BitmapMesh动画
一、概要
我们经常用到Canvas.drawBitmap方法,却很少用到Canvas.drawBitmapMesh方法。这个方法为我们做图片变形提供了无限可能,同时也对数学功底有较高的要求。下面先看一下方法介绍:
/**
* Draw the bitmap through the mesh, where mesh vertices are evenly distributed across the
* bitmap. There are meshWidth+1 vertices across, and meshHeight+1 vertices down. The verts
* array is accessed in row-major order, so that the first meshWidth+1 vertices are distributed
* across the top of the bitmap from left to right. A more general version of this method is
* drawVertices().
*
* Prior to API level {@value Build.VERSION_CODES#P} vertOffset and colorOffset were ignored,
* effectively treating them as zeros. In API level {@value Build.VERSION_CODES#P} and above
* these parameters will be respected.
*
* @param bitmap The bitmap to draw using the mesh
* @param meshWidth The number of columns in the mesh. Nothing is drawn if this is 0
* @param meshHeight The number of rows in the mesh. Nothing is drawn if this is 0
* @param verts Array of x,y pairs, specifying where the mesh should be drawn. There must be at
* least (meshWidth+1) * (meshHeight+1) * 2 + vertOffset values in the array
* @param vertOffset Number of verts elements to skip before drawing
* @param colors May be null. Specifies a color at each vertex, which is interpolated across the
* cell, and whose values are multiplied by the corresponding bitmap colors. If not
* null, there must be at least (meshWidth+1) * (meshHeight+1) + colorOffset values
* in the array.
* @param colorOffset Number of color elements to skip before drawing
* @param paint May be null. The paint used to draw the bitmap
*/
public void drawBitmapMesh(@NonNull Bitmap bitmap, int meshWidth, int meshHeight,
@NonNull float[] verts, int vertOffset, @Nullable int[] colors, int colorOffset,
@Nullable Paint paint) {
super.drawBitmapMesh(bitmap, meshWidth, meshHeight, verts, vertOffset, colors, colorOffset,
paint);
}
简单翻译一下:
- 此方法将Bitmap看做一张网,通过网的形状决定图片绘制形状
- meshWidth和meshHeight分别为横向和纵向分割网格数
- 所有网格顶点均匀分布,且排序为从左到右,从上到下
- verts为变换后所有网格顶点的坐标数组
- Android P版本之前vertOffset和colorOffset两个参数无效
下面通过一张简图来解释BitmapMesh的绘制原理:

如上,原图均匀分割成8*8格,对应(8+1)*(8+1)个顶点,假设原顶点坐标数组为origs[],通过遍历并按照特定算法重新计算后,得出新顶点坐标数组verts[],drawBitmapMesh根据verts[]重新绘制图片。
原理很好理解,本质上是两个数组的变换,关键是变换算法的设计。
二、实例讲解
下面通过一个简单实例讲解Canvas.drawBitmapMesh的具体用法,先看效果图:
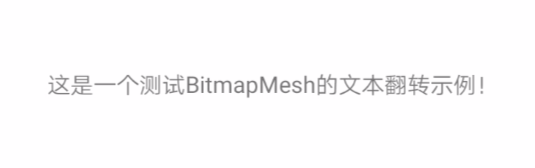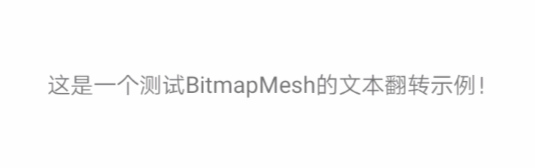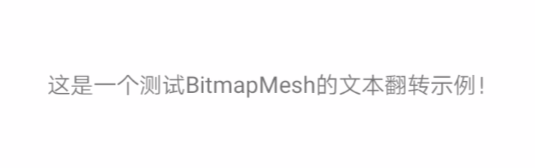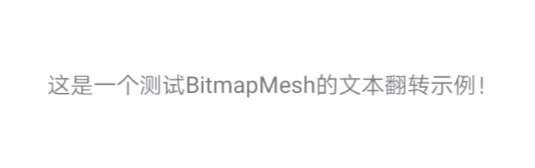
核心代码如下:
public class BitmapMeshView extends TextView {
//横向、纵向划分格数:80*80
private static final int WIDTH = 80;
