spark sortShuffleWriter源码学习
查看的源码为spark2.3
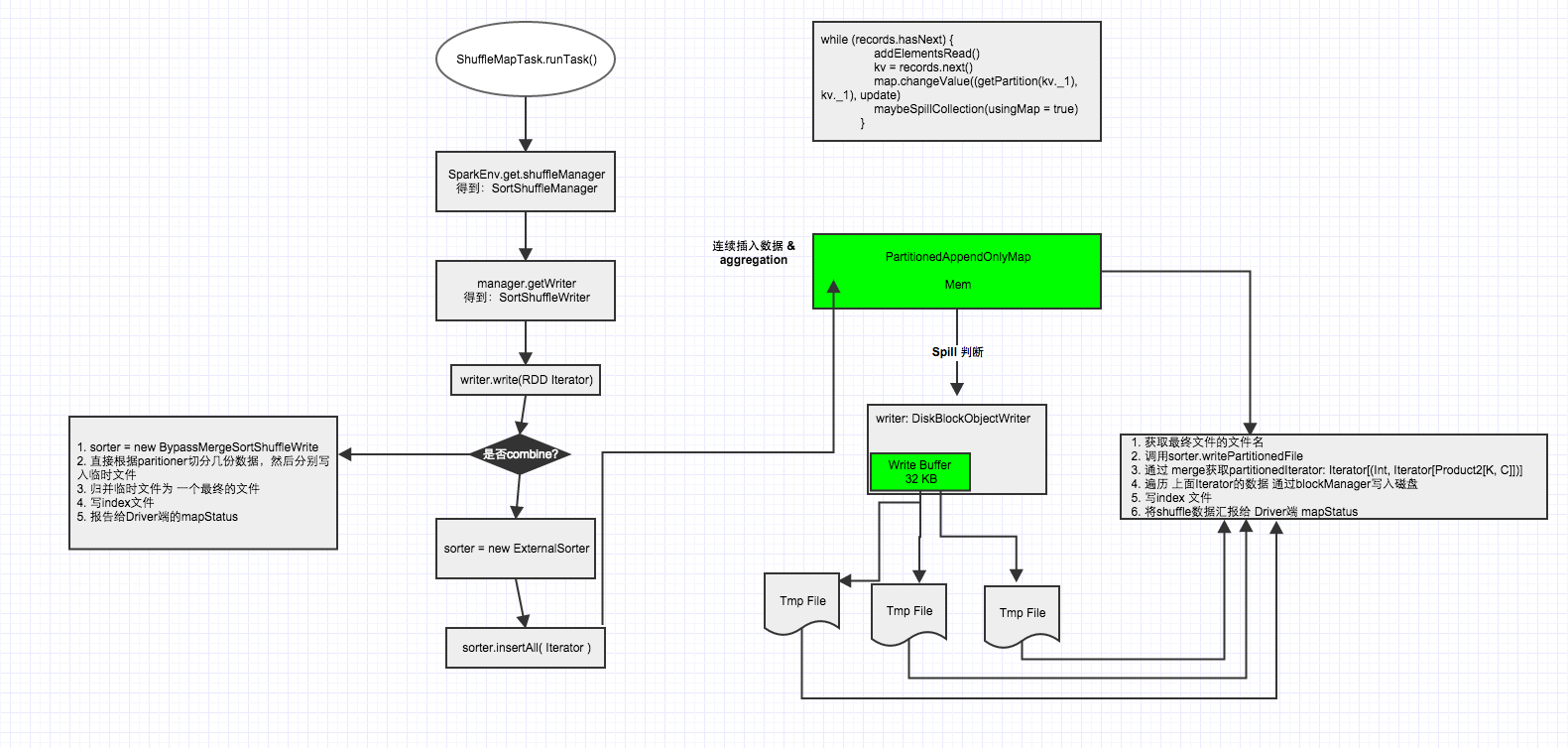
调用ShuffleMapTask的runTask方法
org.apache.spark.scheduler.ShuffleMapTask#runTask
ShuffleMapTask继承了org.apache.spark.scheduler.Task,重写了Task的runTask方法,在该方法中关于shuffle部分主要是获取shuffleManager,然后得到sortShuffleManager,然后再通过manager获取writer,得到sortShuffleWriter,然后调用writer方法
override def runTask(context: TaskContext): MapStatus = {
// Deserialize the RDD using the broadcast variable.
val threadMXBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean
val deserializeStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
val deserializeStartCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) {
threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime
} else 0L
val ser = SparkEnv.get.closureSerializer.newInstance()
val (rdd, dep) = ser.deserialize[(RDD[_], ShuffleDependency[_, _, _])](
ByteBuffer.wrap(taskBinary.value), Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader)
_executorDeserializeTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - deserializeStartTime
_executorDeserializeCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) {
threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime - deserializeStartCpuTime
} else 0L
//定义writer对象
var writer: ShuffleWriter[Any, Any] = null
try {
//获取shuffleManager
val manager = SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager
//通过shuffleManager获取Writer对象,这里的partitionId传入的其实是mapId,每个map有个mapId
writer = manager.getWriter[Any, Any](dep.shuffleHandle, partitionId, context)
//调用write方法。write方法如下
writer.write(rdd.iterator(partition, context).asInstanceOf[Iterator[_ <: Product2[Any, Any]]])
writer.stop(success = true).get
} catch {
case e: Exception =>
try {
if (writer != null) {
writer.stop(success = false)
}
} catch {
case e: Exception =>
log.debug("Could not stop writer", e)
}
throw e
}
}
调用SortShuffleWriter的write方法
org.apache.spark.shuffle.sort.SortShuffleWriter#write
SortShuffleWriter继承了org.apache.spark.shuffle.ShuffleWriter并重写了其write方法
/** Write a bunch of records to this task's output */
override def write(records: Iterator[Product2[K, V]]): Unit = {
//根据是否存在map端聚合获取ExternalSorter对象(sorter)
sorter = if (dep.mapSideCombine) {
require(dep.aggregator.isDefined, "Map-side combine without Aggregator specified!")
new ExternalSorter[K, V, C](
context, dep.aggregator, Some(dep.partitioner), dep.keyOrdering, dep.serializer)
} else {
// In this case we pass neither an aggregator nor an ordering to the sorter, because we don't
// care whether the keys get sorted in each partition; that will be done on the reduce side
// if the operation being run is sortByKey.如果没有map-side聚合,那么创建sorter对象时候,aggregator和ordering将不传入对应的值
new ExternalSorter[K, V, V](
context, aggregator = None, Some(dep.partitioner), ordering = None, dep.serializer)
}
//通过insertAll方法先写数据到buffer
sorter.insertAll(records) // Don't bother including the time to open the merged output file in the shuffle write time,
// because it just opens a single file, so is typically too fast to measure accurately
// (see SPARK-3570). //通过blockManager获取对应mapId.shuffleId的文件输出路径
val output = shuffleBlockResolver.getDataFile(dep.shuffleId, mapId)
//返回与“path”位于同一目录中的临时文件的路径。
val tmp = Utils.tempFileWith(output)
try {
val blockId = ShuffleBlockId(dep.shuffleId, mapId, IndexShuffleBlockResolver.NOOP_REDUCE_ID)
//将所有的数据合并到一个文件中
val partitionLengths = sorter.writePartitionedFile(blockId, tmp)
//生成index文件,也就是每个reduce通过该index文件得知它哪些是属于它的数据
shuffleBlockResolver.writeIndexFileAndCommit(dep.shuffleId, mapId, partitionLengths, tmp)
mapStatus = MapStatus(blockManager.shuffleServerId, partitionLengths)
} finally {
if (tmp.exists() && !tmp.delete()) {
logError(s"Error while deleting temp file ${tmp.getAbsolutePath}")
}
}
}
ExternalSorter类
创建ExternalSorter对象时,各参数对应的意思。
class ExternalSorter[K, V, C](
context: TaskContext,
aggregator: Option[Aggregator[K, V, C]] = None,
partitioner: Option[Partitioner] = None,
ordering: Option[Ordering[K]] = None,
serializer: Serializer = SparkEnv.get.serializer) aggregator:在RDD shuffle时,map/reduce-side使用的aggregator
partitioner:对shuffle的输出,使用哪种partitioner对数据做分区,比如hashPartitioner或者rangePartitioner
ordering:根据哪个key做排序
serializer:使用哪种序列化,如果没有显示指定,默认使用spark.serializer参数值
从一个high level的角度看ExternalSorter到底做了什么?
