NIO的初步入门
NIO
- java NIO简介
Java NIO 简介 是从java1.4版本开始引入的一个新的IO AP可以替代标准java IO API
NIO与原来的IO有同样的作用和目的,但是使用方式完全不同,NIO支持面向缓冲区的,基于通道的IO操作,NIO将以更加高效的方式进行文件的读与写操作。
2Java NIO 与IO的主要区别
|
IO |
NIO |
|
面向流 |
面向缓冲区 |
|
阻塞IO |
非阻塞 |
|
无 |
选择器 |
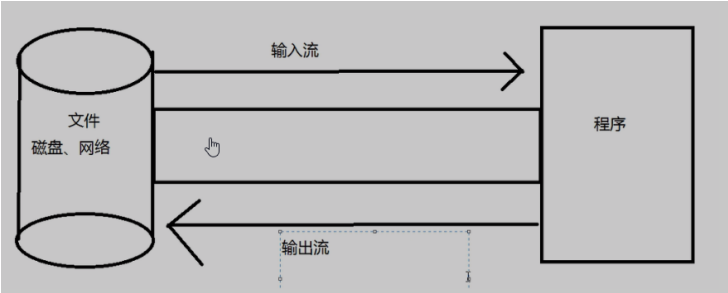
传统IO
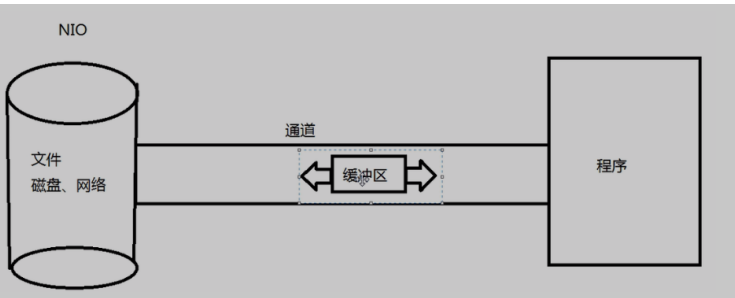
NIO 通道负责连接,缓冲区负责数据的传输。
/**
* Buffer(缓冲区)用于存储数据 本质就是数组,存储不同数据类型的数据
* 根据数据类型不同(boolean 除外),提供了相应类型的缓冲区。
* ByteBuffer
* CharBuffer
* ShortBuffer
* IntBuffer
* LongBuffer
* FloatBuffer
* DoubleBuffer
* 上述缓冲区的管理方式几乎一致,通过allocate()获取缓冲区
* 缓冲区中存取数据的两个核心方法
* put() 存入数据到缓冲区中
* get() 获取缓冲区中的数据
* 缓存区中的四个核心属性
* private int mark = -1; 标记,表示记录当前position 的位置 可以通过reset()恢复到mark的位置
* private int position = 0;位置,缓存区中正在操作数据的位置
* private int limit; 界限,表示缓冲区中可以操作数据的大小 (limit后面的数据我们是不能就进行读写的)
* private int capacity; 容量:表示缓存区中组最大存储数据的容量,一旦声明不可改变
* 0<=mark<= position<=limit<=capacity
*
* 直接缓冲区与非直接缓冲区
* 非直接缓冲区:通过allocate()方法分配缓冲区,将缓冲区建立子字JVM的内存中
*
* 直接缓冲区:通过allocateDirect()方法分配直接缓冲区。将缓冲区建立在物理内存中,可以提高效率
*/
@Test
public void test01(){
/*创建直接缓冲区*/
ByteBuffer bytebuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate();//给缓冲区设置一个大小
// ByteBuffer bytebufferD = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);//给缓冲区设置一个大小,直接缓冲区 /*判断是不是直接缓冲区*/
System.out.println(bytebuffer.isDirect()); System.out.println("==================allocated"); System.out.println(bytebuffer.position());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.capacity());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.limit()); //利用put()存入数据到缓冲区中
String str = "aynu";
bytebuffer.put(str.getBytes()); System.out.println("================put================="); System.out.println(bytebuffer.position());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.capacity());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.limit()); System.out.println("===================flip==================");
//切换到读取数据的模式
bytebuffer.flip(); System.out.println(bytebuffer.position());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.capacity());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.limit()); //利用get()方法读取缓冲区中的数据
System.out.println("===============get=====================");
byte[] dst = new byte[bytebuffer.limit()];
bytebuffer.get(dst);
System.out.println(new String(dst,,dst.length)); System.out.println(bytebuffer.position());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.capacity());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.limit()); //rewind 可重复读数据
System.out.println("==================rewind===================");
bytebuffer.rewind();
System.out.println(bytebuffer.position());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.capacity());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.limit()); //clear()清空缓冲区 但是缓冲区的数据还在,但是处于被遗忘状态,就是核心属性都变成了最初状态
System.out.println("================clear==================");
bytebuffer.clear(); System.out.println(bytebuffer.position());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.capacity());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.limit()); //可以取出数据
System.out.println((char) bytebuffer.get()); }
执行结果
false
==================allocated ================put================= ===================flip================== ===============get=====================
aynu ==================rewind=================== ================clear================== a Process finished with exit code
执行结果
@Test
public void test02(){
String str ="abced"; //设置缓冲区大小
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(); //存放数据
buffer.put(str.getBytes()); //切换到读数据的模式
buffer.flip(); /*创建一个数组将读取的数据保存到这个里面*/
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.limit()];
