(epoch,np.mean(test_accuracy_sum),np.mean(test_cost_sum))) #tensorflow的saver,用于保存模型
if remove_model_file(FLAGS.model_file_name) == True: #删除原先模型文件
saver.save(sess,FLAGS.model_file_name)
print('模型保存成功!') '''
测试
'''
if __name__ == '__main__':
#alexnet_main()
alexnet_improve_main()
由于网络比较大训练时间比较长,我只训练了5次,并设置每次训练的batch_size=512。运行结果如下:

然后我们可以在之前训练的基础上继续训练。后面我又稍微对程序进行了改进,加入了检查点的保存,每迭代一轮保存一次参数,并在输出的时候打印出时间,然后运行几轮后输出如下:

我们可以执行以下程序,查看我们保存的模型数据:然后截取部分内容显示:
from tensorflow.python.tools.inspect_checkpoint import print_tensors_in_checkpoint_file
print_tensors_in_checkpoint_file('./alexnet_improve_param/alexnet_model.ckpt',None,True)

我们以输出层为例,为什么输出的张量名字为out/out/b和out/w,这是因为我们在定义Alexnet网络的时候定义了一个函数:
def fc(x, num_out,name, relu=True):
'''
全连接网络
'''
num_in = int(x.get_shape()[-1])
with tf.name_scope(name) as scope: # Create tf variables for the weights and biases
weights = tf.get_variable(scope+'w', shape=[num_in, num_out],
dtype = tf.float32,
initializer = tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer_conv2d())
'''
或者写成
shape=[num_in, num_out]
weights = tf.get_variable(scope+'w', shape=shape,dtype = tf.float32) ''' biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[num_out]),dtype=tf.float32,trainable=True,name=scope+'b') if relu:
act = tf.nn.xw_plus_b(x, weights, biases)
# Apply ReLu non linearity
relu = tf.nn.relu(act, name=scope)
return relu
else:
act = tf.nn.xw_plus_b(x, weights, biases, name=scope)
return act
并且输出层定义如下:
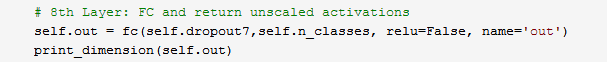
当给fc()函数传入name为'out'时候,get_variable()函数首先去查找是否定义了out/w(scope输出的是字符串为out/)张量,如果没有会创建一个,所以在保存的模型里有名称为out/w的张量。对于偏置我们使用的是Variable()函数,这个函数会始终创建新的变量,如果名称重复会自行处理,并且默认会在变量名称前加上name_scope()中定义的名称作为前缀。所以biases的名称就变成了out/out/b,因此如果我们想保存的张量名字是out/b的话,我们应该把fc()函数中biases这一行改成:
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[num_out]),dtype=tf.float32,trainable=True,name='b')
最新文章
- 修改TNSLSNR的端口
- for循环中i--的妙用 及 两变量互换数值的问题
- dstoon系统中学习
- NopCommerce Url分析
- mysql中datetime比较大小问题 (转的)
- .net变量判断
- Eclipse 安装 CDT
- ASP.NET MVC 开源项目学习之ProDinner (一)
- ASP.net UrlRewrite的防盗链功能
- .net之单元测试
- js点击打开弹窗
- PADS LAYOUT到底怎么走线
- Eclipse和PyDev搭建完美Python开发环境(Windows篇)(转)
- Linux 下一个 Mysql error 2002 错误解决
- javascript常见面试题
- BZOJ-2463
- PHP实现网页爬虫
- ACM 今年暑假不AC
- Java 必看的 Spring 知识汇总!有比这更全的算我输!
- Spring Cloud (十四):Spring Cloud 开源软件都有哪些?