mysql基础知识语法汇总整理(二)
2024-09-26 23:56:06
insert
/*insert*/
insert into 表名(字段列表) values(值列表);
--蠕虫复制 (优点:快速复制数据,测试服务器压力)
insert into 表名1_插入 select (字段列表) from 表名2_复制;
例如:create table copy(
id int(10) unsigned not null comment 'id',
name char(20) not null default '' comment '名字'
)engine=InnoDB default charset=utf8 comment='复制表';
insert into copy values(1,'admin_a'),(2,'admin_b'),(3,'admin_c'); create table append(
id int(10) unsigned not null comment 'id',
name char(20) not null default '' comment '名字'
)engine=InnoDB default charset=utf8 comment='插入表';
insert into append select * from copy;
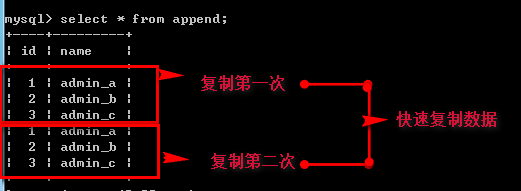
--主键(唯一索引)重复
insert into 表名(字段列表) values(值列表) on duplicate key update 字段1=值1,字段n=值n;
例如:create table conflict(
id int(10) unsigned not null primary key comment 'id',
name char(20) not null default '' comment '名字'
)engine=InnoDB default charset=utf8 comment='冲突表';
insert into conflict values(1,'admin_a');
insert into conflict values(1,'admin_b');--报错 解决:当主键不冲突的时候,相当于一条插入语句;当主键有冲突的时候,相当于一条更新语句.

insert into conflict values(1,'admin_b') on duplicate key update name='admin_b';

select
/*select*/
select [select选项] *|字段列表 [as 字段别名] from 表名 [where子句][group by子句][having子句][order by子句][limit子句]; --select选项: 系统在查询到相关数据之后,如何显示.
--select选项的两个值:
all: 默认值,保留所有的查询结果.
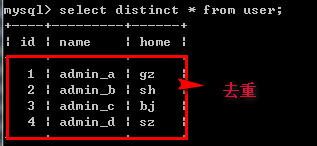
distinct: 去重,去掉重复的查询结果.
例如:create table user(
id int(10) unsigned not null comment 'id',
name char(20) not null default '' comment '名字',
home varchar(50) not null default '' comment '家庭地址'
)engine=InnoDB default charset=utf8 comment='用户表';
insert into user values(1,'admin_a','gz'),(2,'admin_b','sh'),(3,'admin_c','bj'),(4,'admin_d','sz');
select all * from user;
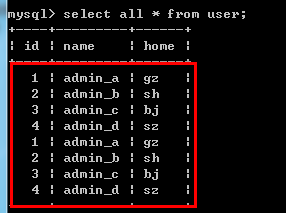
select distinct * from user;
--关键字 as:可以为每个列使用别名. 适用于简化列标识,避免多个列标识符重复. 也可省略as.
例如:create table score(
Math int(3) not null default 0 comment '数学',
English int(3) not null default 0 comment '英语',
Chinese int(3) not null default 0 comment '语文'
)engine=InnoDB default charset=utf8 comment='成绩表';
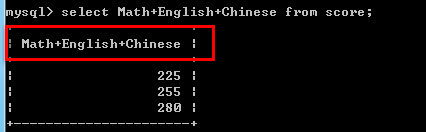
insert into score values(65,75,85),(75,85,95),(85,95,100);
select Math+English+Chinese from score;
select (Math+English+Chinese) as sum from score;
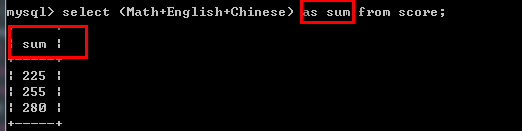
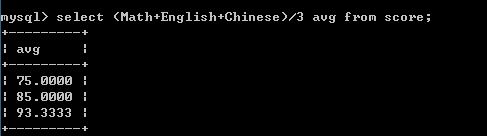
select (Math+English+Chinese)/3 avg from score;--省略as
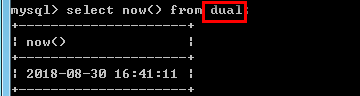
--虚拟表的名称:dual
--Mysql中执行select语句在适当的时候会自动创建一个虚拟表.
select now() from dual;
--where子句 (条件查询)
--从from获得的数据源中进行查询
--整型: 1表示真(返回查询记录);0表示假(不返回记录)
--表达式由运算符和运算数组成.
