Spring Boot启动过程(六):内嵌Tomcat中StandardHost、StandardContext和StandardWrapper的启动
看代码有助于线上出现预料之外的事的时候,不至于心慌。。。
StandardEngine[Tomcat].StandardHost[localhost]的启动与StandardEngine不在同一个线程中,它的start:
// Start our child containers, if any
Container children[] = findChildren();
List<Future<Void>> results = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
results.add(startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(children[i])));
} boolean fail = false;
for (Future<Void> result : results) {
try {
result.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"), e);
fail = true;
} }
if (fail) {
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"));
}
private static class StartChild implements Callable<Void> {
private Container child;
public StartChild(Container child) {
this.child = child;
}
@Override
public Void call() throws LifecycleException {
child.start();
return null;
}
}
这个start流程中,initInternal方法是ContainerBase的代码,还是那个初始化startStopExecutor的,线程名例如Thread[localhost-startStop-1,5,main],这次是用来初始化host的子容器的,然后是StandardHost中的startInternal方法,主要是注册了一个errorValue,如果现有的pipeline中没有errorvalue,则反射创建org.apache.catalina.valves.ErrorReportValve实例,并加入pipeline中,容器pipeline加入Value时会发布一个Container.ADD_VALVE_EVENT事件,与engine一样,之后进入ContainerBase的startInternal,但是这次Realm是null不需要启动,然后findChildren出StandardEngine[Tomcat]. StandardHost [localhost].StandardContext[],然后同样新开个线程new StartChild,start同样是上面的代码,需要特别说明的是,这次before_init的事件有监听的了,FixContextListener,DisablePersistSessionListener,MemoryLeakTrackingListener;FixContextListener监听的处理,会加入一个用于不做用户身份认证的安全检查的Value:
Context context = (Context) event.getLifecycle();
if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.CONFIGURE_START_EVENT)) {
context.setConfigured(true);
}
// LoginConfig is required to process @ServletSecurity
// annotations
if (context.getLoginConfig() == null) {
context.setLoginConfig(
new LoginConfig("NONE", null, null, null));
context.getPipeline().addValve(new NonLoginAuthenticator());
}
DisablePersistSessionListener监听只处理start事件,所以这里只判断了一下发现不是就出去了,其实这里可以思考下,有没有更好的办法,让监听不只是广播方式,能不能用订阅方式,先不细想了,接着看代码,MemoryLeakTrackingListener只监听了after_start事件,这步同样什么都没做。
于是来到了StandardContext的initInternal,它的super.initInternal又是一个startStopExecutor,ContainerBase的super.initInternal就不再说了,发送j2ee.object.created消息:
Notification notification = new Notification("j2ee.object.created",
this.getObjectName(), sequenceNumber.getAndIncrement());
broadcaster.sendNotification(notification);
Notification是EventObject的子类,代表由MBean发出的通知,MBean server发出的通知会包含发出的MBean的引用,如果MBean注册了监听,可以通过object name或引用获取消息发出者,官方建议使用object name;sendNotification方法:
/**
* Sends a notification.
*
* If an {@code Executor} was specified in the constructor, it will be given one
* task per selected listener to deliver the notification to that listener.
*
* @param notification The notification to send.