buffer.get(bytes,,);
//将读取到的数据组委字符串输出来
System.out.println(new String (bytes,,)); System.out.println("基本属性的大小");
System.out.println("position1========"+buffer.position()); /*通过mark 进行标记*/
buffer.mark();
buffer.get(bytes,,);
System.out.println(new String(bytes,,));
System.out.println("position2========"+buffer.position()); //reset() 重置,恢复到mark的位置
buffer.reset();
System.out.println("position3========"+buffer.position()); //判断缓冲区中是否还有剩余的数据
if(buffer.hasRemaining()){ //获取缓冲区中可以操作的数量
System.out.println(buffer.remaining());
}
}
ab
基本属性的大小
position1========
ce
position2========
position3======== Process finished with exit code
执行结果
====================================================================
import java.nio.Buffer;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer; /**
* Description: NIOproject-01
* Created by lenovo on 2019/4/22 15:01
*/
public class TestNio { public static void main (String[] args){ String str ="zhulina";
//创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(); //将数据存放到缓存区中
buffer.put(str.getBytes()); //转换为读取模式
buffer.flip(); //一定要写在前面否则会错哦 //读取数据
byte[] b= new byte[buffer.limit()]; //读取缓冲区的数据
buffer.get(b); //将数据打印在控制台,我并没有读取缓冲区的数据
System.out.println(new String(b,,b.length).toString()); }
}
===================================================================
3.缓冲区(Buffer)和通道
Java NIO系统的核心在于 通道(channel)和缓冲区(buffer。通道表示打开到IO设备(例如:文件,套接字)的而连接。若需要使用NIO系统,需要获取用于连接IO设备的通道以 及用于容纳数据的缓冲区,然后操作缓冲区,对数据进行处理。
简言之,channel负责传输,buffer负责存储。
缓冲区(buffer)
一个用于特定基本数据类型的容器,有java.nio包定义的,所有缓冲区都是buffer抽象类的子类。
JavaNIO 中的Buffer主要用于与NIO通道进行交互,数据是从通道读入缓冲区,从缓冲区写入通道中的。
4.文件通道
5.NIO的非阻塞时式网络通信
选择器
SockerChannel ,ServerSockertChannel ,DatagramChannel
6.管道
7.Java NIO2(Path,Paths与Files)
测试用例1:
TestNioSocket
import org.junit.Test; import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.WritableByteChannel;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption;
import java.util.WeakHashMap; /**
* Description: NIOproject-01
* Created by lenovo on 2019/4/23 21:25
*/
public class MyTest { @Test
public void Client() throws IOException {
/*建立网络通道*/
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", )); /*建立文件通道*/
FileChannel fileChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("E:\\sturts2\\NIOproject-01\\src\\main\\webapp\\1.txt"), StandardOpenOption.READ); /*建立缓冲区*/
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(); /*将通道中的数据读入到缓冲区中*/
while (fileChannel.read(buffer)!=-){
buffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(buffer);
buffer.clear(); }
// socketChannel.shutdownOutput();
/*写上一个客户端的响应*/ int len =; /* while ((len=buffer.limit())!=-1){
buffer.flip();
System.out.println("客户端"+ new String(buffer.array(),0,len)); buffer.clear(); }*/
socketChannel.close();
fileChannel.close(); } @Test
public void Server() throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); FileChannel fileChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("E:\\sturts2\\NIOproject-01\\src\\main\\webapp\\2.txt"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE); /*绑定连接*/
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress()); /*建立缓冲区*/
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(); /*获取客户端的通道*/
SocketChannel acceptChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept(); while (acceptChannel.read(buffer)!=-){
buffer.flip();
fileChannel.write(buffer);
buffer.clear();
}
/*建立一个响应*/
/*
int len=0;
while ((len= buffer.limit())!=-1){ buffer.flip();
System.out.println("客户端给出的响应"+new String(buffer.array(),0,len));
buffer.clear(); }*/
serverSocketChannel.close();
fileChannel.close();
acceptChannel.close(); } }
TestNioSocket
import com.sun.org.apache.bcel.internal.generic.Select;