--运算数: 变量(字段)、值、函数返回值
--比较运算符(常用示例)
<, >, <=, >=, =, !=或<>, IS NULL
between and | not between and --例如: between A and B; 相当于区间[A,B].
in | not in --例如:in表示某个值出现; not in表示没出现在一个集合之中.
is null | is not null --空值查询
like --通配符; _ :代表任意的单个字符; % :代表任意的字符
--逻辑运算符
&&(AND), ||(OR), !(NOT), XOR异或
例如:create table student(
id int(10) unsigned not null auto_increment comment 'id',
name char(10) not null default '' comment '名字',
score smallint(5) not null default 0 comment '成绩',
class varchar(20) not null default '' comment '班级',
primary key (id)
)engine=InnoDB default charset=utf8 comment='学生表';
insert into student(name,score,class) values('uzi',100,'A'),('ming',90,'B'),('mlxg',80,'C'),('xiye',95,'A'),('letme',85,'B');
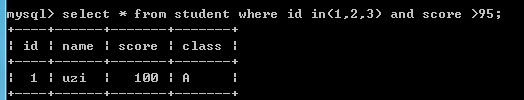
select * from student where id in(1,2,3) and score >95;--查询ID 1,2,3并且score大于95
select * from student where id between 2 and 5 and name like 'm%';--查询ID 区间[2,5]并且模糊查询name字段以“m”开头的学生信息

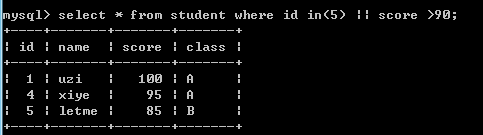
select * from student where id in(5) || score >90;--查询ID 5,或score大于90
--group by子句 (分组)
--group by 字段/别名 [排序方式] 分组后排序: asc 升序(默认),desc 降序
--统计函数需配合group by使用:
count 返回不同的非NULL统计值 count(*)、count(字段)
sum 求和; max 求最大值; min 求最小值; avg 求平均值
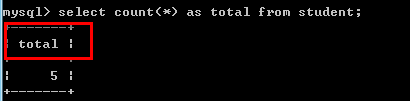
例如:select count(*) as total from student;
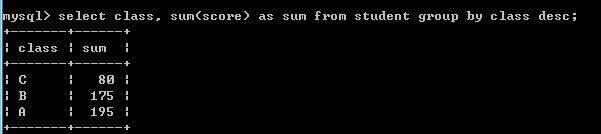
select class, sum(score) as sum from student group by class desc;--查询各个班级总成绩,分组班级降序.
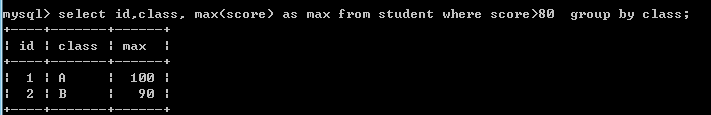
select id,class, max(score) as max from student where score>80 group by class;--查询各个班级最高成绩,分数要大于80,分组班级升序.
--having 子句 (条件查询)
--where功能、用法相同,执行时机不同.
--本质区别:where子句是把磁盘上的数据筛选到内存上,而having子句是把内存中的数据再次进行筛选.