*/
public void sendNotification(Notification notification) { if (notification == null) {
return;
} boolean enabled; for (ListenerInfo li : listenerList) {
try {
enabled = li.filter == null ||
li.filter.isNotificationEnabled(notification);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (logger.debugOn()) {
logger.debug("sendNotification", e);
} continue;
} if (enabled) {
executor.execute(new SendNotifJob(notification, li));
}
}
}
发完消息就转变状态为初始化完成,因为监听器是注册在context容器上的,于是after_init事件又触发了那三个监听器,这一阶段监听器什么都没处理走了下过场而已;before_start同走过场;然后StandardContext的startInternal方法,发布了个j2ee.state.starting消息object name为Tomcat:j2eeType=WebModule,name=//localhost/,J2EEApplication=none, J2EEServer=none;setConfigured(false)还没有正确的配置;设置WebResourceRoot,WebResourceRoot提供整个应用资源处理类的各种方法,内嵌用的实现类是StandardRoot,set的过程中加了写锁:
try {
setResources(new StandardRoot(this));
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.resourcesInit"), e);
ok = false;
}
StandardRoot的属性allResources:
private final List<List<WebResourceSet>> allResources =
new ArrayList<>();
{
allResources.add(preResources);
allResources.add(mainResources);
allResources.add(classResources);
allResources.add(jarResources);
allResources.add(postResources);
}
http://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-8.0-doc/api/org/apache/catalina/WebResourceRoot.html有相关说明,我就不翻译了。
set之后就是启动resourcesStart,initInternal执行的是StandardRoot的initInternal方法,super.initInternal中依然是那两行代码,register(cache, getObjectNameKeyProperties() + ",name=Cache")会发送MBeanServerNotification. REGISTRATION_NOTIFICATION通知,生成ObjectName这里cacheJmxName是Tomcat:type=WebResourceRoot,host=localhost,context=/,name=Cache;registerURLStreamHandlerFactory里面的代码是TomcatURLStreamHandlerFactory.register()这行代码的注释说这是为了支持war包内的jar资源的。之后是循环上面的allResources,init里面加入的webResourceSet,但是由于全都是空的,所以等于没执行,就不说了,回头再仔细看看什么情况下回不为空,还是内嵌的就是空的。createMainResourceSet主要是设置个主目录,例如/tmp/tomcat-docbase.3031819619941848514.80,然后是各种资源该放在哪个子目录的一些设置代码;这次资源有一个了,所以可以有一个start了,DirResourceSet的;super.initInternal()的super是AbstractFileResourceSet:
//-------------------------------------------------------- Lifecycle methods
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
// Is this an exploded web application?
if (getWebAppMount().equals("")) {
// Look for a manifest
File mf = file("META-INF/MANIFEST.MF", true);
if (mf != null && mf.isFile()) {
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(mf)) {
setManifest(new Manifest(fis));
} catch (IOException e) {
log.warn(sm.getString("dirResourceSet.manifestFail", mf.getAbsolutePath()), e);
}
}
}
}
super.initInternal主要是对base目录进行了一些规范化处理,规范的方法主要是UnixFileSystem中的canonicalize其中还使用ExpiringCache对路径做了缓存,另外还有在normalize方法中对路径中类似"\.."的部分做了处理。WebAppMount是Web应用发布资源的位置,必须以‘/’开头,这里应该是通过它来判断不是war包部署的模式,然后由于manifest没找到,所以方法返回初始化完成,这个资源一路状态变化就启动完了。
回到StandardRoot,接下来是processWebInfLib方法,代码很直观,不解释了:
private void processWebInfLib() {
WebResource[] possibleJars = listResources("/WEB-INF/lib", false);
for (WebResource possibleJar : possibleJars) {
if (possibleJar.isFile() && possibleJar.getName().endsWith(".jar")) {
createWebResourceSet(ResourceSetType.CLASSES_JAR,
"/WEB-INF/classes", possibleJar.getURL(), "/");
}
}
}
接下来也不解释:
// Need to start the newly found resources
for (WebResourceSet classResource : classResources) {
classResource.start();
}
cache.enforceObjectMaxSizeLimit是计算缓存限制的,详细的可以参考http://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-8.0-doc/config/resources.html,至此StandardRoot的启动完成就只剩下改状态了。
回到StandardContext,因为classloader已经有了不需要new了;接着创建Rfc6265CookieProcessor类型的cookieProcessor实例,关于Rfc6265标准参考http://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc6265.txt;character set mapper因为已经初始化好了只判断了下;工作目录处理,先根据host和engine名生成路径如:work/Tomcat/localhost/ROOT,结合前面的base创建目录例如/tmp/tomcat.3726907762383543267.80/work/Tomcat/localhost/ROOT,然后初始化StandardContext中的ApplicationContext类型可继承的全局变量context构造用参数是this(context = new ApplicationContext(this)),返回new ApplicationContextFacade(this);将上面的全路径设置给ServletContext.TEMPDIR属性,并将这个属性设置为只读:
/**
* Set an attribute as read only.
