Linux System Programming 学习笔记(四) 高级I/O
1. Scatter/Gather I/O
#include <sys/uio.h>
struct iovec {
void *iov_base; /* pointer to start of buffer */
size_t iov_len; /* size of buffer in bytes */
};
/* The readv() function reads count segments from the file descriptor fd into the buffers described by iov */
ssize_t readv (int fd, const struct iovec *iov, int count);
/* The writev() function writes at most count segments from the buffers described by iov into the file descriptor fd */
ssize_t writev (int fd, const struct iovec *iov, int count);
注意:在Scatter/Gather I/O操作过程中,内核必须分配内部数据结构来表示每个buffer分段,正常情况下,是根据分段数count进行动态内存分配的,
但是当分段数count较小时(一般<=8),内核直接在内核栈上分配,这显然比在堆中动态分配要快
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/uio.h> int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
struct iovec iov[];
char* buf[] = {
"The term buccaneer comes from the word boucan.\n",
"A boucan is a wooden frame used for cooking meat.\n",
"Buccaneer is the West Indies name for a pirate.\n" }; int fd = open("wel.txt", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC);
if (fd == -) {
fprintf(stderr, "open error\n");
return ;
} /* fill out three iovec structures */
for (int i = ; i < ; ++i) {
iov[i].iov_base = buf[i];
iov[i].iov_len = strlen(buf[i]) + ;
} /* with a single call, write them out all */
ssize_t nwrite = writev(fd, iov, );
if (nwrite == -) {
fprintf(stderr, "writev error\n");
return ;
}
fprintf(stdout, "wrote %d bytes\n", nwrite);
if (close(fd)) {
fprintf(stdout, "close error\n");
return ;
} return ;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/uio.h>
#include <sys/stat.h> int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
char foo[], bar[], baz[];
struct iovec iov[];
int fd = open("wel.txt", O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -) {
fprintf(stderr, "open error\n");
return ;
} /* set up our iovec structures */
iov[].iov_base = foo;
iov[].iov_len = sizeof(foo);
iov[].iov_base = bar;
iov[].iov_len = sizeof(bar);
iov[].iov_base = baz;
iov[].iov_len = sizeof(baz); /* read into the structures with a single call */
ssize_t nread = readv(fd, iov, );
if (nread == -) {
fprintf(stderr, "readv error\n");
return ;
} for (int i = ; i < ; ++i) {
fprintf(stdout, "%d: %s", i, (char*)iov[i].iov_base);
}
if (close(fd)) {
fprintf(stderr, "close error\n");
return ;
} return ;
}
writev的简单实现:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/uio.h> ssize_t my_writev(int fd, const struct iovec* iov, int count)
{
ssize_t ret = ;
for (int i = ; i < count; ++i) {
ssize_t nr = write(fd, iov[i].iov_base, iov[i].iov_len);
if (nr == -) {
if (errno == EINTR)
continue;
ret -= ;
break;
}
ret += nr;
}
return nr;
}
In fact, all I/O inside the Linux kernel is vectored; read() and write() are implemented as vectored I/O with a vector of only one segment
2. epoll
/* A successful call to epoll_create1() instantiates a new epoll instance and returns a file descriptor associated with the instance */
#include <sys/epoll.h>
int epoll_create(int size);
parameter size used to provide a hint about the number of file descriptors to be watched;
nowadays the kernel dynamically sizes the required data structures and this parameter just needs to be greater than zero
(2) controling epoll
/* The epoll_ctl() system call can be used to add file descriptors to and remove file descriptors from a given epoll context */
#include <sys/epoll.h>
int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event* event); struct epoll_event {
__u32 events; /* events */
union {
void* ptr;
int fd;
__u32 u32;
__u64 u64;
} data;
};
a. op parameter
EPOLL_CTL_ADD // Add a monitor on the file associated with the file descriptor fd to the epoll instance associated with epfd
EPOLL_CTL_DEL // Remove a monitor on the file associated with the file descriptor fd from the epoll instance associated with epfd
EPOLL_CTL_MOD // Modify an existing monitor of fd with the updated events specified by event
b. event parameter
EPOLLET // Enables edge-triggered behavior for the monitor of the file ,The default behavior is level-triggered
EPOLLIN // The file is available to be read from without blocking
