【Java SE进阶】Day10 缓冲流、转换流、序列化流 、打印流
2024-10-21 05:45:15
一、缓冲流
1、概述
- 比普通流更强大的IO流,可以增加读写的效率
- 组成
- 缓冲输入流:BufferedInputStream、BufferedReader
- 缓冲输出流:BufferedOutputStream、BufferedWriter
1、字节缓冲输出流(构造传递具体输出流)
- BufferedOutputStream
public class Demo01BufferOutputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建FileOutputStream对象,构造方法中绑定输出的目的地
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\a.txt");
//2.创建BufferedOutputStream对象,构造方法中传递FileOutputStream对象,提高FileOutputStream对象效率
BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
//3.使用BufferedOutputStream对象中的方法write,把数据写入到内部缓冲区中
bos.write("我把数据写入到内部缓冲区中".getBytes());
bos.flush();
bos.close();
}
}
2、字节缓冲输入流
- BufferedInputStream
public class Demo02BufferedInputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建FileInputStream对象,构造方法中绑定要读取的数据源
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\a.txt");
//2.创建BufferedInputStream对象,构造方法中传递FileInputStream对象,提高FileInputStream对象的读取效率
BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(fis);
//3.使用BufferedInputStream对象中的read方法,读取文件
//int read()从输入流中读取数据的下一个字节
/*int len=0;//记录每次读取到的字节
while((len=bis.read())!=-1){
System.out.println(len);
}*/
//int read(byte[] b)
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];//数组长度表示一次能读取的最大字节数
int len=0;//每次读取的有效字节个数
while((len=bis.read(bytes))!=-1){
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,len));
}
bis.close();
}
}
- 效率测试
- 缓冲流+数组>缓冲流+单字节>普通流+数组>普通流+单字节
4、字符缓冲输出流
- BufferedWriter
public class Demo04BufferedWriter {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建字符缓冲输出流对象,构造方法中传递字符输出流
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\d.txt"));
//2.调用字符缓冲输出流中的方法write,把数据写入到内存缓冲区中
for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
bw.write("传智播客");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("\n\r");
//sout调用的方法就是newLine
}
//3.调用字符缓冲输出流中的方法flush,把内存缓冲区的数据刷新到文件中
bw.flush();
//4.释放资源
bw.close();
}
}
5、字符缓冲输入流
- BufferedReader
public class Demo05BufferedReader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建字符缓冲输入流对象BufferedReader,构造方法中传递字符输入流
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\d.txt"));
//2.使用字符输入流对象中的方法read和readLine读取文本
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(line);
}
//3.释放资源
br.close();
}
}
6、练习:对文本的内容进行排序
- HashMap会自动按照键的顺序进行排序
public class Demo06TestSort {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建一个HashMap集合对象,可以存储每行文本的学号,value存储每行的文本