import org.junit.Test; import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Scanner; /**
*使用NIO完成网络通信的三个核心
* 1.通道(Channel)负责连接
*
*java.nio.channels.Channel接口
* |--SelectableChannel
* |---SocketChannel
* |---ServerSocketChannel
* |---DatagramChannel
*
* |---Pipe>SinkChannel
* |---PipeSourceChannel
*
*
* 2.缓冲区(Buffer) 负责数据的存取
*
*
* 3.选择器(Selector)是SelectableChannel的多路复用 。用于监控SelectableChannel的IO状况
*
*
*
*/ public class TestNonBlockingNio {
//客户端
@Test
public void Client() throws IOException { //获取通道
SocketChannel sChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", )); //切换非阻塞模式
sChannel.configureBlocking(false); //3.分配制定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(); //4.发送数据给服务端
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); while (scan.hasNext()){
String str = scan.next();
buf.put((new Date().toString()+"\n"+str).getBytes());
buf.flip();
sChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear(); } //5.关闭通道
sChannel.close(); }
//服务端
@Test
public void Server() throws IOException {
//1.获取通道
ServerSocketChannel ssChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); //2.切换非阻塞模
ssChannel.configureBlocking(false); //3.绑定连接
ssChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress()); //4.获取选择器
Selector selector = Selector.open(); //5.将通道注册到选择器上面,并且指定 监听接受事件
ssChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); //6.轮询式的获取选择器上已经准备就绪的事件
while (selector.select()>){
//获取当前选择器中所有注册的选择键(已就绪的监听事件)
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while (it.hasNext()){
//8.获取准备就绪的事件
SelectionKey sk = it.next(); //9.判断是什么事件准备就绪
if (sk.isAcceptable()){
//10若接收就绪获取客户端连接 SocketChannel sChannel = ssChannel.accept(); //11.切换非阻塞模式
sChannel.configureBlocking(false); //12.将该通道注册到选择器上
sChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ); }else if(sk.isReadable()){
//13.获取当前选择器上 ’读就绪‘ 状态的通道 SocketChannel sChannel = (SocketChannel) sk.channel(); //14.读取数据
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(); int len=; while ((len =sChannel.read(buf))>){
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),,len));
buf.clear(); }
}
//15.取消选择键selectorkey
it.remove(); } } } }
TestNonBlockingNio
import org.junit.Test; import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.DatagramChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Scanner; /**
* Description: NIOproject-01
* Created by lenovo on 2019/4/23 11:09
*/
public class TestNonBlokingNio2 {
@Test
public void send() throws IOException {
DatagramChannel dc = DatagramChannel.open(); dc.configureBlocking(false); ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); while (scanner.hasNext()){
String str = scanner.next();
buf.put((new Date().toString()+":\n"+str).getBytes());
buf.flip();
dc.send(buf,new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",));
buf.clear();
}
dc.close();
} @Test
public void review() throws IOException {
DatagramChannel dc = DatagramChannel.open(); dc.configureBlocking(false); dc.bind(new InetSocketAddress()); Selector selector = Selector.open(); while (selector.select()>){
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while (it.hasNext()){ SelectionKey sk = it.next(); if (sk.isReadable()){
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(); dc.receive(buf);
buf.flip(); System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),,buf.limit()));
buf.clear(); }
} it.remove(); } }
}
TestNonBlokingNio2
import org.junit.Test; import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption; /**
* Description: NIOproject-01
* Created by lenovo on 2019/4/22 21:58
*/
public class TestBlockNio2 { //客户端
@Test
public void Client() throws IOException {