*/
void setAttributeReadOnly(String name) { if (attributes.containsKey(name))
readOnlyAttributes.put(name, name); }
之后是对扩展进行验证,这里说一下,StandardContext中不管是这里的获取资源还是之后的读取classloader都是加了读锁的:
// Validate required extensions
boolean dependencyCheck = true;
try {
dependencyCheck = ExtensionValidator.validateApplication
(getResources(), this);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.extensionValidationError"), ioe);
dependencyCheck = false;
}
catalina.useNaming用于是否开启命名服务支持,开启了就会注册NamingContextListener监听器:
if (!dependencyCheck) {
// do not make application available if depency check fails
ok = false;
}
// Reading the "catalina.useNaming" environment variable
String useNamingProperty = System.getProperty("catalina.useNaming");
if ((useNamingProperty != null)
&& (useNamingProperty.equals("false"))) {
useNaming = false;
}
if (ok && isUseNaming()) {
if (getNamingContextListener() == null) {
NamingContextListener ncl = new NamingContextListener();
ncl.setName(getNamingContextName());
ncl.setExceptionOnFailedWrite(getJndiExceptionOnFailedWrite());
addLifecycleListener(ncl);
setNamingContextListener(ncl);
}
}
ClassLoader oldCCL = bindThread()里有个ThreadBindingListener,不过因为webApplicationClassLoader是null,所以等于没执行,返回的是null,里面的逻辑还不少,命名服务也没开ContextBindings.bindThread于是也没执行。
old的没有,但是loader还是有的,到了loader的start了,主要要说的是WebappLoader的startInternal方法,classloader创建:
classLoader = createClassLoader();
classLoader.setResources(context.getResources());
classLoader.setDelegate(this.delegate);
buildClassPath的主要功能是遍历各个层次的classloader并将其中classpath的jar拼成一个字符串,例如:/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-oracle/jre/lib/charsets.jar:/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-oracle/jre/lib/deploy.jar:/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-oracle/jre/lib/ext/cldrdata.jar...,是以':'作为分隔是因为我的开发环境是linux,在windows中应该是';':
while (loader != null) {
if (!buildClassPath(classpath, loader)) {
break;
}
loader = loader.getParent();
}
if (delegate) {
// Delegation was enabled, go back and add the webapp paths
loader = getClassLoader();
if (loader != null) {
buildClassPath(classpath, loader);
}
}
delegate之前提过了,是会向基loader类委托的;setClassPath的最后一句:servletContext.setAttribute(Globals.CLASS_PATH_ATTR, this.classpath)。
setPermissions方法,由于我这第一个判断就返回了,而且看上去代码也很直观,我就不说了:
private void setPermissions() {
if (!Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED)
return;
if (context == null)
return;
// Tell the class loader the root of the context
ServletContext servletContext = context.getServletContext();
// Assigning permissions for the work directory
File workDir =
(File) servletContext.getAttribute(ServletContext.TEMPDIR);
if (workDir != null) {
try {
String workDirPath = workDir.getCanonicalPath();
classLoader.addPermission
(new FilePermission(workDirPath, "read,write"));
classLoader.addPermission
(new FilePermission(workDirPath + File.separator + "-",
"read,write,delete"));
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
for (URL url : context.getResources().getBaseUrls()) {
classLoader.addPermission(url);
}
}
((Lifecycle) classLoader).start(),这个classloader是TomcatEmbeddedWebappClassLoader走的是WebappClassLoaderBase中的start方法,这里因为是内嵌的版本(我没确认,猜测)所以也并没有加载到东西,所以也不细说了:
public void start() throws LifecycleException {
state = LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP;
WebResource classes = resources.getResource("/WEB-INF/classes");
if (classes.isDirectory() && classes.canRead()) {
localRepositories.add(classes.getURL());
}
WebResource[] jars = resources.listResources("/WEB-INF/lib");
for (WebResource jar : jars) {
if (jar.getName().endsWith(".jar") && jar.isFile() && jar.canRead()) {
localRepositories.add(jar.getURL());
jarModificationTimes.put(
jar.getName(), Long.valueOf(jar.getLastModified()));
}
}
state = LifecycleState.STARTED;
}
然后生成ObjectName例如:Tomcat:context=/,host=localhost,type=TomcatEmbeddedWebappClassLoader,然后注册MBean:getMBeanServer().registerMBean( mbean, oname);WebappLoader的start就没什么了,started之后就是设置了几个属性:
// since the loader just started, the webapp classloader is now
// created.