--where不可以使用统计函数. 一般需用统计函数配合group by才会用到having
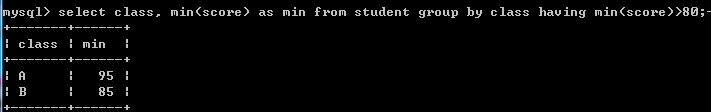
例如:select class, min(score) as min from student where min(score)>80 group by class;--报错
select class, min(score) as min from student group by class having min(score)>80;--查询各个班级最低成绩,分组班级,最低分数大于80
--order by子句 (排序)
--order by 字段1[asc|desc],字段n[asc|desc]
--排序: asc 升序(默认),desc 降序
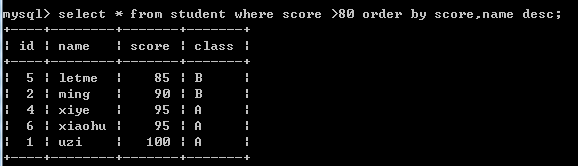
例如:insert into student(name,score,class) values('xiaohu',95,'A');--插入相同班级相同分数,要求多字段排序?
select * from student where score >80 order by score,name desc;--查询score大于80,排序score升序和name降序
--limit 子句 (限制查询结果数量)
--limit offset,length 语法解析: offset是指偏移量,默认为0; length是指需要显示的记录数.
--分页示例说明:
$page = 3; //第三页
$pageSize = 10; //页面显示10条记录
$offset = ($page - 1) * $pageSize; //偏移量为20
limit $offset,$pageSize //实现分页 偏移20,显示10
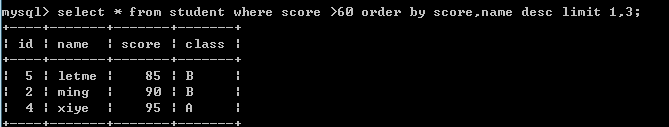
例如:select * from student where score >60 order by score,name desc limit 1,3;--查询score大于80,排序score升序和name降序,偏移量为1,显示3条记录
update
/*update*/
update 表名 set 字段1=值1,字段n=值n [where条件] [order by 字段名 asc|desc] [limit];
delete
/*delete*/
delete from 表名 [where条件] [order by 字段名 asc|desc] [limit];
联合查询
/*联合查询 关键字:union*/
--联合查询:就是将多个查询结果进行纵向上的拼接. (select语句2的查询结果放在select语句1查询结果的后面)
--语法:
select语句1
union [all | distinct]
select 语句2
union [all | distinct]
select 语句n
例如:查询A班级最高成绩和B班级最低成绩?
(select name, class,score from student where class='A' order by score desc limit 1)
union
(select name, class,score from student where class='B' order by score limit 1);

连接查询
/*连接查询*/
将多个表的字段进行连接,可以指定连接条件.
--交叉连接 cross join
select *|字段列表 from 表名1 cross join 表名2; 一张表的一条记录去连接另一张表中的所有记录,并且保存所有的记录包含两个表的所有的字段.
结果上看,就是对两张表做笛卡尔积,有n1*n2条记录.
例如:select * from student cross join score;

--内连接 inner join
select *|字段列表 from 左表 [inner] join 右表 on 左表.字段 = 右表.字段 [五子句]; 数据在左表中存在,同时在右表中又有对应的匹配的结果才会被保存. 如果没有匹配上,数据没有意义不会保存.
通常就是两张表中存在相同的某个字段.(项目中通常是关联主键ID) using() 用法连接两表公共字段. 例如:using(ID)
例如:create table teacher(
id int(10) unsigned not null auto_increment comment 'id',
name char(10) not null default '' comment '名字',
class varchar(20) not null default '' comment '班级',
primary key (id)
)engine=InnoDB default charset=utf8 comment='教师班级表';
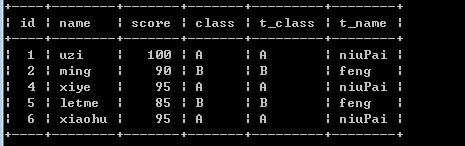
insert into teacher(name,class) values('niuPai','A'),('feng','B');
select student.*, teacher.class as t_class, teacher.name as t_name from student join teacher on student.class = teacher.class;
--外连接外 outer join
如果数据不存在,也会出现在连接结果中.