private static final int HEIGHT = 80;
private Bitmap bitmap = null;
//顶点数:81*81
private final int COUNT = (WIDTH + 1) * (HEIGHT + 1);
//顶点坐标数组
private final float[] orig = new float[COUNT * 2];
//转换后顶点坐标数组
private final float[] verts = new float[COUNT * 2];
float bitmapWidth;
float unitWidth;
float bitmapHeight;
float halfHeight;
private static final double HALF_PI = Math.PI / 2;
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
startPlay();
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
public void startPlay() {
initBitmap();
ValueAnimator va = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0, 1.3f); //因变形区域是0.3,所以最大1.3才能保证完全展开
va.setDuration(1200);
va.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
float value = (float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
calcuVerts(value);
invalidate();
}
});
va.start();
}
private void initBitmap() {
if (bitmap == null) {
buildDrawingCache(); //获取View截图
bitmap = getDrawingCache();
bitmapWidth = bitmap.getWidth();
unitWidth = bitmapWidth * 0.3f; //变形区域长度
bitmapHeight = bitmap.getHeight();
halfHeight = bitmapHeight / 2; //1/2高度
/*算出顶点原始坐标*/
int index = 0;
for (int y = 0; y <= HEIGHT; y++) {
float fy = bitmapHeight * y / HEIGHT;
for (int x = 0; x <= WIDTH; x++) {
float fx = bitmapWidth * x / WIDTH;
orig[index * 2 + 0] = verts[index * 2 + 0] = fx;
orig[index * 2 + 1] = verts[index * 2 + 1] = fy;
index += 1;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 计算转换后的顶点坐标
* @param input 已展开比例
*/
private void calcuVerts(float input) {
for (int j = 0; j <= HEIGHT; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i <= WIDTH; i++) {
float startX = input * bitmapWidth; //变形部分最右端x值
float cx = i * 1.0f / WIDTH * bitmapWidth; //当前顶点x坐标
float cy = j * 1.0f / HEIGHT * bitmapHeight; //当前顶点y坐标
float toHalf = cy - halfHeight; //距离垂直中线的距离
if (cx >= startX) { //右侧未展开区域
verts[(j * (WIDTH + 1) + i) * 2 + 1] = halfHeight; //计算y坐标
verts[(j * (WIDTH + 1) + i) * 2] = cx; //计算x坐标
} else if (cx <= startX - unitWidth) { //左侧完全展开区域
verts[(j * (WIDTH + 1) + i) * 2 + 1] = cy;
verts[(j * (WIDTH + 1) + i) * 2] = cx;
} else { // 中间正在展开区域
float ratio = (startX - cx) / unitWidth;
verts[(j * (WIDTH + 1) + i) * 2 + 1] = (float) (halfHeight + toHalf * Math.sin(HALF_PI * ratio));
verts[(j * (WIDTH + 1) + i) * 2] = (float) (cx - toHalf * Math.cos(HALF_PI * ratio) * 1f);
}
}
}
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
if (bitmap != null) {
canvas.drawBitmapMesh(bitmap, WIDTH, HEIGHT, verts, 0, null, 0, null);
} else {
super.onDraw(canvas);
}
}
}
代码注释已经非常详细,不再一一解读。正如上面所说,drawBitmapMesh的重点是顶点坐标变换算法的设计,体现在本示例即是calcuVerts(float input)函数的设计。这是我们下面讲解的重点:
首先看下图
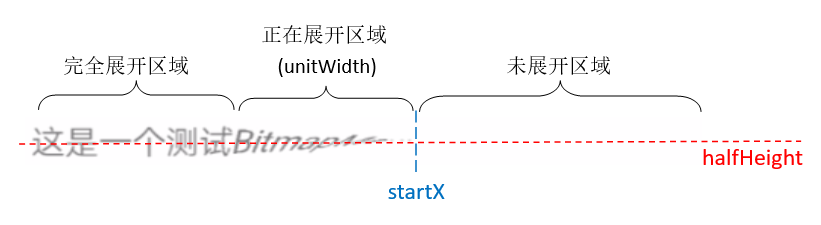
我们把这条文本分成三段:完全展开区域、正在展开区域、未展开区域。我们需要分别计算出这三段文本对应的顶点坐标:
(1)完全展开区域的顶点坐标和原始坐标是一样的:
else if (cx <= startX - unitWidth) { //左侧完全展开区域
verts[(j * (WIDTH + 1) + i) * 2 + 1] = cy;
verts[(j * (WIDTH + 1) + i) * 2] = cx;
}
(2)未展开区域的顶点y坐标都是halfHeight
if (cx >= startX) { //右侧未展开区域
verts[(j * (WIDTH + 1) + i) * 2 + 1] = halfHeight; //计算y坐标
verts[(j * (WIDTH + 1) + i) * 2] = cx; //计算x坐标
}
(3)重点是正在展开区域的坐标计算
我们把正在展开区域放大,假设(cx,cy)是其中某个原顶点坐标,(cx',cy')是经过计算变换后的顶点坐标,算法的重点是通过(cx,cy)计算出(cx',cy')。

根据动画效果不难想象点 (cx',cy') 实际上位于点 (cx,cy) 绕 (cx,halfHeiht) 圆心的弧线上,参考上面的辅助线
$cy' = halfHeight - h = halfHeight - |toHalf| * sinθ$
$cx' = cx + w = cx + |toHalf| * cosθ$
我们继续分析,在变形区域内,
- (cx,cy)距startX越远,展开幅度越大,θ角度越大,最大为90°,即(cx',cy')和(cx,cy)重合
- (cx,cy)距startX越近,展开幅度越小,θ角度越小,最小为0°,即(cx',cy')位于中线上
- θ角度呈线性变化,即θ = HALF_PI * (startX - cx) / unitWidth
- 因View坐标系Y轴是向下的,所以toHalf实际上是负值
综上分析,得出正在展开区域的顶点坐标算法:
else { // 中间正在展开区域
float ratio = (startX - cx) / unitWidth;
verts[(j * (WIDTH + 1) + i) * 2 + 1] = (float) (halfHeight + toHalf * Math.sin(HALF_PI * ratio));
verts[(j * (WIDTH + 1) + i) * 2] = (float) (cx - toHalf * Math.cos(HALF_PI * ratio) * 1f);
}
上述(1)(2)(3)共同组成了目标顶点坐标的算法。
再结合动画原理,startX从0到bitmapWidth+unitWidth过渡,就形成了文本完全展开的动画。
三、总结
Canvas的drawBitmapMesh方法是一个很强大的存在,但是想用它做出逼真的效果需要很强的数学和物理基础。坐标变换算法的设计和代码实现是该方法的关键。下面列举两个Github上的开源项目:

Github源码地址:https://github.com/NanBox/RippleLayout
对应博客地址:https://blog.csdn.net/a49220824/article/details/70476008
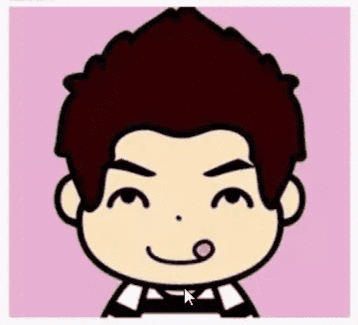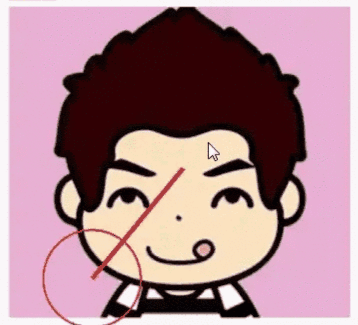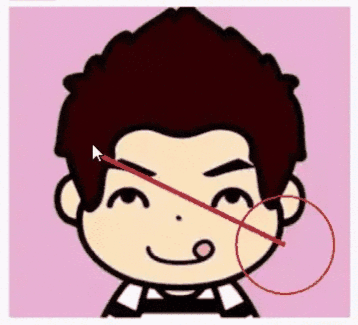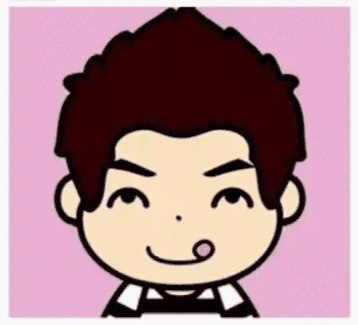
Github源码地址:https://github.com/DeesonWoo/MyDrawBitmapMeshDemo
最新文章
- AngularJs angular.identity和angular.noop详解
- 每天一个 Linux 命令(17):whereis 命令
- C++:类的创建
- 模板引擎:Velocity&FreeMarker(转)
- AFNetworking 官方文档
- 单词缩写(abbr.cpp)每日一题
- selenium+python 自动化中界面滚动条操作方法
- 瞎j8封装第二版之数据库连接池
- javascript 之作用域链-10
- HDU - 4858 项目管理
- oracle竖表转横表字段合并
- html中script标签的使用方法
- python学习第9-10天,函数。
- 移动端H5页面返回并且刷新页面(BFcache)
- .NET DLL 加密工具
- 【转载】C# 中的委托和事件(详解:简单易懂的讲解)
- <基础> PHP 进阶之 函数(Function)
- Spring IOC(四)FactoryBean
- HTML初学小技巧
- C#编程(六十九)----------DLR简介
热门文章
- netty byteBuf (二)
- 洛谷 P3227 BZOJ 3144 [HNOI2013]切糕
- Docker--微软dotconf截图
- asp.net--WebService知识点
- MySQL Workbench出现:Error Code: 2013. Lost connection to MySQL server during query的问题解决
- POJ 2914
- _DataStructure_C_Impl:求图G中从顶点u到顶点v的一条简单路径
- SERVICE_NAME和SERVICE_NAMES和GLOBAL_DBNAME的各自己定义
- ORACLE 树形查询 树查询
- ViewPage+Frament+listView滑动效果