第一:反复的将数据填充到内存buffer中(如果需要通过key做map-side聚合,则使用PartitionedAppendOnlyMap;如果不需要,则使用PartitionedPairBuffer),如下
// Data structures to store in-memory objects before we spill. Depending on whether we have an
// Aggregator set, we either put objects into an AppendOnlyMap where we combine them, or we
// store them in an array buffer.
@volatile private var map = new PartitionedAppendOnlyMap[K, C]
@volatile private var buffer = new PartitionedPairBuffer[K, C]
第二:在buffer中,通过key计算partition ID,通过partition ID对数据进行排序(partition ID可以理解为reduce ID,意思就是数据被分给了哪个reduce),为了避免对key调用多次partitioner,spark会将partition ID跟每一条数据一起存储。
第三:当buffer达到内存限制时(buffer默认大小32k,由spark.shuffle.file.buffer参数决定),会将buffer中的数据spill到文件中(每次spill都会生成一个文件),如果我们需要做map-side聚合,该文件生成时会通过partition ID先做排序,然后通过key或者key的hashcode值做二次排序。
第四:将spill形成的多个文件合并包括还在内存中的数据,文件合并时候将会排序,排序方式跟上面一样,生成数据文件dataFile以及索引文件indexFile
第五:最后调用stop方法,删除所有中间文件
结合下图更好理解

mapTask通过externalSorter生成多个文件,也就是fileSegment,最后每个map任务的所有filesegment将会合并成一个file
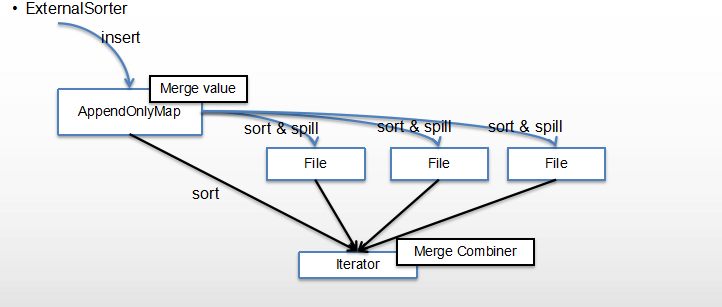
上图数据插入的是appendOnlyMap,也就是使用了map-side聚合,所以有merger value,appendOnlyMap在满了以后(默认32k)将spill成文件,多次spill生成多个文件,最后merge所有文件包括还在内存buffer中的数据。
调用ExternalSorter的insertAll方法
这一步主要是往buffer写数据,对数据分partition ID,buffer满了spill数据到磁盘且对数据排序
def insertAll(records: Iterator[Product2[K, V]]): Unit = {
// TODO: stop combining if we find that the reduction factor isn't high如果合并比例不高的话,就不会继续合并了
// 通过创建ExternalSorter对象时传入的aggregator获取是否存在合并
val shouldCombine = aggregator.isDefined
if (shouldCombine) {
// Combine values in-memory first using our AppendOnlyMap
val mergeValue = aggregator.get.mergeValue
val createCombiner = aggregator.get.createCombiner
var kv: Product2[K, V] = null
val update = (hadValue: Boolean, oldValue: C) => {
//合并值方式
if (hadValue) mergeValue(oldValue, kv._2) else createCombiner(kv._2)
}
while (records.hasNext) {
addElementsRead()
kv = records.next()
//这个map就是该类中定义的PartitionedAppendOnlyMap,getPartition方法通过key获取所属Partition ID(hashPartitioner)
map.changeValue((getPartition(kv._1), kv._1), update)
// buffer满的话将内存中的数据spill成文件
maybeSpillCollection(usingMap = true)
}
} else {
// Stick values into our buffer
while (records.hasNext) {
addElementsRead()
val kv = records.next()
//这个buffer就是该类中定义的PartitionedPairBuffer
buffer.insert(getPartition(kv._1), kv._1, kv._2.asInstanceOf[C])
maybeSpillCollection(usingMap = false)
}
}
}
insertAll方法中调用maybeSpillCollection方法
/**
* Spill the current in-memory collection to disk if needed.