-- 左外连接 left join
select *|字段列表 from 左表 left [outer] join 右表 on 左表.字段 = 右表.字段 [五子句];
如果数据不存在,左表记录会出现,而右表为null填充
例如:select student.*, teacher.class as t_class, teacher.name as t_name from student left join teacher on student.class = teacher.class;
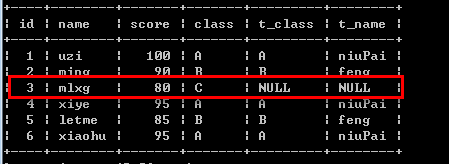
-- 右外连接 right join
select *|字段列表 from 右表 right [outer] join 左表 on 右表.字段 = 左表.字段 [五子句];
如果数据不存在,右表记录会出现,而左表为null填充
--自然连接 natural join
自动判断连接条件完成连接.
--自然内连接 natural inner join
select *|字段列表 from 左表 natural [inner] join 右表;
自然内连接其实就是内连接,这里的匹配条件是由系统自动指定. --自然外连接 natural outer join
自然外连接分为自然左外连接和自然右外连接.匹配条件也是由系统自动指定. --自然左外连接 natural left join
select *|字段列表 from 左表 natural left [outer] join 右表; --自然右外连接 natural right join
select *|字段列表 from 右表 natural right [outer] join 左表;
注意:项目中使用最多是内连接和外连接.
子查询
/*子查询*/
子查询(内查询)在主查询(外查询)之前一次执行完成,子查询的结果被主查询使用.
使用子查询需用括号包裹.
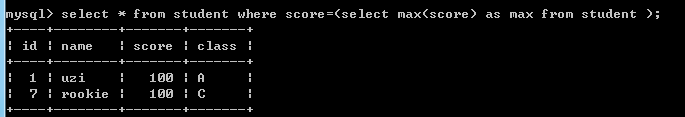
例如:insert into student(name,score,class) values('rookie',100,'C');
select * from student where score=(select max(score) as max from student);--查询班级最高成绩学生的记录
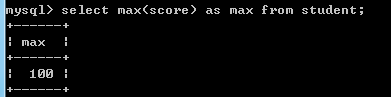
根据子查询返回值的形式:
1.单一值: 返回单行单列的子查询,也叫标量子查询.
例如:select max(score) as max from student;
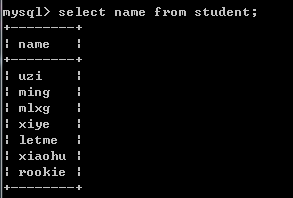
2.一列: 返回单列的子查询,也叫列子查询.
例如:select name from student;
3.一行: 返回一行的子查询,也加行子查询.
select *|字段列表 from 表名 where(字段1,字段n)=(行子查询结果)
例如:select * from student where score=(select min(score) as min from student);--查询班级最低成绩学生的记录
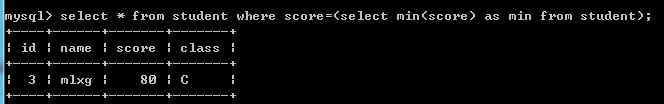
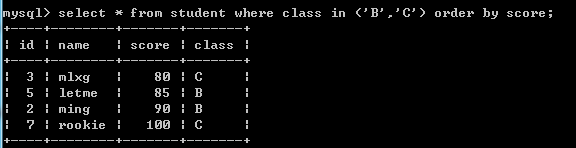
4.多行多列: 返回多行多列的子查询,也叫表子查询.
例如:select * from student where class in ('B','C') order by score;--查询B班和C班,排序score字段升序
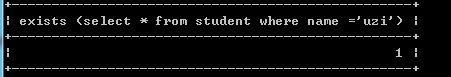
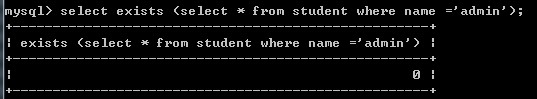
--exists
--主要作用就是判断后面的select语句有没有查询到数据.结果为true有返回数据,否则就是false.
例如:select exists (select * from student where name ='uzi');--有
select exists (select * from student where name ='admin');--无
视图
/*视图*/
视图是一张虚拟表,它表示一张表的部分数据和多张表的综合数据,视图的结构和数据都是建立在基表上.