setClassLoaderProperty("clearReferencesRmiTargets",
getClearReferencesRmiTargets());
setClassLoaderProperty("clearReferencesStopThreads",
getClearReferencesStopThreads());
setClassLoaderProperty("clearReferencesStopTimerThreads",
getClearReferencesStopTimerThreads());
setClassLoaderProperty("clearReferencesHttpClientKeepAliveThread",
getClearReferencesHttpClientKeepAliveThread());
这里的unbindThread因为前面的bind几乎没做什么,所以什么也没做;接着的bindThread主要讲线程与classloader做了绑定: Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader (webApplicationClassLoader),至于threadBindingListener.bind()由于threadBindingListener用了个空实现,所以这里什么也没做。
接下来用读锁取到Realm并start它;接下来发布configure_start事件,FixContextListener中执行了context.setConfigured(true)。
终于到了StandardWrapper(StandardEngine[Tomcat].StandardHost[localhost].StandardContext[].StandardWrapper[default])的start了,initInternal直接就是ContainerBase的初始化startStopExecutor,startInternal方法是发了个j2ee.state.starting的消息,ObjectName是Tomcat:j2eeType=Servlet, WebModule=//localhost/, name=default, J2EEApplication=none, J2EEServer=none,然后又到ContainerBase的startInternal,然而由于它没有子容器了,所以这里并没有StartChild的任务产生;于是开始执行它的Value,先start它的pipeline,startInternal方法依然是StandardPipeline的,按顺序start,由于到这的时候一个都没有,所以执行的是basic的,StandardWrapperValve的initInternal中只有一句注释:Don't register this Valve in JMX;startInternal的最后是threadStart,但由于backgroundProcessorDelay是-1所以并没有启动背景线程;setAvailable(0L)设置可用,它的说明 The date and time at which this servlet will become available (in milliseconds since the epoch), or zero if the servlet is available;然后发送一个消息j2ee.state.running,ObjectName是Tomcat:j2eeType=Servlet,WebModule=//localhost/,name=default,J2EEApplication=none,J2EEServer=none;
StandardWrapper就启动完了,回到StandardContext,start它的pipeline;与StandardWrapper的pipeline不同,它之前被注册过NonLoginAuthenticator,它的startInternal方法定义在AuthenticatorBase,方法中设置了jaspicAppContextID(例如:Tomcat/localhost ),然后获取上级容器也就是host的pipeline中的所有Value,并找到其中SingleSignOn类型的Value,明显是用于单点登录的,我这里没有,于是又去找了上一级容器engine当然还是没有,于是就往下走了;实例化了一个StandardSessionIdGenerator,设置安全随机数生成算法我这里是SHA1PRNG,生成器类名为null,生成器provider也是null,然后就是下一个Value对象StandardContextValve的start,只不过它的start是标准的什么额外事都没干,于是回到了StandardContext中。下面一段主要是执行了TomcatEmbeddedContext中的setManager方法:
@Override
public void setManager(Manager manager) {
if (manager instanceof ManagerBase) {
((ManagerBase) manager).setSessionIdGenerator(new LazySessionIdGenerator());
}
super.setManager(manager);
}
这里判断是true,LazySessionIdGenerator整个的代码:
class LazySessionIdGenerator extends StandardSessionIdGenerator {
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
}
}
TomcatEmbeddedContext的super.setManager(manager)的super是StandardContext,在写锁中执行的,spring中多数的set都是交换的方式,先set个old保存下来,然后判断新值和old是否相同,不相同用新的并将新值绑定容器,相同直接返回;getServletContext().setAttribute(Globals.RESOURCES_ATTR, getResources())没什么好解释的;setNamingResources(new NamingResourcesImpl());然后init这个namingResources,NamingResourcesImpl的initInternal,在设置当前已知命名资源前设置resourceRequireExplicitRegistration用于避免时序问题,重复注册是正常的,后面一段我不想解释:
for (ContextResource cr : resources.values()) {
try {
MBeanUtils.createMBean(cr);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn(sm.getString(
