学习笔记——python(继承)
学习笔记(Python继承)
有几种叫法(父类-子类、基类-派生类)
先拿代码演示一下:
class father:
def work(self):
print("work>>>>>") def car(self):
print("car>>>>>>>>>") class son(father): #想要继承就得添加父类
def study(self):
print("study>>>>>>>>>>") obj = son()
obj.work() #在上面方法中,work中的self是形参,此时指向的是obj
#除此之外还很重要的是,self永远指向调用方法的调用者(比如这里指向obj)
#work>>>>>
由上述代码可以看出此时obj是调用子类的对象,但是却可以使用父类的方法,其主要原因是子类后添加了父类,如果没有加父类,则调用不了父类的方法从而报错,这种形式叫做继承
(self 永远指向调用方法的调用者)
1、当继承父类的方法时,如果不想调用父类的某些方法,则就需要自己在子类中重写
(下面类中重写父类中的work方法,先别去想太多限制)
class son(father):
def study(self):
print("study>>>>>>>>>>") def work(self):
print("s.work") #不想继承就自己写(重写) #此时在调用方法时,先从子类的方法中查找,如果有该方法则先调用,没有的话就去父类中调用
obj = son()
obj.work() #s.work
2、当继承父类方法时,自己子类重写了但是还是想要去执行父类被重写的方法,则进行下面操作:
def work(self):
print("s.work")
super(son,self).work() #方一:调用super方法,super(当前类的名,self).父类被重写的方法())
father.work(self) #方二:这种方法是主动调用父类方法,此时的self需要我们主动添加,表示父类也要执行其对象方法
3、python和C++一样可以继承多个父类
class uncle:
def video(self):
print("uncle.video")
class father(uncle):
def work(self):
print("father.work")
class mother:
def car(self):
print("mother.car") class son(father,mother):
def study(self):
print("son.study")
(1)多个父类继承是从左到右开始继承:
obj = son()
obj.car() # mother.car
(此时是先在father类中找car()方法,没有则再跳转到mother类中)
(2)如果继承的父类之上还有父类,则“一直寻找到底”,有则调用,无则继承下一个父类去找寻方法
obj = son()
obj.video() # uncle.video
(3)上面两种说法是基于其最终父类不是指向同一个,而现在的第三种判断则是基于最终父类是同一个的情况下而进行的讨论,代码如下:
class aunt:
def computer(self):
print("aunt.computer") class uncle:
def video(self):
print("uncle.video") class father(uncle):
def work(self):
print("father.work") class mother(aunt):
def car(self):
print("mother.car") class son(father, mother):
def study(self):
print("son.study") obj = son()
obj.computer() #aunt.computer
其执行的顺序如下图: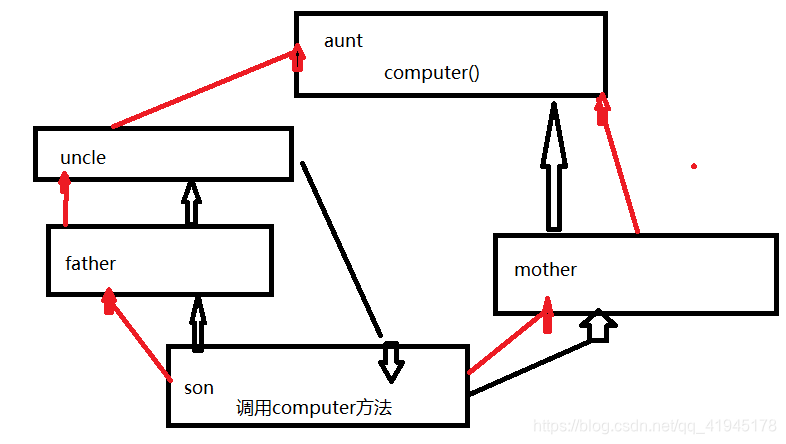
红线是往上继承,黑线是代码执行的流程
还是跟(1)(2)差不多,但是不一样的是,在左侧一直未找到所调用的方法时,并没有有一直找到底,而是在最后一个父类前回到son子类,开始在mother类中寻找,最后才指向aunt类并找到其computer()方法
((3)总结:如果有共同父类,则在寻找方法时,不会一直寻到底,而是在寻到底之前的父类换到最原始给的父类中去寻找,如果都找不到才会找寻到底父类)怎么好理解就怎么去记忆
(4)self.方法()使用时代码执行的顺序
(下面代码修改了一些)
class uncle:
def video(self):
print("uncle.video")
class father(uncle):
def work(self):
print("father.work")
self.car()
def car(self):
print("father.car")
class mother:
def car(self):
print("mother.car") class son(mother,father):
def study(self):
print("son.study")
obj = son()
obj.work() #father.work
#mother.car
对象在去父类找寻方法时,由于mother类没有其方法,在father类下找到并执行后,方法内还有self.car(),按道理来说应该是同一类下有该方法就优先执行,但是结果却是mother.car,其原因很简单,当碰到self.方法()时,就应该返回到其对象(self所指向的对象,此代码是obj)所调用的类中再去执行其方法的调用(对于上述代码,就是再次调用obj.car(),然后先从方法的子类中寻找,再向其父类中找寻方法,第一个父类时mother,在mother类中有car()方法,所以就直接调用执行了,over!)
(5)类中的__init__()方法是在找寻到的第一个时去执行:
class uncle:
def __init__(self):
print("uncle.init")
def video(self):
print("uncle.video")
class father(uncle):
def __init__(self):
print("father.init")
def work(self):
print("father.work")
class mother:
def car(self):
print("mother.car") class son(father,mother):
def study(self):
print("son.study")
obj = son() #father.init
(上述代码father类还继承了一个父类,它们同时有__init__方法,但是先遍历到子类father,所以就先调用其类下的init方法,每当执行其类的对象时,只会执行一次最先遇到的__init__的方法)
最新文章
- 第3月第13天 cpp模版 Iterator模式 proactor
- Linux用户密码重置方法
- html canvas 骰子1
- jsp实现一条横线中间有字的样式
- MSP430设置串口波特率的方法
- Sql的一些概念
- STL之容器基本操作
- hdu 2066 一个人的旅行
- 开发板上修改时间方法date命令【转】
- angularjs小知识
- Android 多线程:使用Thread和Handler (从网络上获取图片)
- C语言数组内存初始化
- ThinkPHP 关联模型(二十)
- 《剑指Offer》算法题——替换空格
- vs远程调试
- foreach 内嵌的使用
- 关于Selenium3+python3.6自动化测试中iframe切换
- (python)数据结构---元组
- Python实战一
- Slick.js+Animate.css 结合让网页炫动起来