EPOLLOUT // The file is available to be written to without blocking
对于结构体struct epoll_event 里的data成员,通常做法是将data联合体里的fd设置为第二个参数fd,即 event.data.fd = fd
To add a new watch on the file associated with fd to the epoll instance epfd :
#include <sys/epoll.h> struct epoll_event event;
event.data.fd = fd;
event.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLOUT int ret = epll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, &event);
if (ret) {
fprintf(stderr, "epll_ctl error\n");
}
To modify an existing event on the file associated with fd on the epoll instance epfd :
#include <sys/epoll.h> struct epoll_event event;
event.data.fd = fd;
event.events = EPOLLIN; int ret = epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, fd, &event);
if (ret) {
fprintf(stderr, "epoll_ctl error\n");
}
To remove an existing event on the file associated with fd from the epoll instance epfd :
#include <sys/epoll.h> struct epoll_event event; int ret = epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, fd, &event);
if (ret) {
fprintf(stderr, "epoll_ctl error\n");
}
(3) waiting for events with epoll
#include <sys/epoll.h>
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event* events, int maxevents, int timeout);
The return value is the number of events, or −1 on error
#include <sys/epoll.h> #define MAX_EVENTS 64 struct epoll_event* events = malloc(sizeof(struct epoll_event) * MAX_EVENTS);
if (events == NULL) {
fprintf(stdout, "malloc error\n");
return ;
} int nready = epoll_wait(epfd, events, MAX_EVENTS, -);
if (nready < ) {
fprintf(stderr, "epoll_wait error\n");
free(events);
return ;
} for (int i = ; i < nready; ++i) {
fprintf(stdout, "event=%ld on fd=%d\n", events[i].events, events[i].data.fd);
/* we now can operate on events[i].data.fd without blocking */
}
free(events);
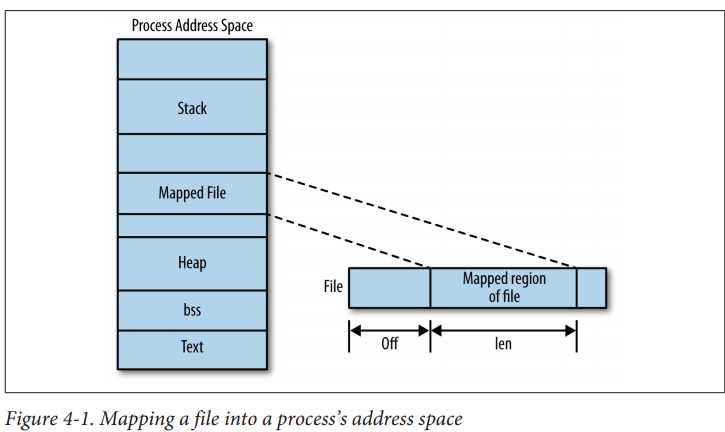
3. Mapping Files into Memory
/* A call to mmap() asks the kernel to map len bytes of the object represented by the file descriptor fd,
starting at offset bytes into the file, into memory
*/
#include <sys/mman.h>
void* mmap(void* addr, size_t len, int prot, int flags, int fd, off_t offset);
void* ptr = mmap(, len, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, fd, );
int munmap (void *addr, size_t len);
munmap() removes any mappings that contain pages located anywhere in the process address space starting at addr,
which must be page-aligned, and continuing for len bytes
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <fcntl.h> int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if (argc < ) {
fprintf(stderr, "usage:%s <file>\n", argv[]);
return ;
} int fd = open(argv[], O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -) {
fprintf(stderr, "open error\n");
return ;
} struct stat sbuf;
if (fsat(fd, &sbuf) == -) {
fprintf(stderr, "fstat error\n");
return ;
} if (!S_ISREG(sbuf.st_mode)) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s is not a file\n", argv[]);
return ;
}
void* ptr = mmap(, sbuf.st_size, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, fd, );
if (ptr == MAP_FAILED) {
fprintf(stderr, "mmap error\n");
return ;
} if (close(fd)) {
fprintf(stderr, "close error\n");
return ;
} for (int i = ; i < sbuf.st_size; ++i) {
fputc(ptr[i], stdout);
} if (munmap(ptr, sbuf.st_size) == -) {
fprintf(stderr, "munmap error\n");
return ;
}
return ;
}
#include <sys/mman.h>
int msync (void *addr, size_t len, int flags);
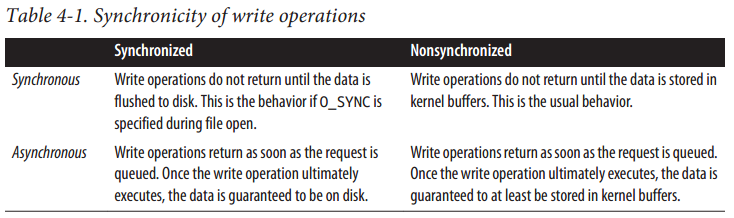
4. 同步 异步

5. I/O调度和I/O性能
Linus Elevator I/O scheduler
The Deadline I/O Scheduler
The Anticipatory I/O Scheduler
The CFQ I/O Scheduler
The Noop I/O Scheduler
最新文章
- SOA相关资料整理分享
- JQery判断checkbox是否被选三种方式
- lamp php的ssl,ssh支持
- Java中有四种常见的Map实现方法
- Hadoop FS shell commands
- ahjesus fstab修改错误了如何修复
- Posix线程编程指南(2) 线程私有数据
- Zend Server安装后首次运行就出现Internal Server Error的解决(转)
- UC浏览器 分享到朋友圈和微信好友
- docker四种网络模式
- easyui datagrid footer 页脚问题
- 实践 config drive - 每天5分钟玩转 OpenStack(170)
- C语言实现整数和16进制互相转换
- docker容器安装及使用技巧
- PHP 5 Directory 函数
- [Swift]LeetCode452. 用最少数量的箭引爆气球 | Minimum Number of Arrows to Burst Balloons
- 创建vs离线安装程序(不联网安装vs)
- ERROR 2002 (HY000): Can&#39;t connect to local MySQL server through socket
- 100base-T