SocketChannel sChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", )); FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("1.png"), StandardOpenOption.READ); ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(); while (inChannel.read(buf)!=-){
buf.flip();
sChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
sChannel.shutdownOutput(); //接收服务端的反馈
int len =;
while ((len= sChannel.read(buf)) !=-){
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),,len));
buf.clear();
}
inChannel.close();
sChannel.close(); } //服务端
@Test
public void Server() throws IOException { ServerSocketChannel ssChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("1.png"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
ssChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress());
SocketChannel sChannel = ssChannel.accept(); ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate();
while (sChannel.read(buf)!=-){
buf.flip();
outChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
//发送反馈给客户端 buf.put("服务端接收数据成功".getBytes());
buf.flip();
sChannel.write(buf); sChannel.close();
ssChannel.close();
outChannel.close(); }
}
TestBlockNio2
import org.junit.Test; import java.io.*;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.CharBuffer;
import java.nio.MappedByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.charset.CharacterCodingException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder;
import java.nio.charset.CharsetEncoder;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.SortedMap; /**
* Channel 用于源节点与目标节点的连接,在java NIO 中负责缓冲区数据的传输,Channel本身不存储数据,因此需要配合
* 缓冲区进行传输
* 二.通道的主要实现类
* fillChannel
* socketChannel
* serverSocketChannel
* DatagramChannel
*
* 三.获取通道
* 1.java 针对支持通道的类提供了 getChannel()方法
* 本地IO
* FileInputStream/FileOutPutStream
* RandomAccessFile
*
* 网络 IO
* Socket
* ServerSocker
* DatagramSocket
* 2.在jdk 1.7中的NIO.2 针对各个通道提供了静态方法 open()
* 在jdk 1.7 中的NIO.2 的files 工具类的newByteChannel()
* 四 通道之间的数据传输
* transferForm()
* transferTo()
*
* 五分散(scatter)与聚集(Gather)
* 分散读取(scattering reads):将通道中的数据分散到多个缓冲区中
* 聚集写入(Gathering Writes):将多个缓冲区中的数据聚集到同道中
*
*六字符集
* 编码 字符串---》字节数组
* 解码 字节数组---》字符串
*/
public class TestChannel { @Test
public void Test01() { //1.利用通道完成文件的复制(非直接缓冲区) FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
FileChannel inputchannel = null;
FileChannel outChannel = null;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("E:\\sturts2\\NIOproject-01\\src\\main\\webapp\\1.png");
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("E:\\sturts2\\NIOproject-01\\src\\main\\webapp\\2.png"); //获取通道
inputchannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
outChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel(); //分配指定大小缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(); //将通道中的数据存放入缓冲区中
while (inputchannel.read(buffer)!=-){
//切换到读取数据的模式
buffer.flip(); //将缓存区中的数据写入到通道中
outChannel.write(buffer); buffer.clear();//清空缓存区 }
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (inputchannel!=null) { try {
inputchannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (outChannel!=null){ try {
outChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (fileInputStream!=null){ try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (fileOutputStream!=null){ try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} } }
@Test
public void Test02(){
//使用直接缓冲区完成文件的复制(内存映射文件)
long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); FileChannel inChannel = null;
FileChannel outChannel = null;
try {
inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("E:\\sturts2\\NIOproject-01\\src\\main\\webapp\\1.png"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("E:\\sturts2\\NIOproject-01\\src\\main\\webapp\\3.png"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.READ,StandardOpenOption.CREATE); //内存映射文件
