Codeforces Round #349 (Div. 2) C. Reberland Linguistics DP+set
First-rate specialists graduate from Berland State Institute of Peace and Friendship. You are one of the most talented students in this university. The education is not easy because you need to have fundamental knowledge in different areas, which sometimes are not related to each other.
For example, you should know linguistics very well. You learn a structure of Reberland language as foreign language. In this language words are constructed according to the following rules. First you need to choose the "root" of the word — some string which has more than 4 letters. Then several strings with the length 2 or 3 symbols are appended to this word. The only restriction — it is not allowed to append the same string twice in a row. All these strings are considered to be suffixes of the word (this time we use word "suffix" to describe a morpheme but not the few last characters of the string as you may used to).
Here is one exercise that you have found in your task list. You are given the word s. Find all distinct strings with the length 2 or 3, which can be suffixes of this word according to the word constructing rules in Reberland language.
Two strings are considered distinct if they have different length or there is a position in which corresponding characters do not match.
Let's look at the example: the word abacabaca is given. This word can be obtained in the following ways: 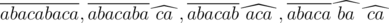 , where the root of the word is overlined, and suffixes are marked by "corners". Thus, the set of possible suffixes for this word is {aca, ba, ca}.
, where the root of the word is overlined, and suffixes are marked by "corners". Thus, the set of possible suffixes for this word is {aca, ba, ca}.
The only line contains a string s (5 ≤ |s| ≤ 104) consisting of lowercase English letters.
On the first line print integer k — a number of distinct possible suffixes. On the next k lines print suffixes.
Print suffixes in lexicographical (alphabetical) order.
abacabaca
3
aca
ba
ca
The first test was analysed in the problem statement.
In the second example the length of the string equals 5. The length of the root equals 5, so no string can be used as a suffix.
题意:
给你一串字符串,将后长与5的(只要在5后面)后半段分为只含三个或者两个的字母的连续后缀
后缀:满足不连续相同可以间隔相同;
将所有满足条件的分法的所有后缀放入集合,按字典序输出
题解:





#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e4+, M = 1e6+, mod = 1e9+, inf = 1e9+;
typedef long long ll; char a[N];
set<string > s;
int f[N][];//i开始到l是否可行
int main() {
scanf("%s",a);
int n = strlen(a);
a[n] = '';
a[n+] ='';
a[n+] = '';
if(n<=) {
cout<<<<endl;
return ;
}
if(n->=) {
string tmp;
tmp = tmp + a[n-]+ a[n-];
s.insert(tmp);
f[n-][] = ;
}
if(n->=) {
string tmp;
tmp = tmp + a[n-]+ a[n-]+ a[n-];
s.insert(tmp);
f[n-][] = ;
}
for(int i=n-;i>=;i--) {
string s1 = "",s2 = "";
s1 = s1 + a[i] + a[i+];
s2 = s2 + a[i+] + a[i+];
if((s1!=s2&&f[i+][])||f[i+][]) {
f[i][] = ;
s.insert(s1);//cout<<s1<<endl;
}
if(i+<n) {
s1 = "",s2 = "";
s1 = s1 + a[i] + a[i+] + a[i+];
s2 = s2 + a[i+] + a[i+] + a[i+];
if((s1!=s2&&f[i+][])||f[i+][]) {
f[i][] = ;
s.insert(s1);
//cout<<s1<<endl;
}
}
}
cout<<s.size()<<endl;
for(set<string > ::iterator it=s.begin();it!=s.end();it++) cout<<(*it)<<endl;
return ;
}
最新文章
- 常用原生JS方法总结(兼容性写法)
- linux的计划
- python打怪之路【第一篇】:99乘法表
- 64位 ubuntu android studio gradle 权限不够 缺少文件和权限导致
- iOS-沙盒路径总结、文件管理NSFileManager总结
- 【转】Quartus II调用modelsim无缝仿真
- SpringMVC 登陆判断
- centos 服务器配置(二) 之ftp配置
- C随便练练手的题
- artTemplate的使用总结
- fastjson将bean转成字符串时首字母变小写问题
- mysql(5.7)在CentOs7下的安装、配置与应用
- WIX 学习笔记 - 2 第一个WIX 项目 HelloWIX
- 在Linux下的找不同-打补丁
- oracle常用函数及关键字笔记
- Vue中之nextTick函数源码分析
- 3、支付结果 /items/result?point=1&orderNo=201903211035400001
- Codeforces 286B Shifting (看题解)
- 前端js如何生成一个对象,并转化为json字符串
- ffmpeg+nginx+video实现rtsp流转hls流,通过H5查看监控视频