"namingResources.mbeanCreateFail", cr.getName()), e);
}
}
for (ContextEnvironment ce : envs.values()) {
try {
MBeanUtils.createMBean(ce);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn(sm.getString(
"namingResources.mbeanCreateFail", ce.getName()), e);
}
}
for (ContextResourceLink crl : resourceLinks.values()) {
try {
MBeanUtils.createMBean(crl);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn(sm.getString(
"namingResources.mbeanCreateFail", crl.getName()), e);
}
}
init之后是start,start中只发布了个configure_start事件。
setInstanceManager(new DefaultInstanceManager(context, injectionMap, this, this.getClass().getClassLoader())),InstanceManager主要是用于创建和回收实例,然后绑定:
getServletContext().setAttribute(
InstanceManager.class.getName(), getInstanceManager());
InstanceManagerBindings.bind(getLoader().getClassLoader(), getInstanceManager());
还有:
getServletContext().setAttribute(
JarScanner.class.getName(), getJarScanner());
合并参数mergeParameters由于我这里是空的,所以什么也没做;然后遍历initializers并onStartup:
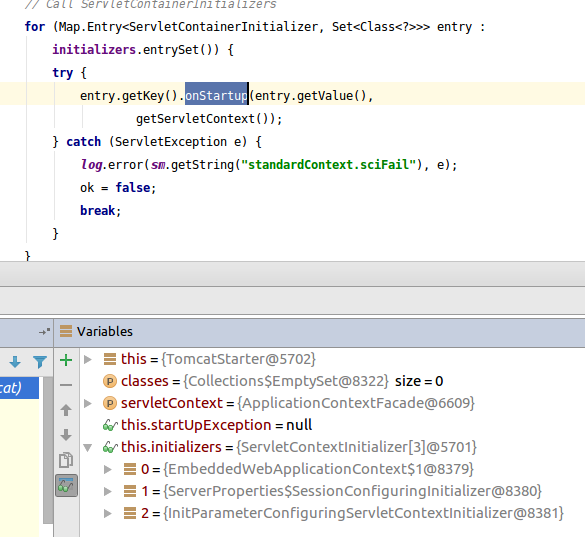
先是进入到TomcatStarter的onStartup,这里又是:
for (ServletContextInitializer initializer : this.initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
先是执行:
private org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletContextInitializer getSelfInitializer() {
return new ServletContextInitializer() {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
selfInitialize(servletContext);
}
};
}
EmbeddedWebApplicationContext中的selfInitialize ,prepareEmbeddedWebApplicationContext正常情况下先打一条日志Initializing Spring embedded WebApplicationContext然后servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this)然后将this绑定servletContext,如果启动Info级别日志,会打印类似这样的日志:Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in 3150193 ms;然后new ExistingWebApplicationScopes,这玩意的注释说它允许与非嵌入式相同的方式注册作用域到ApplicationContextInitializer,先执行了一个静态代码块:
static {
Set<String> scopes = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
scopes.add(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_REQUEST);//request
scopes.add(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_SESSION);//session
scopes.add(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_GLOBAL_SESSION);//global session
SCOPES = Collections.unmodifiableSet(scopes);
}
但是似乎在我这add白做了,因为构造函数中从bean工厂并没取到Scope实例:
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
for (String scopeName : SCOPES) {
Scope scope = beanFactory.getRegisteredScope(scopeName);
if (scope != null) {
this.scopes.put(scopeName, scope);
}
}
真正注册作用域是在下一句WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory, getServletContext()):
beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_REQUEST, new RequestScope());
beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_SESSION, new SessionScope(false));
beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_GLOBAL_SESSION, new SessionScope(true));
if (sc != null) {
ServletContextScope appScope = new ServletContextScope(sc);
beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_APPLICATION, appScope);
// Register as ServletContext attribute, for ContextCleanupListener to detect it.