HashMap<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();//【HashMap输入数据后会自动排序】
//2.创建字符缓冲输入流对象,构造方法中绑定字符输入流
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\in.txt"));
//3.创建字符缓冲输出流对象,构造方法中绑定字符输出流
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\out.txt"));
//4.使用字符缓冲输入流中的方法readline,逐行读取文本
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
//5.对读取到的文本进行切割,获取行中的序号和文本内容
String[] arr=line.split("\\.");//转义字符
//6.将切割好的序号和文本中的内容存储到HashMap集合中(key是有序的,会自动排序)
map.put(arr[0],arr[1]);
}
//7.遍历HashMap集合,获取每一个键值对
for (String key:map.keySet()){
String value = map.get(key);
//8.将每一个键值对,转换为一个文本行
line= key +"."+ value;
//9.将拼接好的文本,使用字符缓冲输出流中的方法write,写入到文件中
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();//写的时候不会把换行符写进去
}
//10.释放资源
bw.close();
br.close();
}
}
二、转换流
1、字符编码和字符集
- 字符编码
- 编码:字符按规则存储为二进制数
- 解码:将二进制数按规则解析显示
- 编码表:文字与二进制的对应规则
- 字符集Charset(编码表)
- ASCII
- GBK字符集:双字节编码
- Unicode字符集(UTF-8等):中文3个字节编码
2、编解码引出的问题
- IDEA默认以UTF-8编码,而windows默认为GBK编码
- 转换流的原理
- 包括转换输入流InputStreamReader和转换输出流OutputStreamWriter
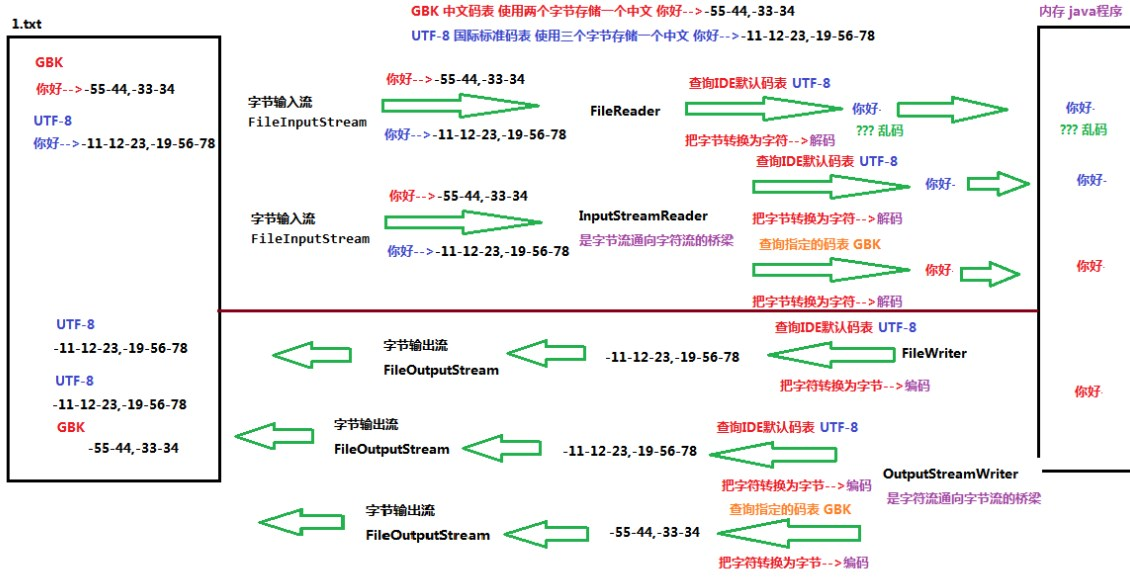
- 字符输入流FileReader先通过FileInputStream读入默认编码的二进制码,再通过字符输入流FileReader查询默认编码表,将其解码为对应的字符,放至内存
- 字符输出流FileWriter先通过FileOutputStream查询默认码表,将字符转换为二进制编码字节,再通过字符输出流FileWriter将其解码为对应的字符,存入硬盘
- 转换输入流InputStreamReader先通过FileInputStream读入默认编码的二进制码,再通过转换流InputStreamReader按指定的编码表解码为对应的字符,放至内存
- 转换输出流OutputStreamWriter先通过FileOutputStream查询指定的编码表,将字符编码为对应的二进制字节,在通过字符输出流FileWriter将其解码为对应的字符,存入硬盘
3、OutputStreamWriter
- 是Writer的子类
/*
使用转换流OutputStreamWriter写UTF-8格式的文件
* */
private static void write_utf_8() throws IOException {
//1、创建一个OutputStreamWriter对象,构造方法中传递字节输出流和指定的编码表名【默认是UTF-8格式编码】6字节
OutputStreamWriter osw =new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\utf_8.txt"),"utf-8");
//2、使用OutputStreamWriter对象中的方法write,将字符转换为字节存储缓冲区中【编码】
osw.write("你好");
//3、使用OutputStreamWriter对象中的方法flush,把内存缓冲区中的字节刷新到文件中(使用字节流写字节的过程)
osw.flush();
//4、释放资源
osw.close();
}
4、InputStreamReader
- 是Reader的子类
/*
使用InputStreamReader读取UTF-8格式的文件
* */
private static void read_utf_8() throws IOException {
//1、创建InputStreamReader对象,构造方法中传递字节输入流和指定的字节编码表名称,默认就是UTF-8,可以不指定
InputStreamReader isr =new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\utf_8.txt"),"utf-8");
//2、使用InputStreamReader对象中的方法read读取文件
int len=0;
while((len=isr.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)len);
