CUDA C Programming Guide 在线教程学习笔记 Part 13
▶ 纹理内存访问补充(见纹理内存博客 http://www.cnblogs.com/cuancuancuanhao/p/7809713.html)
▶ 计算能力
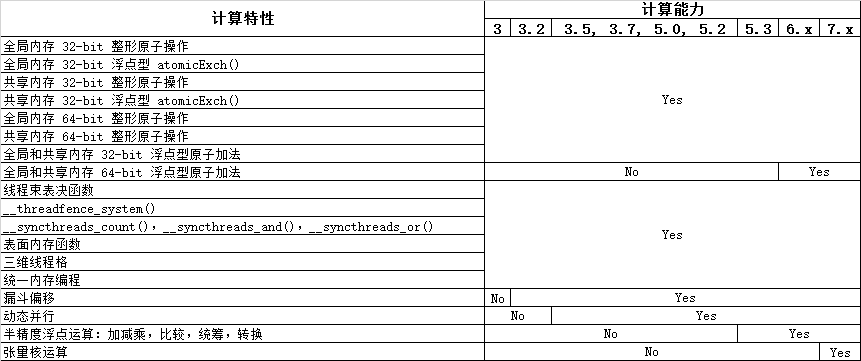
● 不同计算能力的硬件对计算特性的支持。
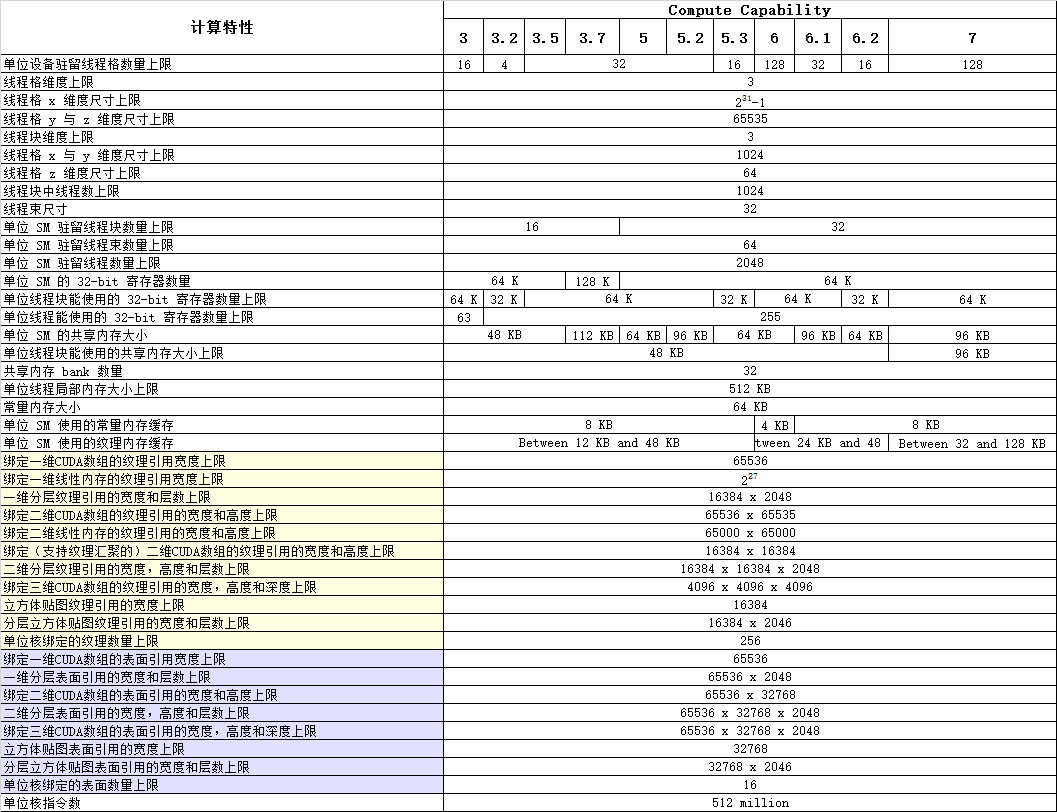
● 不同计算能力的硬件技术特性(重要)。
● 浮点运算技术标准描述(原文)
■ All compute devices follow the IEEE 754-2008 standard for binary floating-point arithmetic with the following deviations:
There is no dynamically configurable rounding mode; however, most of the operations support multiple IEEE rounding modes, exposed via device intrinsics;
There is no mechanism for detecting that a floating-point exception has occurred and all operations behave as if the IEEE-754 exceptions are always masked, and deliver the masked response as defined by IEEE-754 if there is an exceptional event; for the same reason, while SNaN encodings are supported, they are not signaling and are handled as quiet;
The result of a single-precision floating-point operation involving one or more input NaNs is the quiet NaN of bit pattern 0x7fffffff;
Double-precision floating-point absolute value and negation are not compliant with IEEE-754 with respect to NaNs; these are passed through unchanged;
Code must be compiled with -ftz=false, -prec-div=true, and -prec-sqrt=true to ensure IEEE compliance (this is the default setting; see the nvcc user manual for description of these compilation flags).
Regardless of the setting of the compiler flag -ftz,
Atomic single-precision floating-point adds on global memory always operate in flush-to-zero mode, i.e., behave equivalent to FADD.F32.FTZ.RN,
Atomic single-precision floating-point adds on shared memory always operate with denormal support, i.e., behave equivalent to FADD.F32.RN.
■ IEEE-754R 标准,CUDA 设备上函数 fminf(),fmin(),fmaxf(),fmax() 在有且仅有一个参数为NaN时,返回值将是另一个参数。
■ 浮点数转化为整数,且超出整形格式边界时,IEEE-754 称为未定义,而 CUDA 设备将该数映射到整形格式边界(改格式能表示的最大或最小的数)。
■ 整数除以零或整数溢出时,IEEE-754 称为未定义,而 CUDA 设备将抛出一个非特定的值。
● 各代 CC 设备的新特性介绍
■ 调整共享内存和 L1 缓存的平衡
// driver_types.h
enum __device_builtin__ cudaFuncCache
{
cudaFuncCachePreferNone = , // 默认缓存模式
cudaFuncCachePreferShared = , // 扩大共享内存缩小 L1 缓存
cudaFuncCachePreferL1 = , // 扩大 L1 缓存缩小共享内存
cudaFuncCachePreferEqual = // 等量大小的共享内存和 L1 缓存
}; // cuda_runtime_api.h
extern __host__ cudaError_t CUDARTAPI cudaDeviceSetCacheConfig(enum cudaFuncCache cacheConfig);
最新文章
- 分析MariaDB初始化脚本mysql_install_db
- __cdecl 、__fastcall、__stdcall
- 树莓派启用root账户
- linux常用命令之--用户与用户组管理命令
- java 容器类大集结
- STK 10.1.3
- java算法之冒泡排序法
- Effective C++_笔记_条款00_基本术语
- Struts1项目转成Struts2项目步奏
- Java多线程JUC
- linux IPtable防火墙 禁止和开放端口
- reStructuredText语法简单说明
- 为什么学习linux
- Python Socket 通信
- Web Deploy
- 【BZOJ】4430: [Nwerc2015]Guessing Camels赌骆驼
- Webstorm2016使用技巧——SVN插件使用(svnToolBox)
- 【五】MongoDB管理之生产环境说明
- tarjan求割点
- pandas小结