sc.setAttribute(ServletContextScope.class.getName(), appScope);
} beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletRequest.class, new RequestObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletResponse.class, new ResponseObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(HttpSession.class, new SessionObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(WebRequest.class, new WebRequestObjectFactory());
if (jsfPresent) {
FacesDependencyRegistrar.registerFacesDependencies(beanFactory);
}
registerResolvableDependency将类型与对应的装配对象注册进bean工厂。existingScopes.restore里的代码:
public void restore() {
for (Map.Entry<String, Scope> entry : this.scopes.entrySet()) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Restoring user defined scope " + entry.getKey());
}
this.beanFactory.registerScope(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(beanFactory, getServletContext())把相应的变量key与值注册给bean工厂,如servletContext、contextParameters和contextAttributes;从bean工厂中获取所有org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletContextInitializer类型的bean,如filterRegistrationBean和dispatcherServletRegistration然后add给ServletContextInitializerBeans实例的initializers;addAdaptableBeans方法先从bean工厂中获取javax.servlet.MultipartConfigElement类型的对象,然而javax.servlet.Servlet没在bean工厂里找到,所以add什么也没做;javax.servlet.Filter找到characterEncodingFilter、hiddenHttpMethodFilter、httpPutFormContentFilter、requestContextFilter;ServletListenerRegistrationBean.getSupportedTypes()取的是ServletListenerRegistrationBean的SUPPORTED_TYPES,不过全都没找到,所以什么也没做:
static {
Set<Class<?>> types = new HashSet<Class<?>>();
types.add(ServletContextAttributeListener.class);
types.add(ServletRequestListener.class);
types.add(ServletRequestAttributeListener.class);
types.add(HttpSessionAttributeListener.class);
types.add(HttpSessionListener.class);
types.add(ServletContextListener.class);
SUPPORTED_TYPES = Collections.unmodifiableSet(types);
}
然后是对找到的进行排序:
List<ServletContextInitializer> sortedInitializers = new ArrayList<ServletContextInitializer>();
for (Map.Entry<?, List<ServletContextInitializer>> entry : this.initializers
.entrySet()) {
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(entry.getValue());
sortedInitializers.addAll(entry.getValue());
}
this.sortedList = Collections.unmodifiableList(sortedInitializers); public static void sort(Object[] array) {
if (array.length > 1) {
Arrays.sort(array, INSTANCE);
}
} private int doCompare(Object o1, Object o2, OrderSourceProvider sourceProvider) {
boolean p1 = (o1 instanceof PriorityOrdered);
boolean p2 = (o2 instanceof PriorityOrdered);
if (p1 && !p2) {
return -1;
}
else if (p2 && !p1) {
return 1;
} // Direct evaluation instead of Integer.compareTo to avoid unnecessary object creation.
int i1 = getOrder(o1, sourceProvider);
int i2 = getOrder(o2, sourceProvider);
return (i1 < i2) ? -1 : (i1 > i2) ? 1 : 0;
}
然后对这些初始化器进行beans.onStartup(servletContext);filterRegistrationBean执行的AbstractFilterRegistrationBean的,主要执行了这两句:
FilterRegistration.Dynamic added = servletContext.addFilter(name, filter);
...
configure(added);
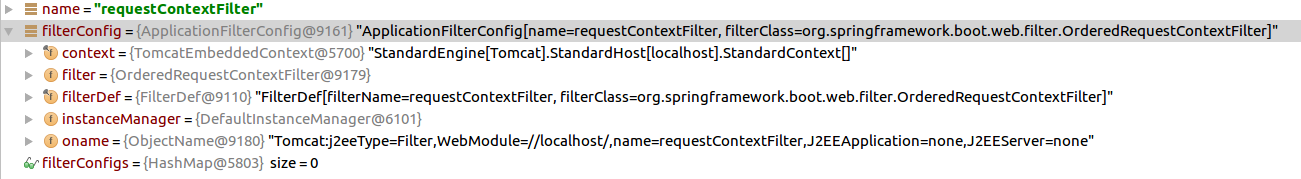