MappedByteBuffer inmapBuffer = inChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, , inChannel.size());
MappedByteBuffer outmapBuffer = outChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, , inChannel.size()); //直接对缓冲区进行数据的读写操作
byte[] dst = new byte[inmapBuffer.limit()];
inmapBuffer.get(dst);
outmapBuffer.put(dst);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (inChannel!=null){ try {
inChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (outChannel!=null){ try {
outChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} }
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗费时间为"+(end-start)); } //通道之间的数据传输(直接缓冲区)
@Test
public void test03() throws IOException { FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get(""), StandardOpenOption.READ);
FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get(""), StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.CREATE); // inChannel.transferTo(0,inChannel.size(),outChannel);
outChannel.transferFrom(inChannel,,inChannel.size()); inChannel.close();
outChannel.close();
}
/*分散和聚集*/
@Test
public void test04() throws IOException { RandomAccessFile raf1 = new RandomAccessFile("1.txt", "rw"); //获取通道
FileChannel channel = raf1.getChannel(); //分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf1 = ByteBuffer.allocate();
ByteBuffer buf2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(); //3.分散读取
ByteBuffer[] bufs = {buf1,buf2};
long read = channel.read(bufs); for(ByteBuffer byteBuffer: bufs){
byteBuffer.flip();//切换到读操作
}
System.out.println(new String(bufs[].array(),,bufs[].limit()));
System.out.println("=================================");
System.out.println(new String(bufs[].array(),,bufs[].limit())); //4.聚集写入
RandomAccessFile raf2 = new RandomAccessFile("2.txt", "rw");
FileChannel channel1 = raf2.getChannel();
channel1.write(bufs); } @Test
public void test05(){
//字符集
Map<String, Charset> map = Charset.availableCharsets(); Set<Map.Entry<String, Charset>> entries = map.entrySet(); for (Map.Entry<String,Charset> entry: entries
) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"="+entry.getValue());
} }
@Test
public void Test06() throws CharacterCodingException {
Charset charset = Charset.forName("GBK"); //获取编码器
CharsetEncoder encoder = charset.newEncoder(); //获取解码器
CharsetDecoder decoder1 = charset.newDecoder(); //指定缓冲区大小
CharBuffer buffer = CharBuffer.allocate();
buffer.put("中国");
buffer.flip(); //编码
ByteBuffer encode = encoder.encode(buffer); for(int i=;i<;i++){
System.out.println(encode.get()); } //解码
encode.flip();
CharBuffer decode2 = decoder1.decode(encode);
System.out.println(decode2.toString()); System.out.println("================================="); // Charset charset1 = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
Charset charset1 = Charset.forName("GBK");
encode.flip();
CharBuffer decode3 = charset1.decode(encode);
System.out.println(decode3.toString()); } }
TestChannel
import org.junit.Test; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; /**
* Description: NIOproject-01
* Created by lenovo on 2019/4/22 15:07
*/
public class TestNio {
/**
* Buffer(缓冲区)用于存储数据 本质就是数组,存储不同数据类型的数据
* 根据数据类型不同(boolean 除外),提供了相应类型的缓冲区。
* ByteBuffer
* CharBuffer
* ShortBuffer
* IntBuffer
* LongBuffer
* FloatBuffer
* DoubleBuffer
* 上述缓冲区的管理方式几乎一致,通过allocate()获取缓冲区
* 缓冲区中存取数据的两个核心方法
* put() 存入数据到缓冲区中
* get() 获取缓冲区中的数据
* 缓存区中的四个核心属性
* private int mark = -1; 标记,表示记录当前position 的位置 可以通过reset()恢复到mark的位置
* private int position = 0;位置,缓存区中正在操作数据的位置