视图仅仅是一个表结构,视图的数据并不在数据库中存储,数据保存在基表中. 一张表可以创建多个视图.
-- 视图作用
简化业务逻辑,对客户端隐藏真实的表结构
--创建视图
create [algorithm = undefined | merge | temptable] view 视图名称 [(字段列表)]
as
sql语句 语法解析:
1.视图名必须唯一,同时不能与表重名.
2.指定视图执行的算法,通过algorithm指定.
3.merge: 合并算法,将视图的语句和外层的语句合并后再执行.
4.temptable: 临时表算法,将视图执行的结果生成一张临时表,再执行外层语句.
5.undefined: 未定义型,用哪种算法有MySQL决定,默认算法merge.
6."字段列表"如果存在,数目必须等于select语句检索的列数
例如:create view v_student (v_name,v_score)
as
select name,score from student where score >80;
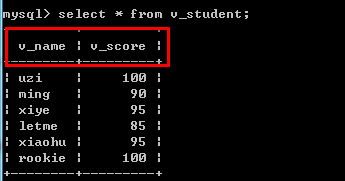
--查看结构
show create view 视图名称 --删除视图
drop view [if exists] 视图名称
注意: 删除视图后,数据库中的数据依然存在.(对当前视图删除) --修改视图结构
alter view 视图名称 [(字段列表)]
as
sql语句
事物
/*事物*/
事物:是并发控制的基本单位.事务就是一系列的操作,这些操作要么都执行,要么都不执行.(事务中可以保存多个SQL语句. 这些SQL语句是一个整体. 要么都执行,要么都不执行.) --事务操作
--开启事务
start transaction; 或者 begin;
--提交事务
commit;
--回滚事务
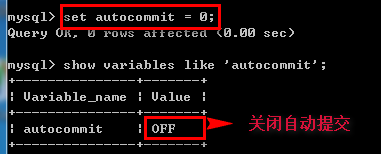
rollback; 注意: 修改事务自动提交 set autocommit = 0 | 1 (0:取消自动提交;1:自动提交)--设置为不自动提交,因为Mysql默认自动提交执行
查看:show variables like 'autocommit';
例如:create table goods(
id int(10) unsigned not null auto_increment comment 'id',
goods_name char(10) not null default '' comment '商品名',
price int(5) not null default '' comment '价格',
primary key (id)
)engine=InnoDB default charset=utf8 comment='商品表';
start transaction;--开启事物
insert into goods(goods_name,price) values('milk','');
insert into goods(goods_name,price) values('bread','');
commit;--提交事物
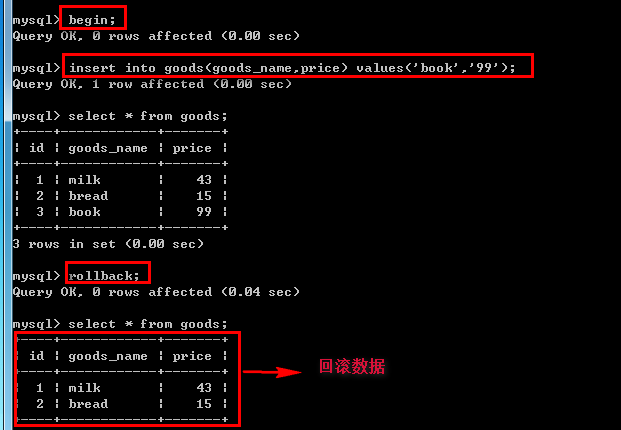
begin;--开启事物
insert into goods(goods_name,price) values('book','');
rollback;--回滚事物
-- 事务的特性
1. 原子性: 事务是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务中的操作要么都执行,要么都不执行.
2. 一致性: 事务前后数据的完整性必须保持一致. (事务开始和结束时,外部数据一致. 在整个事务过程中,操作是连续的.)
3. 隔离性: 多个用户并发访问数据库时,一个用户的事务不能被其它用户的事物所干扰,多个并发事务之间的数据要相互隔离.