name:characterEncodingFilter,filter:OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter,它的配置中这里设定了过滤器转发模式有FORWARD、INCLUDE、REQUEST、ASYNC,拦截路径:"/*";然后是hiddenHttpMethodFilter和OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter,httpPutFormContentFilter和OrderedHttpPutFormContentFilter,requestContextFilter和OrderedRequestContextFilter,cipherFilter和CipherFilter(我这自定义的)。ServletRegistrationBean的:dispatcherServlet和DispatcherServlet,asyncSupported是true,url映射是‘/’,设置StandardWrapper的loadOnStartup、 multipartConfigElement。
到了下一个初始化器SessionConfiguringInitializer:
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
if (this.session.getTrackingModes() != null) {
servletContext.setSessionTrackingModes(this.session.getTrackingModes());
}
configureSessionCookie(servletContext.getSessionCookieConfig());
}
将session中的cookie信息补充进ApplicationSessionCookieConfig的实例中,例如:
config.setName(cookie.getName());
config.setDomain(cookie.getDomain());
config.setPath(cookie.getPath());
config.setComment(cookie.getComment());
config.setHttpOnly(cookie.getHttpOnly());
config.setSecure(cookie.getSecure());
config.setMaxAge(cookie.getMaxAge());
实际中我这里一个都没执行,因为我这的session中cookie信息都是null。
下一个初始化器InitParameterConfiguringServletContextInitializer由于参数没有,所以进去就出来了。
回到listenerStart,listenerStart:org.apache.tomcat.websocket.server.WsContextListener,用前面的DefaultInstanceManager的newInstance创建,然后加到lifecycleListeners中,然后传给applicationLifecycleListenersObjects,然后是newServletContextListenerAllowed=false:当listener发生调用后不允许添加,发布beforeContextInitialized事件,然后WsContextListener的contextInitialized:
ServletContext sc = sce.getServletContext();
if(sc.getAttribute("javax.websocket.server.ServerContainer") == null) {
WsSci.init(sce.getServletContext(), false);
}
init中先是初始化WsServerContainer:
static {
GET_BYTES = "GET ".getBytes(StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1);
ROOT_URI_BYTES = "/".getBytes(StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1);
HTTP_VERSION_BYTES = " HTTP/1.1\r\n".getBytes(StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1);
}
static {
AUTHENTICATED_HTTP_SESSION_CLOSED = new CloseReason(CloseCodes.VIOLATED_POLICY, "This connection was established under an authenticated HTTP session that has ended.");
}
WsServerContainer(ServletContext servletContext) {
this.enforceNoAddAfterHandshake = Constants.STRICT_SPEC_COMPLIANCE; //Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.tomcat.websocket.STRICT_SPEC_COMPLIANCE")
this.addAllowed = true;
this.authenticatedSessions = new ConcurrentHashMap();
this.endpointsRegistered = false;
this.servletContext = servletContext;
//我这里添加了org.apache.tomcat.websocket.server和本地语言en_US(我代码是在英文版ubuntu上跑的)
this.setInstanceManager((InstanceManager)servletContext.getAttribute(InstanceManager.class.getName()));
String value = servletContext.getInitParameter("org.apache.tomcat.websocket.binaryBufferSize");
if(value != null) {
this.setDefaultMaxBinaryMessageBufferSize(Integer.parseInt(value));
}
value = servletContext.getInitParameter("org.apache.tomcat.websocket.textBufferSize");
if(value != null) {
this.setDefaultMaxTextMessageBufferSize(Integer.parseInt(value));
}
//Java WebSocket 规范 1.0 并不允许第一个服务端点开始 WebSocket 握手之后进行程序性部署。默认情况下,Tomcat 继续允许额外的程序性部署。
value = servletContext.getInitParameter("org.apache.tomcat.websocket.noAddAfterHandshake");
if(value != null) {
this.setEnforceNoAddAfterHandshake(Boolean.parseBoolean(value));
