Codeforces Round #285 (Div. 2) A, B , C 水, map ,拓扑
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Misha and Vasya participated in a Codeforces contest. Unfortunately, each of them solved only one problem, though successfully submitted it at the first attempt. Misha solved the problem that costs a points and Vasya solved the problem that costs b points. Besides, Misha submitted the problem c minutes after the contest started and Vasya submitted the problem d minutes after the contest started. As you know, on Codeforces the cost of a problem reduces as a round continues. That is, if you submit a problem that costs p points tminutes after the contest started, you get 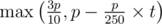 points.
points.
Misha and Vasya are having an argument trying to find out who got more points. Help them to find out the truth.
The first line contains four integers a, b, c, d (250 ≤ a, b ≤ 3500, 0 ≤ c, d ≤ 180).
It is guaranteed that numbers a and b are divisible by 250 (just like on any real Codeforces round).
Output on a single line:
"Misha" (without the quotes), if Misha got more points than Vasya.
"Vasya" (without the quotes), if Vasya got more points than Misha.
"Tie" (without the quotes), if both of them got the same number of points.
500 1000 20 30
Vasya
1000 1000 1 1
Tie
1500 1000 176 177
Misha
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll __int64
#define mod 1000000007
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
const int N=1e5+,M=4e6+,inf=1e9+;
int main()
{
int a,b,c,d;
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c,&d);
int m1=max(*a/,a-(a*c)/);
int m2=max(*b/,b-(b*d)/);
if(m1>m2)
printf("Misha\n");
else if(m1==m2)
printf("Tie\n");
else
printf("Vasya\n");
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Misha hacked the Codeforces site. Then he decided to let all the users change their handles. A user can now change his handle any number of times. But each new handle must not be equal to any handle that is already used or that was used at some point.
Misha has a list of handle change requests. After completing the requests he wants to understand the relation between the original and the new handles of the users. Help him to do that.
The first line contains integer q (1 ≤ q ≤ 1000), the number of handle change requests.
Next q lines contain the descriptions of the requests, one per line.
Each query consists of two non-empty strings old and new, separated by a space. The strings consist of lowercase and uppercase Latin letters and digits. Strings old and new are distinct. The lengths of the strings do not exceed 20.
The requests are given chronologically. In other words, by the moment of a query there is a single person with handle old, and handlenew is not used and has not been used by anyone.
In the first line output the integer n — the number of users that changed their handles at least once.
In the next n lines print the mapping between the old and the new handles of the users. Each of them must contain two strings, old andnew, separated by a space, meaning that before the user had handle old, and after all the requests are completed, his handle is new. You may output lines in any order.
Each user who changes the handle must occur exactly once in this description.
5
Misha ILoveCodeforces
Vasya Petrov
Petrov VasyaPetrov123
ILoveCodeforces MikeMirzayanov
Petya Ivanov
3
Petya Ivanov
Misha MikeMirzayanov
Vasya VasyaPetrov123
思路:map模拟下就好;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll __int64
#define mod 1000000007
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
const int N=1e3+,M=4e6+,inf=1e9+;
string a[N];
string b[N];
map<string,string>m;
int main()
{
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
for(int i=;i<=x;i++)
cin>>a[i]>>b[i];
for(int i=x;i>=;i--)
{
m[a[i]]=b[i];
while(m[b[i]]!="")
{
m[a[i]]=m[b[i]];
m[b[i]]="";
}
}
int ans=;
for(int i=;i<=x;i++)
if(m[a[i]]!="")
ans++;
cout<<ans<<endl;
for(int i=;i<=x;i++)
if(m[a[i]]!="")
cout<<a[i]<<" "<<m[a[i]]<<endl;
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Let's define a forest as a non-directed acyclic graph (also without loops and parallel edges). One day Misha played with the forest consisting of n vertices. For each vertex v from 0 to n - 1 he wrote down two integers, degreev and sv, were the first integer is the number of vertices adjacent to vertex v, and the second integer is the XOR sum of the numbers of vertices adjacent to v (if there were no adjacent vertices, he wrote down 0).
Next day Misha couldn't remember what graph he initially had. Misha has values degreev and sv left, though. Help him find the number of edges and the edges of the initial graph. It is guaranteed that there exists a forest that corresponds to the numbers written by Misha.
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 216), the number of vertices in the graph.
The i-th of the next lines contains numbers degreei and si (0 ≤ degreei ≤ n - 1, 0 ≤ si < 216), separated by a space.
In the first line print number m, the number of edges of the graph.
Next print m lines, each containing two distinct numbers, a and b (0 ≤ a ≤ n - 1, 0 ≤ b ≤ n - 1), corresponding to edge (a, b).
Edges can be printed in any order; vertices of the edge can also be printed in any order.
3
2 3
1 0
1 0
2
1 0
2 0
2
1 1
1 0
1
0 1
The XOR sum of numbers is the result of bitwise adding numbers modulo 2. This operation exists in many modern programming languages. For example, in languages C++, Java and Python it is represented as "^", and in Pascal — as "xor".
思路:总是有度数为1的节点,裸拓扑;
坑点,多个联通块;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll __int64
#define mod 1000000007
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
const int N=1e5+,M=4e6+,inf=1e9+;
vector<int>v[N];
int du[N];
int sum[N];
priority_queue<int>q;
int main()
{
int n;
ll ans=;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&du[i],&sum[i]);
ans+=du[i];
if(du[i]==)
q.push(i);
}
while(!q.empty())
{
int x=q.top();
q.pop();
if(du[x]==)
continue;
du[x]--;
v[x].push_back(sum[x]);
du[sum[x]]--;
sum[sum[x]]^=x;
if(du[sum[x]]==)
q.push(sum[x]);
}
printf("%lld\n",ans/);
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
for(int t=;t<v[i].size();t++)
printf("%d %d\n",i,v[i][t]);
}
return ;
}
/*
4
1 1
1 0
1 3
1 2
*/
最新文章
- 【Ckediter】
- 十天学会DIV+CSS(DIV布局)
- Linux系统上通知网关更新arp
- 9.13 JS循环
- 利用Lambda获取属性名称
- PHP雪花背景验证码
- java(2014版)连接数据库的工具类
- LAMP开发之环境搭建(2014.12.7在ubuntu下)
- Flie类
- 6 支持向量机SVM
- ASP.NET - 编写让别人能读懂的代码
- POJ 2948 DP
- 第七十六节,css颜色和透明度,盒子阴影和轮廓,光标样式
- 设置ulabel的行间距
- 读《Java并发编程的艺术》(二)
- Elasticsearch(GEO)空间检索查询
- AJAX的来龙去脉(由来)-如何被封装出来的--ajax发送异步请求(四步操作)
- SpringMVC_HelloWorld_02
- [Hinton] Neural Networks for Machine Learning - Bayesian
- .net数据库连接防注入参数查询 命令执行 读取 备份 导出导入转化XML格式
热门文章
- POJ 3026 Borg Maze【BFS+最小生成树】
- Introduction to Mathematical Thinking - Week 9 评论答案2
- Decimal fixed point and floating point arithmetic
- mock数据(模拟后台数据)
- 【python】-- Django 中间件、缓存、信号
- MySQL优化器不使用索引的情况
- PAT 1002. A+B for Polynomials (25)
- HDU 3182 Hamburger Magi(状压dp)
- ubuntu17.04 配置go环境变量
- Android之四大组件、六大布局、五大存储