机器学习作业(一)线性回归——Matlab实现
2024-09-06 20:31:15
题目太长啦!文档下载【传送门】
第1题
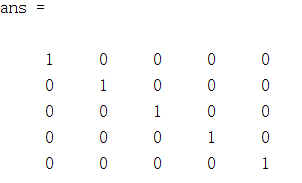
简述:设计一个5*5的单位矩阵。
function A = warmUpExercise()
A = [];
A = eye(5);
end
运行结果:
第2题
简述:实现单变量线性回归。
第1步:加载数据文件;
data = load('ex1data1.txt');
X = data(:, 1); y = data(:, 2);
m = length(y); % number of training examples
% Plot Data
% Note: You have to complete the code in plotData.m
plotData(X, y);
第2步:plotData函数实现训练样本的可视化;
function plotData(x, y)
figure;
plot(x,y,'rx','MarkerSize',10);
ylabel('Profit in $10,000s');
xlabel('Population of City in 10,000s');
end
第3步:使用梯度下降函数计算局部最优解,并显示线性回归;
X = [ones(m, 1), data(:,1)]; % Add a column of ones to x
theta = zeros(2, 1); % initialize fitting parameters
% Some gradient descent settings
iterations = 1500;
alpha = 0.01;
% run gradient descent
theta = gradientDescent(X, y, theta, alpha, iterations);
% print theta to screen
fprintf('Theta found by gradient descent:\n');
fprintf('%f\n', theta);
% Plot the linear fit
hold on; % keep previous plot visible
plot(X(:,2), X*theta, '-')
legend('Training data', 'Linear regression')
hold off % don't overlay any more plots on this figure
第4步:实现梯度下降gradientDescent函数;
function [theta, J_history] = gradientDescent(X, y, theta, alpha, num_iters) % Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples
J_history = zeros(num_iters, 1); for iter = 1:num_iters
theta = theta - alpha/length(y)*(X'*(X*theta-y));
% Save the cost J in every iteration
J_history(iter) = computeCost(X, y, theta);
end end
第5步:实现代价计算computeCost函数;
function J = computeCost(X, y, theta)
m = length(y); % number of training examples
J = 1/(2*m)*sum((X*theta-y).^2);
end
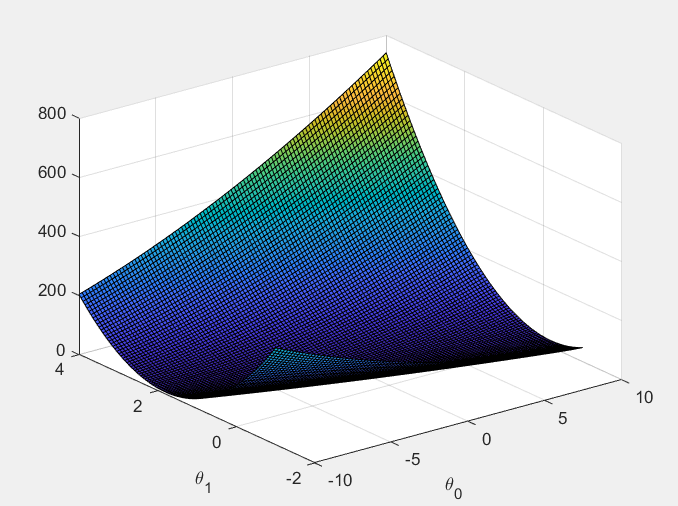
第6步:实现三维图、轮廓图的显示。
% Grid over which we will calculate J
theta0_vals = linspace(-10, 10, 100);
theta1_vals = linspace(-1, 4, 100); % initialize J_vals to a matrix of 0's
J_vals = zeros(length(theta0_vals), length(theta1_vals)); % Fill out J_vals
for i = 1:length(theta0_vals)
for j = 1:length(theta1_vals)
t = [theta0_vals(i); theta1_vals(j)];
J_vals(i,j) = computeCost(X, y, t);
end
end % Because of the way meshgrids work in the surf command, we need to
% transpose J_vals before calling surf, or else the axes will be flipped
J_vals = J_vals';
% Surface plot
figure;
surf(theta0_vals, theta1_vals, J_vals);
xlabel('\theta_0'); ylabel('\theta_1'); % Contour plot
figure;
% Plot J_vals as 15 contours spaced logarithmically between 0.01 and 100
contour(theta0_vals, theta1_vals, J_vals, logspace(-2, 3, 20))
xlabel('\theta_0'); ylabel('\theta_1');
hold on;
plot(theta(1), theta(2), 'rx', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'LineWidth', 2);
运行结果:


第3题
简述:实现多元线性回归。
第1步:加载数据文件;
data = load('ex1data2.txt');
X = data(:, 1:2);
y = data(:, 3);
m = length(y);
[X mu sigma] = featureNormalize(X);
% Add intercept term to X
X = [ones(m, 1) X];
第2步:均值归一化featureNormalize函数实现;
function [X_norm, mu, sigma] = featureNormalize(X) X_norm = X;
mu = zeros(1, size(X, 2));
sigma = zeros(1, size(X, 2));
mu = mean(X,1);
sigma = std(X,0,1);
X_norm = (X_norm-mu)./sigma; end
第3步:使用梯度下降函数计算局部最优解,并显示线性回归;
% Choose some alpha value
alpha = 0.05;
num_iters = 100; % Init Theta and Run Gradient Descent
theta = zeros(3, 1);
[theta, J_history] = gradientDescentMulti(X, y, theta, alpha, num_iters); % Plot the convergence graph
figure;
plot(1:numel(J_history), J_history, '-b', 'LineWidth', 2);
xlabel('Number of iterations');
ylabel('Cost J');
第4步:实现梯度下降gradientDescentMulti函数;
function [theta, J_history] = gradientDescentMulti(X, y, theta, alpha, num_iters) m = length(y); % number of training examples
J_history = zeros(num_iters, 1); for iter = 1:num_iters
theta = theta - alpha/m*(X'*(X*theta-y));
% Save the cost J in every iteration
J_history(iter) = computeCostMulti(X, y, theta);
end end
第5步:实现代价计算computeCostMulti函数;
function J = computeCostMulti(X, y, theta)
m = length(y); % number of training examples
J = 1/(2*m)*sum((X*theta-y).^2);%J=(X*theta-y)'*(X*theta-y)/(2*m);
end
运行结果:

第6步:使用上述结果对“the price of a 1650 sq-ft, 3 br house”进行预测;
X1 = [1,1650,3];
X1(2:3) = (X1(2:3)-mu)./sigma;
price = X1*theta;
预测结果:

第7步:使用正规方程法求解;
%%Load Data
data = csvread('ex1data2.txt');
X = data(:, 1:2);
y = data(:, 3);
m = length(y); % Add intercept term to X
X = [ones(m, 1) X]; % Calculate the parameters from the normal equation
theta = normalEqn(X, y);
第8步:实现normalEqn函数;
function [theta] = normalEqn(X, y)
theta = zeros(size(X, 2), 1);
theta = (X'*X)^(-1)*X'*y;
end
第9步:使用上述结果对“the price of a 1650 sq-ft, 3 br house”再次进行预测;
price = [1,1650,3]*theta;
预测结果:(与梯度下降法结果很接近)

最新文章
- Linux 下 git连接github的使用
- iOS中关于.pch的新建与配置问题
- 【django】request
- Oracle 10g设置IP访问限制
- 黑盒测试用例设计方法&理论结合实际 -> 判定表驱动法
- JavaScript之面向对象学习二(原型属性对象与in操作符)获取对象中所有属性的方法
- asm 盘头损失,破坏
- wpf xmal基础
- CentOS6.4安装go环境
- setTimeout和setInterval不容易注意到的一些细节
- tensorflow 自定义损失函数示例
- vim 当前用户显示行号
- TypeScript入门(一)
- MySQL--BNL/ICP/MRR/BKA
- vba报表制作
- 01List.ashx(班级列表动态页面)
- eclipse 大括号 改为C语言风格
- es 之 Symbol
- Frosh Week
- bzoj 1115: [POI2009]石子游戏Kam -- 博弈论