}
//3、释放资源
isr.close();
}
5、练习:转换文件编码(GBK转UTF-8)
public class Demo10Practice {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建InputStreamReader对象,构造方法中传递字节输入流和指定的编码表名称GBK
InputStreamReader isr =new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\gbk.txt"),"gbk");
//2.创建OutputStreamWriter对象,构造方法中传递字节输出流和指定的编码表名称UTF-8
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\utf8.txt"),"utf-8");
//3.使用InputStreamReader对象中的方法read读取文件
int len=0;
while((len=isr.read())!=-1){
//4.使用OutputStreamWriter对象中的方法write,把读取的数据写入到文件中
osw.write(len);
}
//5.释放资源
osw.close();
isr.close();
}
}
三、序列化
1、概述
序列化:将对象写入到硬盘,以流的方式,名称为ObjectOutputStream.writeObject()
反序列化:从硬盘中读取对象,流名称为ObjectInputStream.readObject(),返回给Object类型对象
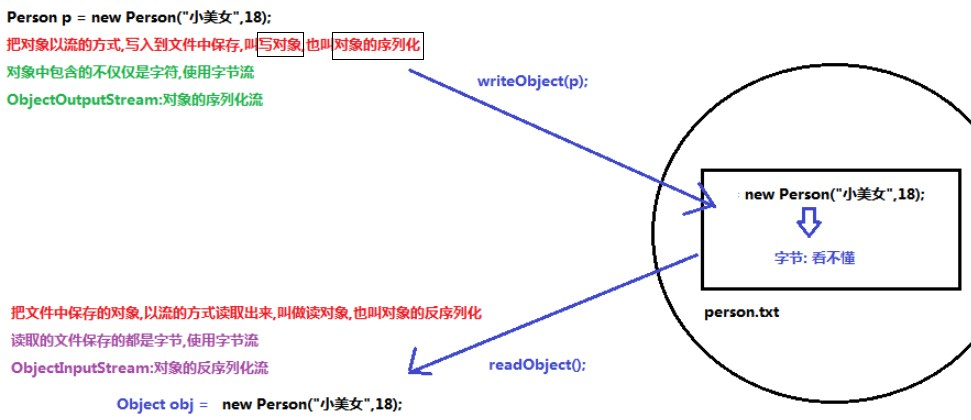
2、序列化流ObjectOutputStream
public class Demo11ObjectOutputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建一个ObjectOutputStream对象,构造方法中传递字节输出流
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\person.txt"));
//2.调用ObjectOutputStream对象中的方法writeObject(),把对象写入到文件中
oos.writeObject(new Person("小美女",18));
//抛出NotSerializableException异常/未被序列化异常
/*
* java.io.NotSerializableException 当实例需要具有序列化接口时,抛出此异常。序列化运行时或实例的类会抛出此异常。
* Serializable为序列化接口,类通过实现 java.io.Serializable 接口以启用其序列化功能。未实现此接口的类将无法使其任何状态序列化或反序列化。
* */
//3.释放资源
oos.close();
}
}
3、反序列化流ObjectInputStream
public class Demo12ObjectInputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException ,ClassNotFoundException {
//1、创建一个ObjectInputStream对象,构造方法中传递字节输入流
ObjectInputStream ois =new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\person.txt"));
//2、使用ObjectInputStream对象中的方法readObject,读取保存对象的文件
Person p = (Person)ois.readObject();//不转型也可以
//readObject方法声明抛出了ClassNotFoundException(.class文件找不到异常)
//当不存在对象的class文件时,抛出此异常
//反序列化的前提:
//1.类必须事先Serializable接口
//2.必须存在类对应的class 文件
//3、释放资源
ois.close();
//4、使用读取出来的对象
System.out.println(p);
}
}
4、瞬态关键字
- transient关键字修饰的成员变量,不能被序列化。序列化再反序列化后输出的是默认值0
- static优先于非静态,被static修饰的成员变量不能被序列化,能序列化的都是对象
5、InvalidClassException
- 原因:序列化后,class文件发生了修改,反序列化就会失败
- 解决方式:显式声明serialVersionUID字段
public class Person implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public String name;
// private int age;
private transient int age;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
6、练习:序列化集合
public class Demo13SeriSet {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//1、定义一个存储Person对象的ArrayList集合