* private int limit; 界限,表示缓冲区中可以操作数据的大小 (limit后面的数据我们是不能就进行读写的)
* private int capacity; 容量:表示缓存区中组最大存储数据的容量,一旦声明不可改变
* 0<=mark<= position<=limit<=capacity
*
* 直接缓冲区与非直接缓冲区
* 非直接缓冲区:通过allocate()方法分配缓冲区,将缓冲区建立子字JVM的内存中
*
* 直接缓冲区:通过allocateDirect()方法分配直接缓冲区。将缓冲区建立在物理内存中,可以提高效率
*/ @Test
public void test01(){
/*创建直接缓冲区*/
ByteBuffer bytebuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate();//给缓冲区设置一个大小
// ByteBuffer bytebufferD = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);//给缓冲区设置一个大小,直接缓冲区 /*判断是不是直接缓冲区*/
System.out.println(bytebuffer.isDirect()); System.out.println("==================allocated"); System.out.println(bytebuffer.position());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.capacity());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.limit()); //利用put()存入数据到缓冲区中
String str = "aynu";
bytebuffer.put(str.getBytes()); System.out.println("================put================="); System.out.println(bytebuffer.position());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.capacity());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.limit()); System.out.println("===================flip==================");
//切换到读取数据的模式
bytebuffer.flip(); System.out.println(bytebuffer.position());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.capacity());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.limit()); //利用get()方法读取缓冲区中的数据
System.out.println("===============get=====================");
byte[] dst = new byte[bytebuffer.limit()];
bytebuffer.get(dst);
System.out.println(new String(dst,,dst.length)); System.out.println(bytebuffer.position());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.capacity());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.limit()); //rewind 可重复读数据
System.out.println("==================rewind===================");
bytebuffer.rewind();
System.out.println(bytebuffer.position());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.capacity());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.limit()); //clear()清空缓冲区 但是缓冲区的数据还在,但是处于被遗忘状态,就是核心属性都变成了最初状态
System.out.println("================clear==================");
bytebuffer.clear(); System.out.println(bytebuffer.position());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.capacity());
System.out.println(bytebuffer.limit()); //可以取出数据
System.out.println((char) bytebuffer.get()); }
@Test
public void test02(){
String str ="abced"; //设置缓冲区大小
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(); //存放数据
buffer.put(str.getBytes()); //切换到读数据的模式
buffer.flip(); /*创建一个数组将读取的数据保存到这个里面*/
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.limit()];
buffer.get(bytes,,);
//将读取到的数据组委字符串输出来
System.out.println(new String (bytes,,)); System.out.println("基本属性的大小");
System.out.println("position1========"+buffer.position()); /*通过mark 进行标记*/
buffer.mark();
buffer.get(bytes,,);
System.out.println(new String(bytes,,));
System.out.println("position2========"+buffer.position()); //reset() 重置,恢复到mark的位置
buffer.reset();
System.out.println("position3========"+buffer.position()); //判断缓冲区中是否还有剩余的数据
if(buffer.hasRemaining()){ //获取缓冲区中可以操作的数量
System.out.println(buffer.remaining());
}
} }
TestNio
最新文章
- nodejs中流(stream)的理解
- wamp 局域网访问
- 如何发布一个Mac应用并使其成为全球付费榜第一
- bean的作用域
- hdu 1999 不可摸数 水题。
- extjs 控件属性
- Inno Setup入门(十一)——完成安装后执行某些程序
- overflow:hiddden与绝对定位的应用场景的事例
- IE8+等兼容、360调用webkit内核小记
- python列表和QVariant
- 《吸血鬼日记》(The Vampire Diaries)经典台词
- Java开源生鲜电商平台-财务系统模块的设计与架构(源码可下载)
- TensorFlow中的设备管理——Device的创建与注册机制
- pojo类自动生成序列化ID
- Confluence 6 如何配置快速导航的同时查找数量
- 洛谷P4007 小 Y 和恐怖的奴隶主(期望dp 矩阵乘法)
- bzoj 4585 烟火表演 - 动态规划 - 可并堆
- highcharts柱状图实现legend和数据列一一对应效果
- Android开发大纲
- SQL Server 数据库同步,订阅、发布、复制、跨服务器