4. 持久性: 一个事务一旦被提交,它对数据库中的数据改变就是永久性的. -- 事务的原理
利用InnoDB的自动提交(autocommit)特性完成. 普通的Mysql执行语句后,当前的数据提交操作均可被其它客户端可见.
事务是暂时关闭“自动提交”机制,需要commit提交持久化数据操作. -- 注意
1. 数据定义语言(DDL)语句不能被回滚. 比如创建或取消数据库的语句; 创建、取消或更改表或存储的子程序的语句.
2. 事务不能被嵌套
用户权限管理
/*用户权限管理*/
用户信息表:mysql数据库的下, user表中
--创建用户
create user 用户名[@主机地址] identified by '密码'; 例如:create user 'user_one'@'localhost' identified by '';--创建一个只能本机访问的用户
create user 'user_two'@'192.168.1.204.%' identified by '';--创建一个可以局域网访问的用户
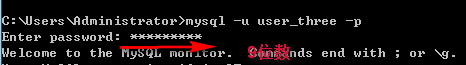
create user 'user_three' identified by '';--创建一个可全网访问的用户
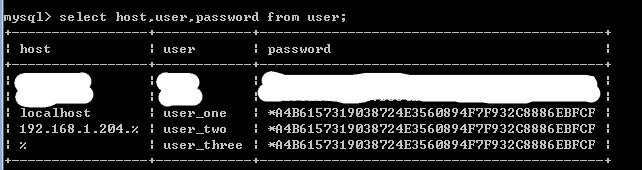
select host,user,password from user;--查看user表,host用户名和密码
--重命名用户
rename user 老用户名[@老主机地址] to 新用户名[@新主机地址]; -- 设置密码
set password = password('修改密码'); -- 为当前用户设置密码
set password for 用户名 = password('修改密码'); -- 为指定用户设置密码
例如:set password for 'user_three' = password(''); -- 指定'user_three'用户设置密码
-- 删除用户
drop user 用户名[@主机地址];
例如:drop user 'user_two'@'192.168.1.204.%'; --分配权限给用户
grant 权限列表 on *|库名 . *|表名 to 用户名[@主机地址] [identified by "用户密码"] [with grant option]; 语法解析:
权限列表: all [privileges]: 表示所有权限; delete:允许使用delete; select:允许使用select; update:允许使用update; insert:允许使用insert 等...
*.* :表示所有库的所有表
库名.表名 :表示某库下面的某表
例如: grant update,insert on *.* to user_one@'localhost' identified by "1234" with grant option;

--刷新权限
flush privileges; --查看权限
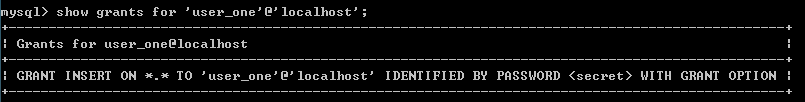
show grants for 用户名[@主机地址];
show grants for 'user_one'@'localhost'; --查看当前用户权限
show grants; --撤消权限
revoke 权限列表 on *|库名 . *|表名 from 用户名[@主机地址];
revoke all privileges, grant option from 用户名[@主机地址];-- 撤销所有权限
例如:revoke update on *.* from 'user_one'@'localhost';
最新文章
- Dev控件VGridView单元格绑定控件
- GoDaddy自动续费信用卡被扣款后的退款方法
- install httpd
- 如何使用yum来下载RPM包而不进行安装
- IIS7 无法访问请求的页面,因为该页的相关配置数据无效
- lightoj 1224
- 50道经典的JAVA编程题 (16-20)
- bzoj1056
- Android UiAutomator 自动化测试编译运行---新手2
- vs2008中使用gdi+的设置
- VisualStudio 扩展开发
- C# 将PDF转为SVG的3种情况
- TopN案例
- Thrift序列化与反序列化
- 关于Jonathan S. Weissman与RIT(罗切斯特理工学院,位于纽约)
- linux系统自签发免费ssl证书,为nginx生成自签名ssl证书
- ceph 的 bufferlist
- 简单说明 Virtual DOM 为啥快
- D13——C语言基础学PYTHON
- Team Foundation Server 2010服务器安装