ArrayList<Person> list=new ArrayList<>();
//2、在ArrayList集合中存储Person对象
list.add(new Person("张三",13));
list.add(new Person("李四",14));
list.add(new Person("王五",15));
//3、创建一个序列化流ObjectOutputStream对象
ObjectOutputStream oos =new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\person.txt"));
//4、使用ObjectOutputStream对象中的方法writeObject,对集合进行序列化
oos.writeObject(list);
//5、创建一个反序列化ObjectInputStream对象
ObjectInputStream ois =new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\person.txt"));
//6、使用ObjectInputStream对象中的方法readObject读取文件中保存的集合
Object o = ois.readObject();
//7、把Object类型的集合转换为ArrayList类型
ArrayList<Person> list2=(ArrayList<Person>)o;
//8、遍历ArrayList集合
for (Person p : list2) {
System.out.println(p);
}
//9、释放资源
ois.close();
oos.close();
}
}
四、打印流
1、默认打印到文件
public class Demo14PrintStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
System.out.println("helloWorld");
//out就是一个打印流printStream
//print和println是打印流的方法
//创建打印流PrintStream对象,构造方法中绑定要输出的目的地
PrintStream ps=new PrintStream("c:\\a.txt");
//如果使用继承自父类的write方法写数据,查看数据的时候会查询编码表 97-->a
ps.write(97);
ps.println(97);
ps.println(8.8);
ps.println("aaa");
ps.println(true);
ps.println(2L);
//释放资源
ps.close();
}
}
2、改变输出流的目的地(打印到文件)
- System.setOut(PrintStream)改变输出语句的目的地,重新分配标准输出流
public class Demo15PrintStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
System.out.println("我在控制台输出");
PrintStream ps =new PrintStream("C:\\a.txt");
System.setOut(ps);
System.out.println("我在打印流的目的地中输出");
ps.close();
}
}
最新文章
- MYSQL 锁机制 分析
- Use Hibernate core API
- OSI模型
- mysql的统计函数
- python input() 与 raw_input()
- [转载]常用Web Service汇总(天气预报、时刻表等)
- Spring AOP + AspectJ Annotation Example---reference
- IC芯片設計
- 一个简化的printf函数
- alv 列标题
- BZOJ_[usaco2007 Nov]relays 奶牛接力跑_离散化+倍增弗洛伊德
- B20J_2836_魔法树_树链剖分+线段树
- Wannafly挑战赛23 T2游戏 SG函数
- python基础学习(八)元组
- vue使用JS的形式进行路由导航
- 小众Python库介绍
- VBA遍历数组的2种方式
- linux保存的设置用户/组ID(set-user-ID)的测试
- Oracle的sqlnet.ora文件配置
- tonymillion/Reachability的使用
热门文章
- innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit 和 sync_binlog 参数详 解
- linux中通过date命令获取昨天或明天时间的方法
- redhat替换yum源时redhat.repo无法删除或禁用的问题
- Beats:在 Beats 中实现动态 pipeline
- 【疫情动态条形图】用Python开发全球疫情排名动态条形图bar_chart_race
- StampedLock:一个并发编程中非常重要的票据锁
- kafka详解(二)--kafka为什么快
- CentOS 7 安全基线检查
- 关于TP5模板输出时间戳问题--A non well formed numeric value encountered
- 利用inotify和rsync服务实现数据实时同步