}
Dynamic fr = servletContext.addFilter("Tomcat WebSocket (JSR356) Filter", new WsFilter());
fr.setAsyncSupported(true);
EnumSet types = EnumSet.of(DispatcherType.REQUEST, DispatcherType.FORWARD);
fr.addMappingForUrlPatterns(types, true, new String[]{"/*"});
}
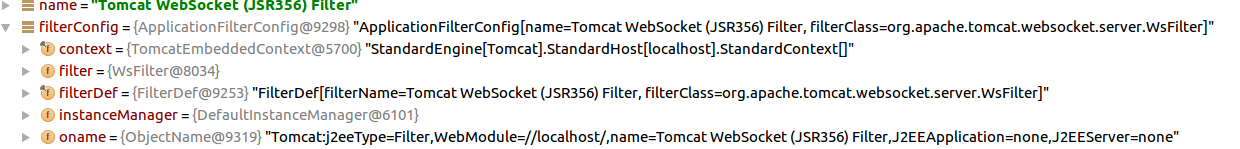
init创建了 WsServerContainer之后,将它设置给servletContext的javax.websocket.server.ServerContainer属性,然后servletContext.addListener(new WsSessionListener(sc))加进前面的applicationLifecycleListenersObjects中,init结束,回到StandardContext发布afterContextInitialized事件,我这到这里listenerStart结束。
checkConstraintsForUncoveredMethods(findConstraints())因为我这里find出来的并没有,所以pass;start StandardManager startInternal先是super(ManagerBase),一进方法先是将两个双端队列sessionCreationTiming和sessionExpirationTiming根据常量TIMING_STATS_CACHE_SIZE用null填满,设置jvmRoute(jvmRoute用于区分多tomcat节点,根据jvmRoute的值来确定当前会话属于哪个节点 ),从engine上取得,之前设置过,getEngine:
public Engine getEngine() {
Engine e = null;
for (Container c = getContext(); e == null && c != null ; c = c.getParent()) {
if (c instanceof Engine) {
e = (Engine)c;
}
}
return e;
}
set给sessionIdGenerator,将之前初始化过的一些sessionIdGenerator值set给新new的SessionIdGeneratorBase,然后start之前的sessionIdGenerator,这个start没做什么特别的,于是回到StandardManager,加载文件(例:/tmp/tomcat.7550276477249965168.80/work/Tomcat/localhost/ROOT/SESSIONS.ser),用于session持久化的,这时候找不到的。
filterStart对filterConfigs同步锁,filterConfigs.put(name, filterConfig):
loadOnStartup(findChildren()),其实都一起start过了就不用了:
该启动StandardContext的后天线程了super.threadStart(),当然因为backgroundProcessorDelay所以也没启,unbindThread说是解绑,其实只是把classloader还原了,别的没做什么,对应着之前的bind。
设置StandardContext的startTime=System.currentTimeMillis(),发j2ee.state.running的通知,ObjectName是Tomcat:J2EEApplication=none, J2EEServer=none, j2eeType=WebModule, name=//localhost/;getResources().gc()因为WebResources引用了一些jar,有些平台可能会对jar加锁,这里先清理,但实际上这里的实现是空的。
DisablePersistSessionListener由于并没有配置session持久化,所以会触发这个监听器,实际只执行了((StandardManager) manager).setPathname(null)。MemoryLeakTrackingListener只走了个过场。
发布after_start事件,这回终于执行了MemoryLeakTrackingListener:
if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.AFTER_START_EVENT)) {
if (event.getSource() instanceof Context) {
Context context = ((Context) event.getSource());
childClassLoaders.put(context.getLoader().getClassLoader(),
context.getServletContext().getContextPath());
}
}
子容器就启动完成了。
==========================================================
咱最近用的github:https://github.com/saaavsaaa
微信公众号:

最新文章
- centos6.5安装sublime text 2
- Javascript判断空对象
- 黑马程序员:Java基础总结----JavaBean 内省
- (简单) POJ 1502 MPI Maelstrom,Dijkstra。
- webService 下得 拦截
- 微服务框架下的思维变化-OSS.Core基础思路
- python迭代器生成器(一)
- akoj-1280另类阶乘问题
- Spring 4.x (二)
- 亲测可用,iptables实现NAT转发。
- 在 CentOS6 上安装 Zabbix2.4 Server
- 使用CLion在MacOS、Linux上编译C++代码
- 20171126-handler消息机制理解
- Unity透明Shader
- ubuntu 下mysql导入出.sql文件
- HTML5+CSS3 表格设计(Table)
- 測试赛C - Eqs(哈希)
- mysql完整备份与恢复
- 【SQL查询】按照多个字段进行排序_order by
- java基础之多线程四:简单案例
热门文章
- hue database is locked
- js 倒计时功能,获取当前时间的年月日,时分秒
- Golang之实现一个负载均衡算法(随机,轮询)
- golang之数组
- PhpStorm (强大的PHP开发环境)2017.3.2 附注册方法
- 用Hash Table(哈希散列表)实现统计文本每个单词重复次数(频率)
- Nginx 出现413 Request Entity Too Large 错误解决方法(上传大小限制)
- PHP语言性能优化——少使用魔术方法
- 修改RocketMQ的NameServer端口
- 安装系统重启的时候出现了error:file '/boot/grub/i386-pc/normal.mod' not found