codeforces 86D D. Powerful array(莫队算法)
题目链接:
5 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
An array of positive integers a1, a2, ..., an is given. Let us consider its arbitrary subarray al, al + 1..., ar, where 1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n. For every positive integer s denote by Ks the number of occurrences of s into the subarray. We call the power of the subarray the sum of productsKs·Ks·s for every positive integer s. The sum contains only finite number of nonzero summands as the number of different values in the array is indeed finite.
You should calculate the power of t given subarrays.
First line contains two integers n and t (1 ≤ n, t ≤ 200000) — the array length and the number of queries correspondingly.
Second line contains n positive integers ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ 106) — the elements of the array.
Next t lines contain two positive integers l, r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n) each — the indices of the left and the right ends of the corresponding subarray.
Output t lines, the i-th line of the output should contain single positive integer — the power of the i-th query subarray.
Please, do not use %lld specificator to read or write 64-bit integers in C++. It is preferred to use cout stream (also you may use%I64d).
3 2
1 2 1
1 2
1 3
3
6
8 3
1 1 2 2 1 3 1 1
2 7
1 6
2 7
20
20
20
Consider the following array (see the second sample) and its [2, 7] subarray (elements of the subarray are colored):
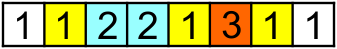 Then K1 = 3, K2 = 2, K3 = 1, so the power is equal to 32·1 + 22·2 + 12·3 = 20.
Then K1 = 3, K2 = 2, K3 = 1, so the power is equal to 32·1 + 22·2 + 12·3 = 20.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e6+;
int n,t;
long long a[N],num[N],ans[N];
struct node
{
/* friend bool operator< ()
{ }*/
int l,r,id,pos;
};
node qu[N];
int cmp(node x,node y)
{
if(x.pos==y.pos)return x.r<y.r;
return x.l<y.l;
}
void solve()
{
long long temp=;
int le=,ri=;
for(int i=;i<=t;i++)
{
while(ri<qu[i].r)
{
ri++;
temp+=((num[a[ri]]<<)+)*a[ri];
num[a[ri]]++;
}
while(ri>qu[i].r)
{
num[a[ri]]--;
temp-=((num[a[ri]]<<)+)*a[ri];
ri--;
}
while(le<qu[i].l)
{
num[a[le]]--;
temp-=((num[a[le]]<<)+)*a[le];
le++;
}
while(le>qu[i].l)
{
le--;
temp+=((num[a[le]]<<)+)*a[le];
num[a[le]]++;
}
ans[qu[i].id]=temp;
}
} int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&t);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%I64d",&a[i]);
}
int sq=sqrt(n);
for(int i=;i<=t;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&qu[i].l,&qu[i].r);
qu[i].id=i;
qu[i].pos=qu[i].l/sq;
}
sort(qu+,qu+t+,cmp);
solve();
for(int i=;i<=t;i++)
{
printf("%I64d\n",ans[i]);
}
return ;
}
最新文章
- Spring中Bean的生命周期方法
- paramiko与MySQL数据库
- js创建table表格
- Eclipse 启动Tomcat后web项目的classes的子文件夹中没有calss文件
- asp下实现多条件模糊查询SQL语句
- poj3177
- web_profile(网站分析)配置
- Vijos P1881 闪烁的星星 (加强自己多一点。。)
- 广告中的AdNetwork、AdExchange、DSP、SSP、RTB和DMP是什么?
- Hdu 3001 Travelling 状态DP
- java总结:Java中获取系统时间(年、月、日)以及下拉菜单默认选择系统年、月、日的方法
- 【SQL】如何使用SQL like 方法和SQL [charlist] 通配符(SQL like的拓展)
- ProtoBuf 常用序列化/反序列化API 转
- U深度U盘安装win7系统教程
- linux清空文件内容的三种方法
- Java Socket/HttpURLConnection读取HTTP网页
- C语言程序设计实习报告
- java8新特性——接口中的静态方法与默认方法
- C++的历史与现状
- 160414、java上传文件以流方式判断类型