【linux高级程序设计】(第九章)进程间通信-管道 3
2024-10-21 04:58:05
有名管道
无名管道和有名管道:
1. 管道是特殊类型的文件,在满足先入先出的原则写可以读写,不能定位读写位置。
2.管道是单向的。
3.无名管道阻塞于读写位置,而有名管道阻塞在创建位置。
4.无名管道一般只用于亲缘关系进程间通信;有名管道以磁盘文件的方式存在,可以实现本机任意两进程间通信。
shell创建有名管道
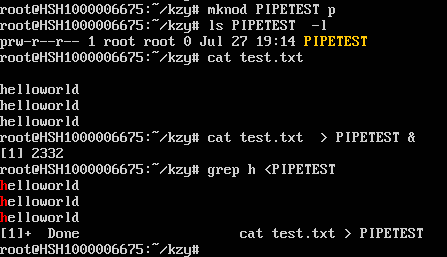
mknod 管道名 p //创建名为PIPETEST的有名管道 mknod为命令 p是参数,表示有名管道
指令 > 管道名 & //将指令结果输入到到管道文件中
指令 < 管道名 //以指定管道名中的内容做为输入
编程实现有名管道
int mkfifo (__const char *__path, __mode_t __mode):建立的有名管道文件必须之前不存在, mode是该文件的权限。成功返回0,否则返回-1.
通过read(), write()实现读写操作。
其阻塞方式见下图(我懒得打字了,就上图吧....)

例子:
写进程
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include<sys/stat.h> #define FIFO_NAME "/tmp/my_fifo" //要创建的有名管道的路径
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
int pipe_fd;
int res;
char buffer[] = "hello world!";
if(access(FIFO_NAME, F_OK) == -) //文件是否存在
{
res = mkfifo(FIFO_NAME, ); //创建管道
if(res != )
{
fprintf(stderr, "Could not create fifo %s\n", FIFO_NAME);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
printf("Process %d opening FIFO O_WRONLY\n", getpid());
pipe_fd = open(FIFO_NAME, O_WRONLY); //打开有名管道
printf("the file's descriptor is %d\n", pipe_fd);
if(pipe_fd != -)
{
res = write(pipe_fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer)); //写数据
if(res == -)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Write error on pipe\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("write data is %s, %d bytes is write\n", buffer, res);
close(pipe_fd);
}
else
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
printf("Process %d finished\n", getpid());
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
读进程
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include<sys/stat.h> #define FIFO_NAME "/tmp/my_fifo" //要创建的有名管道的路径
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
int pipe_fd;
int res;
char buffer[];
int bytes_read = ;
memset(buffer, '\0', sizeof(buffer));
printf("Process %d opening FIFO O_RDONLY\n", getpid());
pipe_fd = open(FIFO_NAME, O_RDONLY); //打开有名管道
printf("the file's descriptor is %d\n", pipe_fd);
if(pipe_fd != -)
{
bytes_read = read(pipe_fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer));
printf("the read data is %s\n", buffer);
close(pipe_fd);
}
else
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
printf("Process %d finished, %d bytes read\n", getpid(), bytes_read);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
运行时,先在一个终端运行写进程,此时写进程会阻塞。
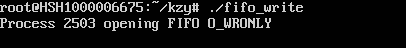
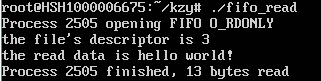
用ctrl+alt+[F1-F6]切换终端,在新终端运行读进程。
读进程端结果为
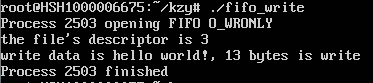
再切换回原终端,写进程也执行完毕。
最新文章
- 关于dll
- HDU1532 网络流:最大流之福德福克森算法
- android Home键和返回键
- ubuntu初次安装后设置root用户密码
- (C#).NET 2.0 ~ 4.0 OS requirements.
- POJ2503——Babelfish(map映射+string字符串)
- 【原】Object 异常静态
- java查询手机号码归属地
- app/desktop/view/index.html 显示授权标识
- git变基--rebase
- mybatis中传入一个List集合作为查询条件的参数
- Dynamics CRM2016 New features in Microsoft Dynamics CRM Online 2015 Update 1 are now available
- 写XML
- 2018-2019-2 20165232《网络对抗技术》Exp1 缓冲区溢出实验
- Python——Tk控件说明
- SolidWorks基础-快速入门
- Beta冲刺 (5/7)
- 20145215《网络对抗》Exp5 MSF基础应用
- Ubuntu 配置vsftpd实现FTP服务器
- odoo开发笔记 -- odoo web机制浅析