*
* @param usingMap whether we're using a map or buffer as our current in-memory collection
* 不同的数据结构(也就是buffer)调用不同的方法
*/
private def maybeSpillCollection(usingMap: Boolean): Unit = {
var estimatedSize = 0L
if (usingMap) {
estimatedSize = map.estimateSize()
//maybeSpill方法会尝试申请buffer内存,如果申请到内存,则spill且返回false。否则true
if (maybeSpill(map, estimatedSize)) {
//appendOnlyMap的数据spill以后,创建一个新的appendOnlyMap
map = new PartitionedAppendOnlyMap[K, C]
}
} else {
estimatedSize = buffer.estimateSize()
if (maybeSpill(buffer, estimatedSize)) {
buffer = new PartitionedPairBuffer[K, C]
}
} if (estimatedSize > _peakMemoryUsedBytes) {
_peakMemoryUsedBytes = estimatedSize
}
}
maybeSpillCollection方法中调用maybeSpill方法,判断是否应该执行spill
/**
* Spills the current in-memory collection to disk if needed. Attempts to acquire more
* memory before spilling.
* 在spill之前会尝试申请内存,最后才判断是否真正执行spill
* @param collection collection to spill to disk
* @param currentMemory estimated size of the collection in bytes
* @return true if `collection` was spilled to disk; false otherwise
*/
protected def maybeSpill(collection: C, currentMemory: Long): Boolean = {
var shouldSpill = false
if (elementsRead % 32 == 0 && currentMemory >= myMemoryThreshold) {
// Claim up to double our current memory from the shuffle memory pool;从上次spill以后,每读取32个元素判断一次,声明申请额外内存
val amountToRequest = 2 * currentMemory - myMemoryThreshold
val granted = acquireMemory(amountToRequest)
myMemoryThreshold += granted
// If we were granted too little memory to grow further (either tryToAcquire returned 0,
// or we already had more memory than myMemoryThreshold), spill the current collection
shouldSpill = currentMemory >= myMemoryThreshold
}
shouldSpill = shouldSpill || _elementsRead > numElementsForceSpillThreshold
// Actually spill
if (shouldSpill) {
_spillCount += 1
logSpillage(currentMemory)
spill(collection)
_elementsRead = 0
_memoryBytesSpilled += currentMemory
releaseMemory()
}
shouldSpill
}
1
最新文章
- cannot use the same dataset for report.dataset and page.dataset
- Linux下链接mysql数据库的命令
- 【HDOJ】【3530】Subsequence
- WSARecv()
- #Leet Code# Same Tree
- 记录jpcap在Ubuntu&Window下的配置过程
- JAVA Static方法与单例模式的理解
- 洛谷-三连击(升级版)-BOSS战-入门综合练习1
- 编写运行最简单的java程序——使用记事本编写java程序
- Python项目实战:福布斯系列之数据采集
- HTML5 开发APP( 环境配置)
- sql将查询结果建立为新表
- keras-yolo3-master
- 网页换肤:原生js与jq
- Vue 学习笔记之快速入门篇
- 单链表的基本操作--c++
- 5 -- Hibernate的基本用法 --6 深入Hibernate映射
- 51Nod 1810 连续区间
- 调用飞信HTTP接口给自己发短信
- DPDK安装依赖项合集 环境合集